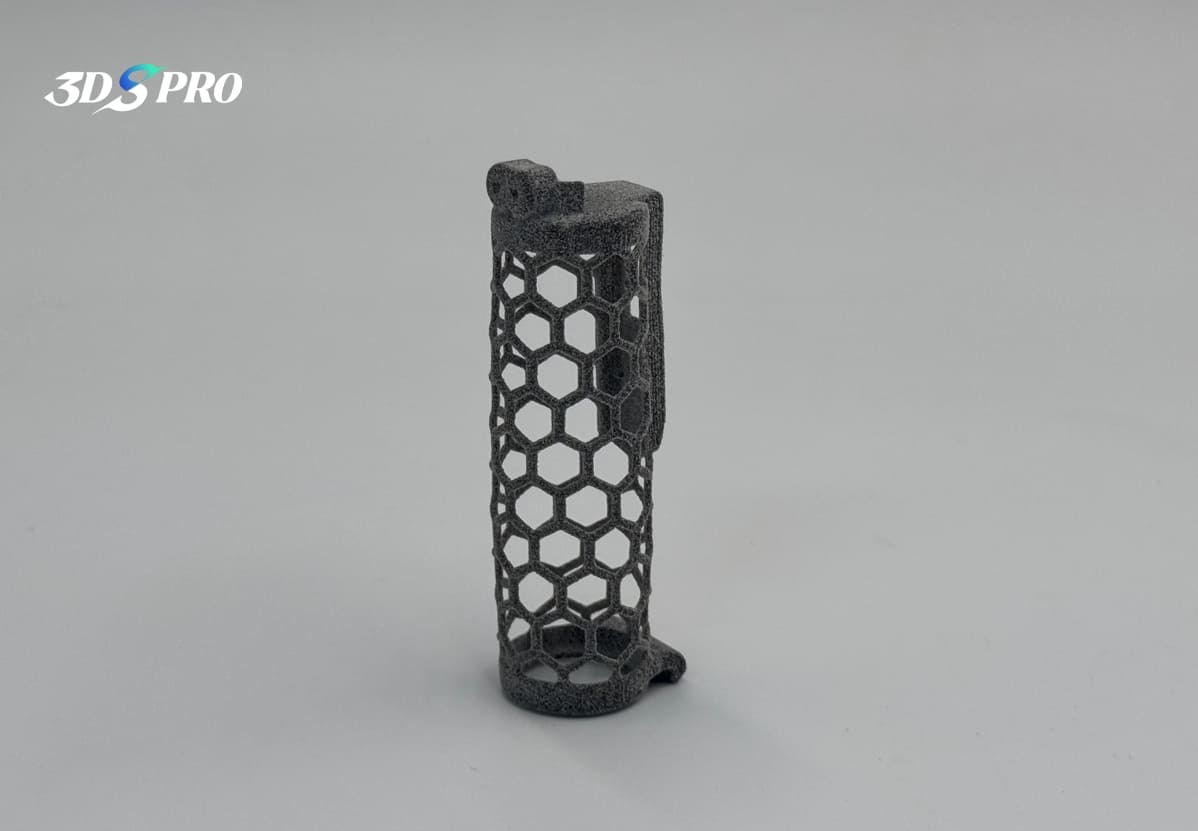
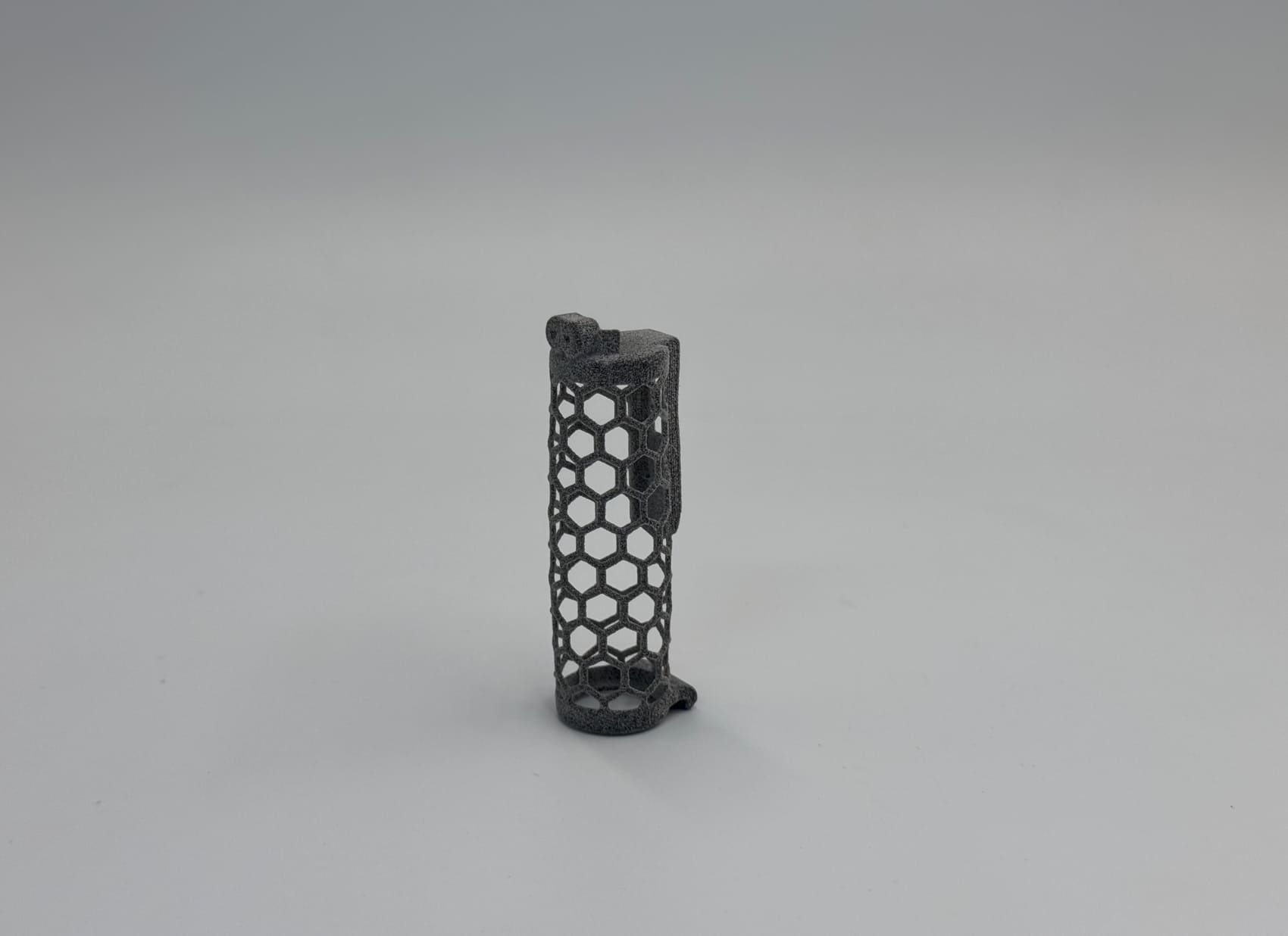
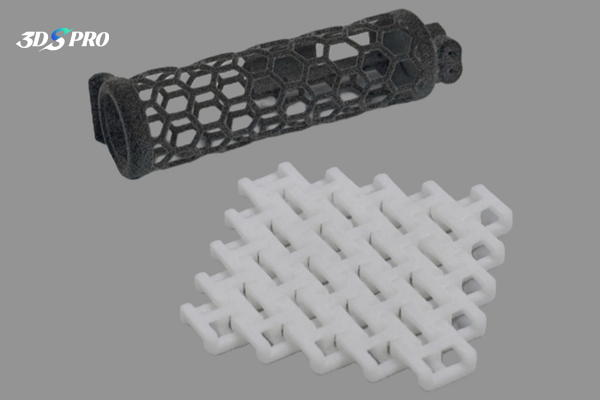
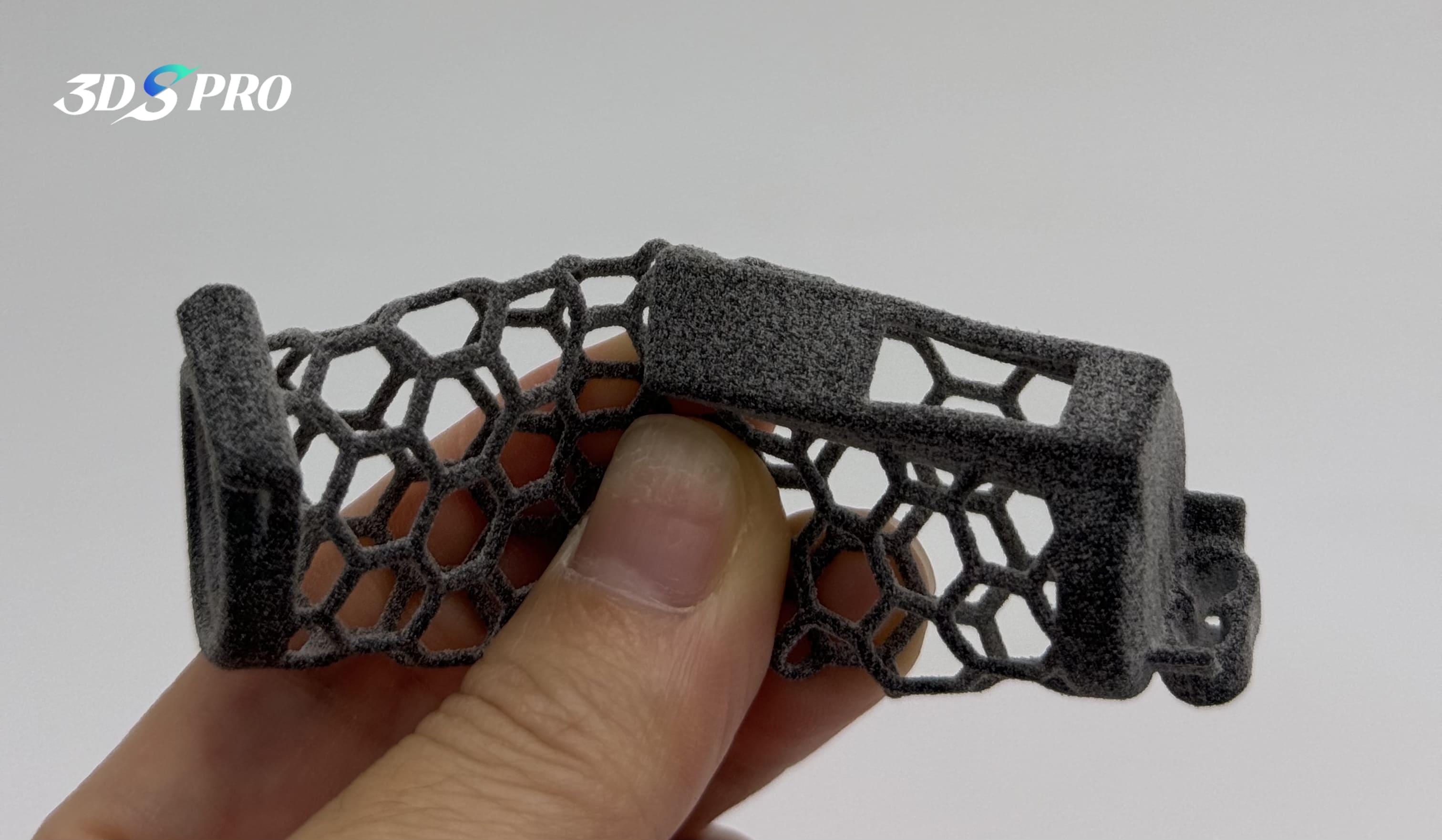
MJF 3D Printed TPU in Honeycomb Structures
● Process: Multi Jet Fusion
● Material: TPU Gray
● Post-processing: Tapping
In addition to printing lattice structures, 3D printing also has the significant capability of directly printing honeycomb structures. For this project, we used Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) 3D printing and TPU material to create a functional prototype with honeycomb structures. While there are many successful examples of honeycomb structures printed with standard plastic materials available online, we wanted to explore whether TPU could achieve the same success. Our attempt was very successful, and we are pleased with the final results! Check this TPU 3D printed functional parts out:
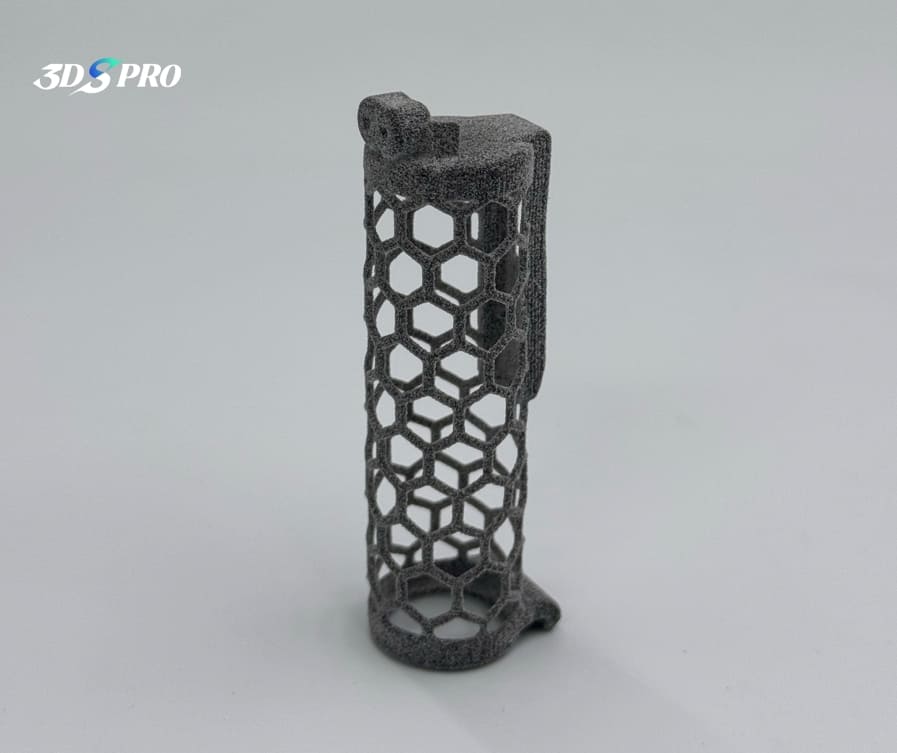

The Material
When printing with TPU, there is a rule of thumb: the softer the material, the more difficult it is to print; conversely, the harder the material, the more likely it is to print successfully. However, we did not want to use materials that were too hard for this project, as they would not effectively demonstrate the soft material properties of TPU to our readers. The combination of very soft hardness and honeycomb structure raised questions about printability. After evaluation by our engineers, we determined that TPU with a Shore A hardness of 80-90 was best suited to ensure the success of this attempt. Using MJF 3D printing was the fastest solution, which enhances the efficiency. Check out the flexibility:
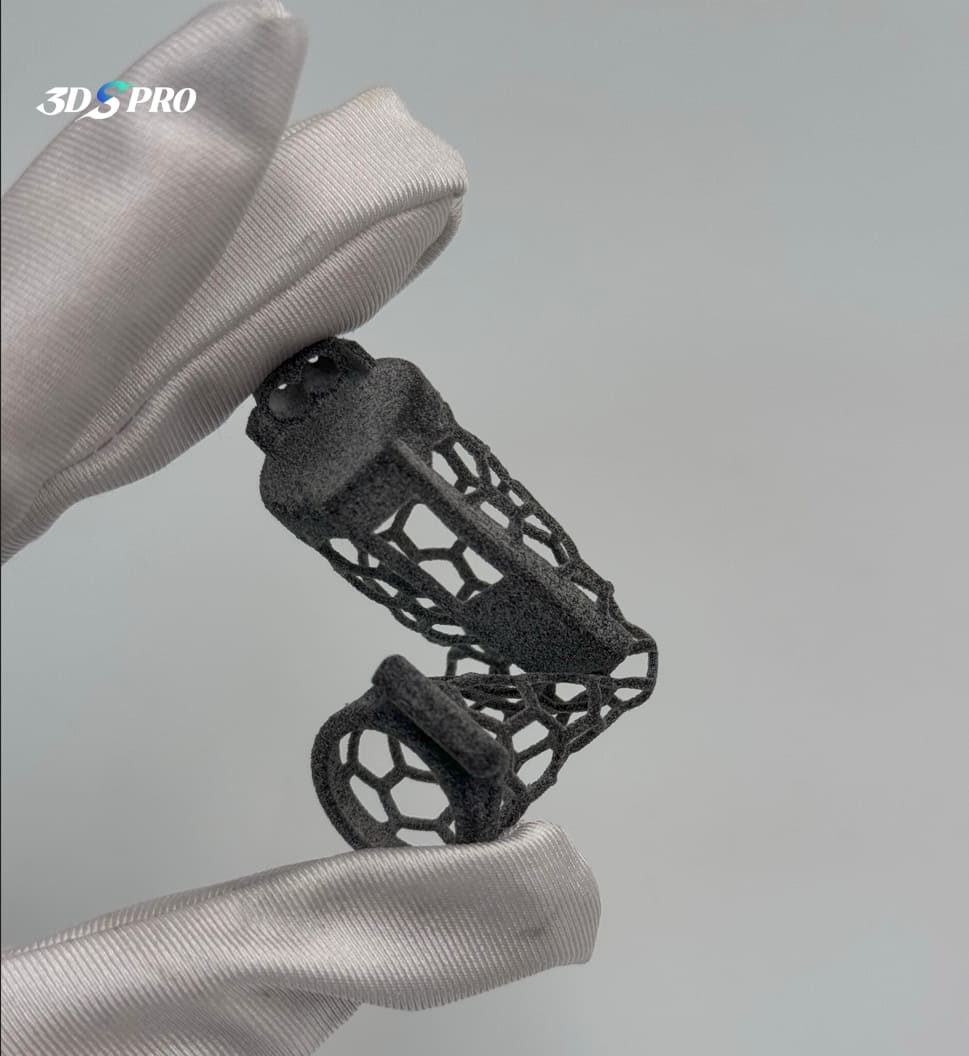


The Process
We offer a variety of Nylon MJF 3D printing services, TPU is the new material for MJF services. Besides, our SLS 3D printing also offers TPU materials.
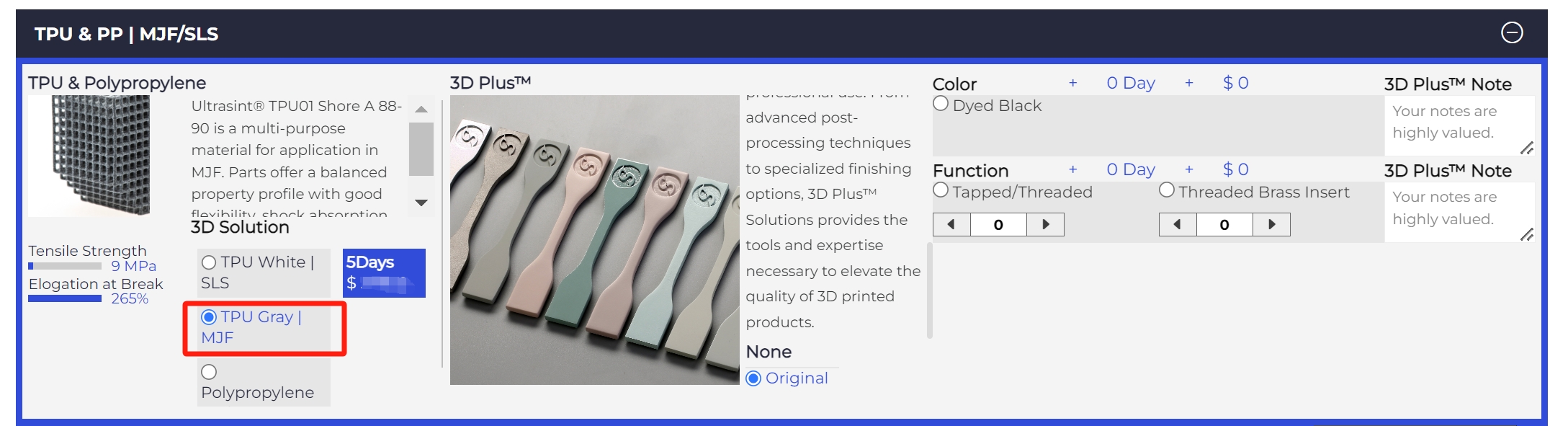
One of MJF's primary advantages is its speed. Due to its ability to selectively fuse the powder, MJF can create parts at a faster rate than other powder bed fusion 3D printing technologies. This results in faster build times and higher throughput, making MJF ideal for low-to-medium volume production runs. Check out our MJF capabilities:
|
Lead Time* |
Maximum Printing Size |
Tolerance |
3D Plus™ Post-processing Services* |
|
48 Hours/72 Hours/5 Days |
380*284*380 mm |
± 300μm or 0.3%mm |
More than 10 Types |
*1. Lead time depends on material selection.
*2. Selecting 3D Plus™ when quoting means you have chosen your preferred post-processing service. If you have a specific special post-processing requirement that you cannot find in our quote system, please contact our Customer Success Manager or success@3dspro.com, we can help you!
Post-processing
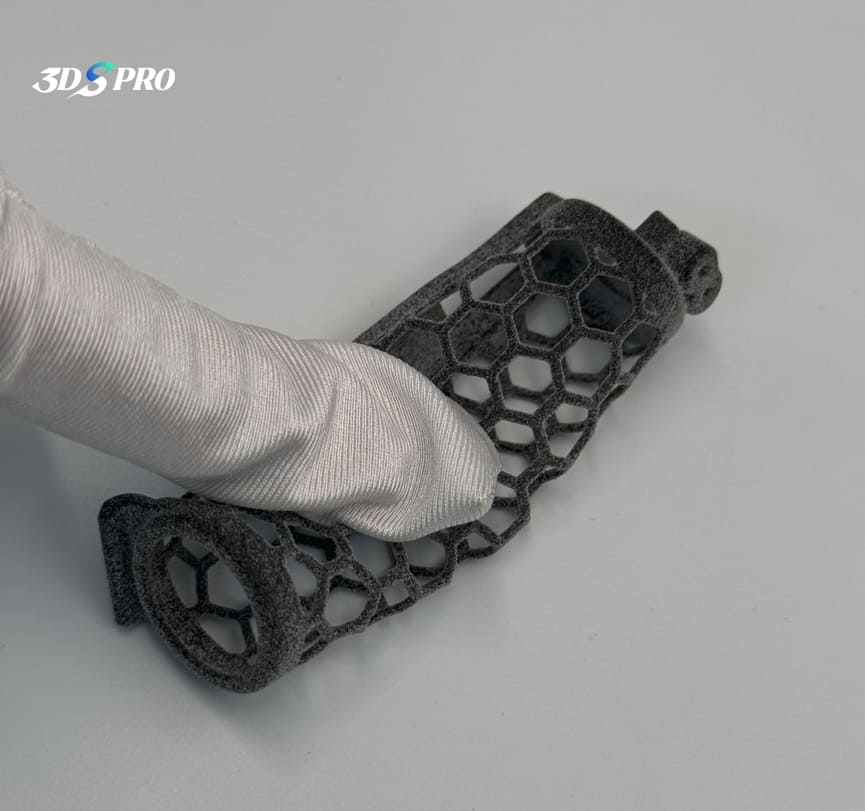
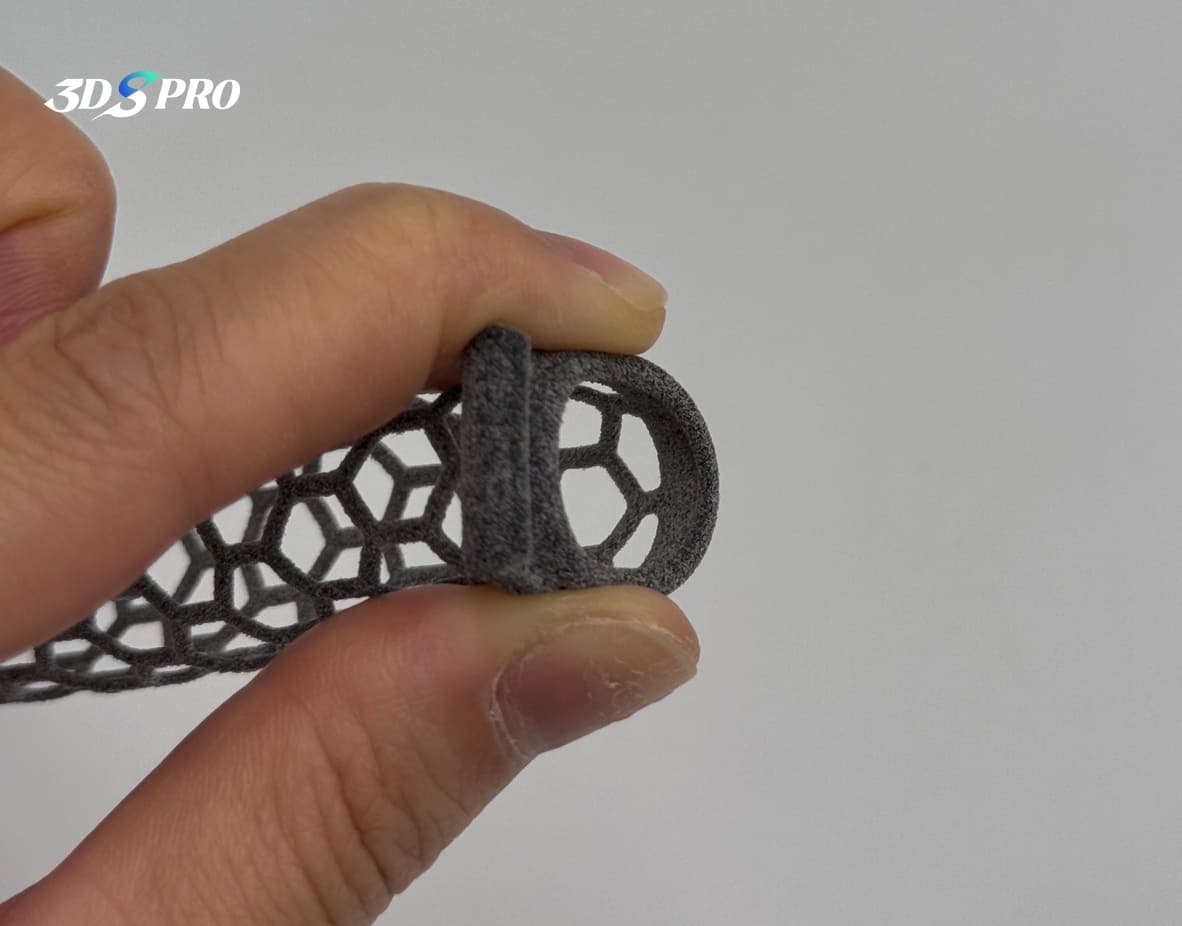
In this project, we post-processed two tapped holes on the TPU functional prototype.
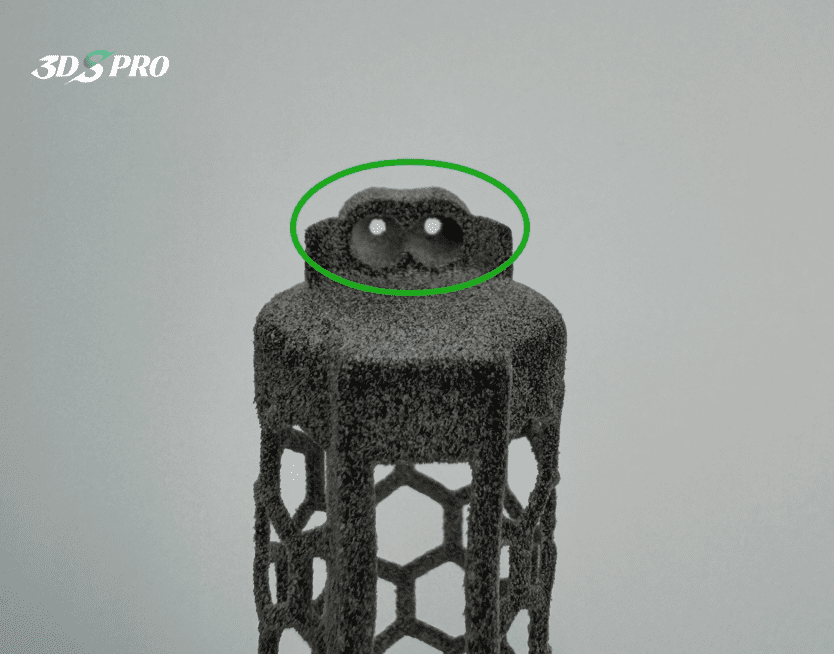
Before post-processing, we ensure that the printed parts can be effectively post-processed, whether for surface treatment or functional purposes. In order to be able to tap holes on the top of the TPU printed parts, our engineers designed the parts with different thicknesses. As you can see, the middle part (cube) is soft and flexible, while the top and bottom parts are designed to be thicker to ensure that the top area has enough hardness to support tapping during post-processing.

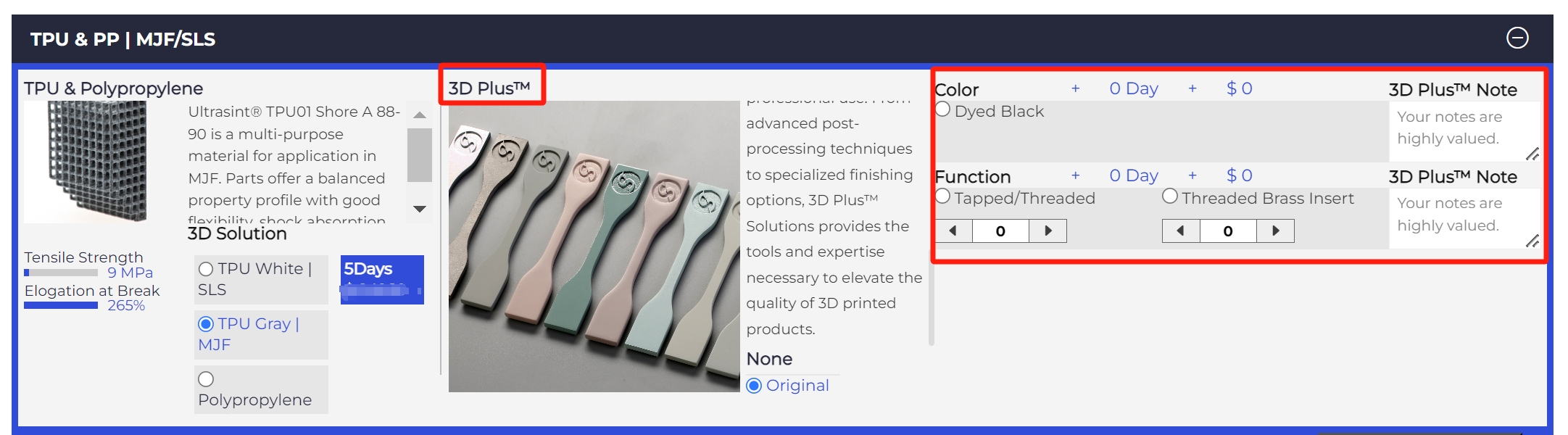
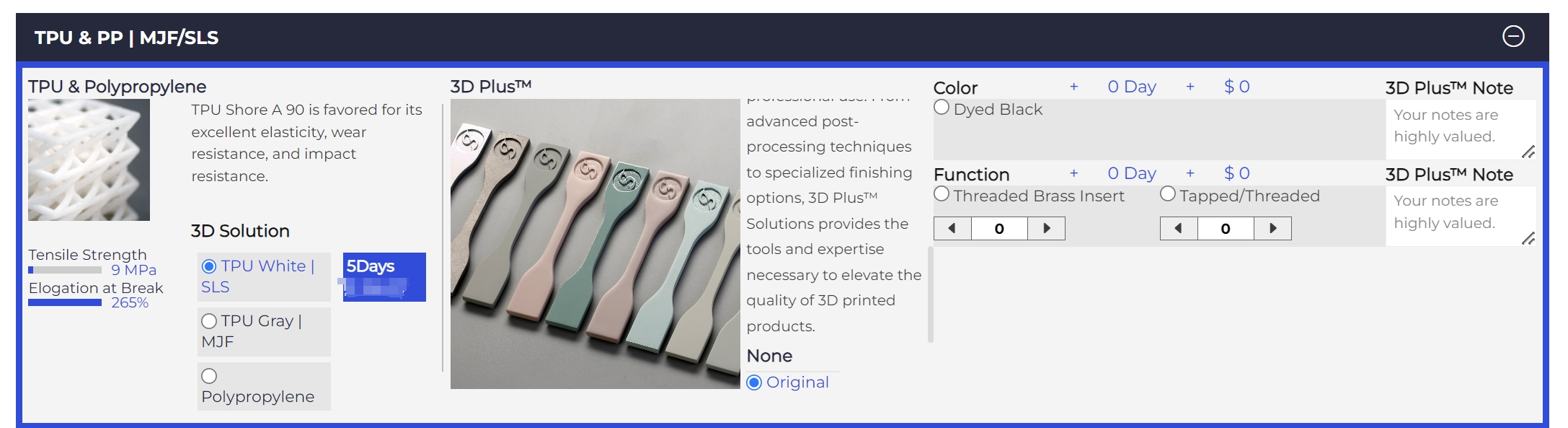
In addition to tapping, threading and dyeing, our 3D Plus™ solution also provides a variety of post-processing options for MJF printed parts. Our 3D Plus™ solution is designed to provide users with a variety of post-processing solutions to enhance the appearance and performance of printed parts. Users can select the required post-processing services through the quotation system under the 3D Plus™ section (see highlights in the picture).
What is TPU 3D Printing?
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a versatile thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) known for its unique combination of properties. It is a class of polyurethane plastics that is both flexible and durable, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
TPU 3D printing involves fusing TPU materials to create flexible and durable parts. 3D printing TPU combines the high durability of plastic with the elasticity of rubber, making it ideal for applications that require repeated bending or compression.
TPU Mechanical Properties
|
Property |
Value Range |
|
Hardness (Shore A) |
60 - 95 |
|
Tensile Strength |
25 - 70 MPa |
|
Elongation at Break |
300% - 700% |
|
Tear Strength |
80 - 200 kN/m |
|
Abrasion Resistance |
Excellent |
|
Density |
1.10 - 1.25 g/cm³ |
|
Compression Set |
10% - 50% (depending on grade) |
TPU material selection on our quote system
1. Scroll down the material list;
2. Select and click on the “TPU & PP” section;
3. Select the TPU material and 3D printing process that suits your needs.

Why is TPU hard to print?
TPU is challenging to print due to its flexibility, which can cause extrusion issues like bending and buckling, leading to jams and inconsistent flow. Its hygroscopic nature means it easily absorbs moisture, resulting in bubbles and poor print quality if not kept dry. Precise temperature control is crucial, as deviations can cause warping and stringing.
Achieving good bed adhesion can be tricky, requiring a heated bed and appropriate adhesives to prevent warping. Additionally, TPU’s elasticity can lead to stringing and oozing if retraction settings are not optimized, making fine-tuning essential for clean prints.
Tips to 3D Print Flexible Materials
1. Slow Print Speed: Print at 20-30mm/s to avoid jams.
2. Keep Filament Dry: Store in a dry box with desiccants.
3. Optimize Temperature: Use 225-245°C for printing and 20-60°C for the bed.
4. Ensure Bed Adhesion: Use a heated bed and adhesives like painter’s tape.
5. Fine-Tune Retraction: Adjust settings to minimize stringing.
6. Use Direct Drive Extruder: Provides consistent extrusion.
7. Adjust Layer Height and Wall Thickness: Find the right balance for flexibility and strength.
TPU 3D Printing Applications
● Automotive Parts: TPU is used in flexible parts such as gaskets, seals, and protective covers that require both durability and flexibility.
● Footwear: TPU is ideal for producing flexible and durable soles that provide comfort and wear resistance.
● Medical Devices: Used in flexible tubes, catheters, and other medical parts that require both flexibility and durability.
● Consumer Electronics: Because TPU is impact-resistant, it is often used in protective cases for phones and other devices.
● Sporting Goods: Commonly used in helmets, protective pads, and other equipment that benefits from TPU's shock absorption and flexibility.
● Industrial Applications: TPU is used to make flexible hoses, belts, and other parts that need to withstand harsh conditions.
● Prototyping and Customization: TPU's flexibility and durability make it ideal for rapid prototyping and production of customized parts with complex geometries.