Why and when to use TPU 3D printing?
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a versatile material used in 3D printing due to its flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance. It's ideal for creating wearable devices, automotive parts, medical devices, and sporting goods that require a soft, rubber-like feel and the ability to withstand wear and impact. TPU is perfect for applications needing both flexibility and durability, such as custom protective gear and grips.
Are you considering TPU 3D printing for a specific project? Let's find out which method is right for your project!
3D Printing TPU Mechanical Properties Cheat Sheet:
|
Shore Hardness |
Tensile Strength |
Elongation at Break |
Abrasion Resistance |
Chemical Resistance |
|
from 85A to 98A |
around 30 MPa |
up to 500% |
excellent |
resistant to oils, greases, and various chemicals |
Methods to Make TPU 3D Prints
There are three main methods for making TPU 3D prints: FDM, SLS, and MJF 3D printing. Each method produces TPU parts with different mechanical properties.
1. SLS 3D Printed TPU
|
What we make? |
Process |
Material |
TPU Hardness |
Color |
|
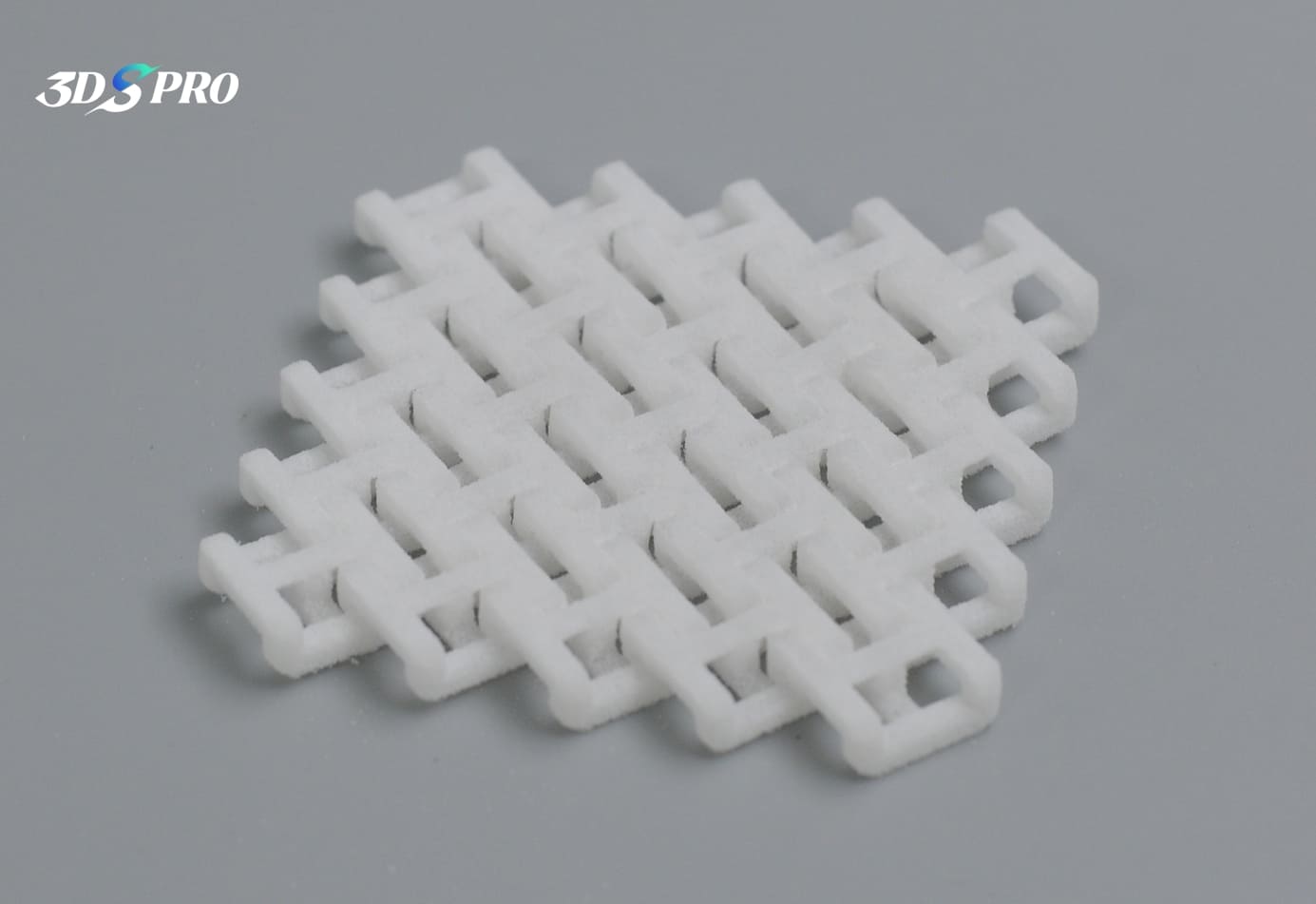
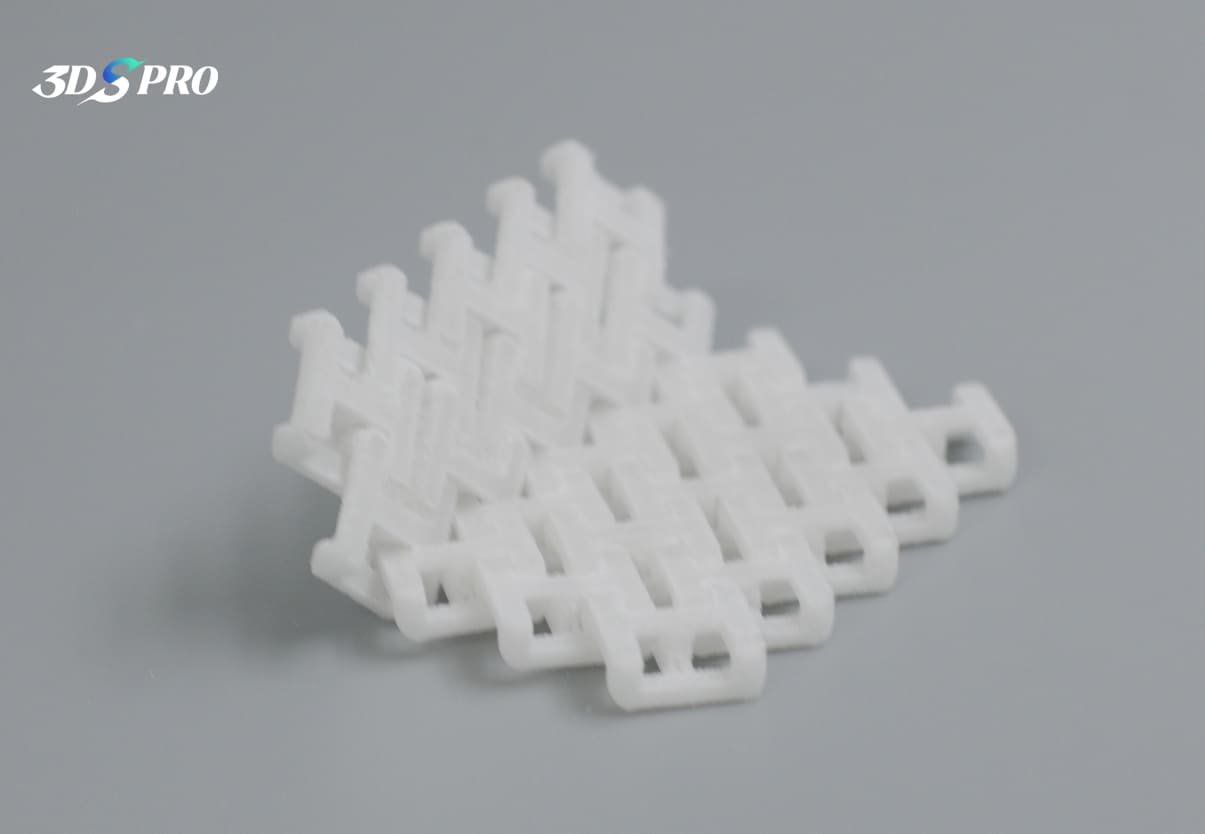
Chainmail Sample |
SLS 3D Printing |
TPU |
85-90A |
White |
The SLS TPU printed chainmail:
1. Light weight.
2. Surface is smooth, feels a bit powdery.
3. Soft and flexible.
4. The chainmail structure is fun. :D

SLS 3D printer preheats dry TPU powder and uses a high-energy laser to sinter each layer according to the 3D model, building the part layer by layer. After printing, the SLS printed TPU part is allowed to cool gradually to prevent warping. Finally, the part is removed from the powder bed, and the excess powder is cleaned off. You will then have a durable TPU part.
SLS can print TPU with fine details and complex geometries without the need for support structures. Compared to FDM, SLS printed TPU parts generally have a smoother surface finish, reducing the need for post-processing. These parts exhibit isotropic mechanical properties in all directions, which increases their strength and durability. SLS printed TPU parts are highly resistant to wear and abrasion.
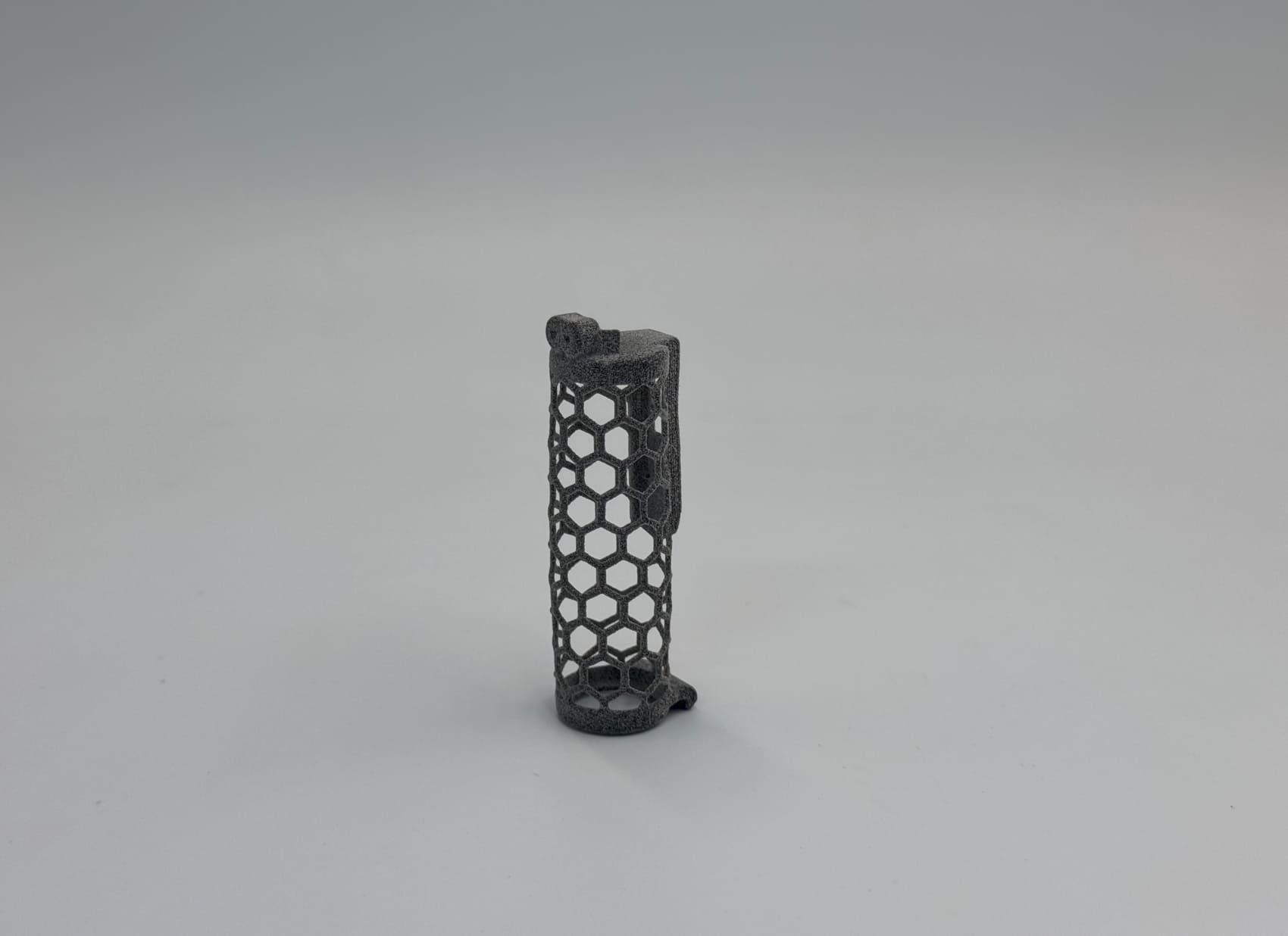
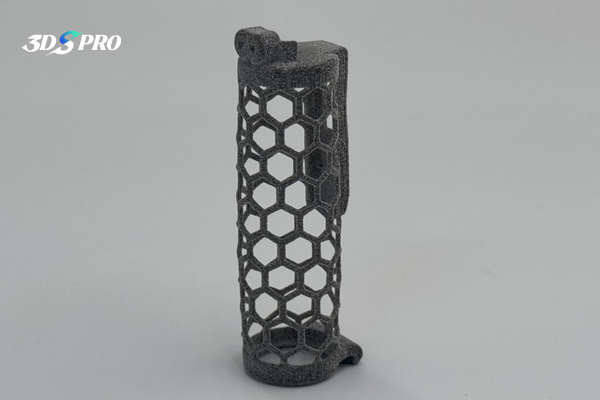
2. MJF 3D Printed TPU

|
What we make? |
Process |
Material |
TPU Hardness |
Color |
|
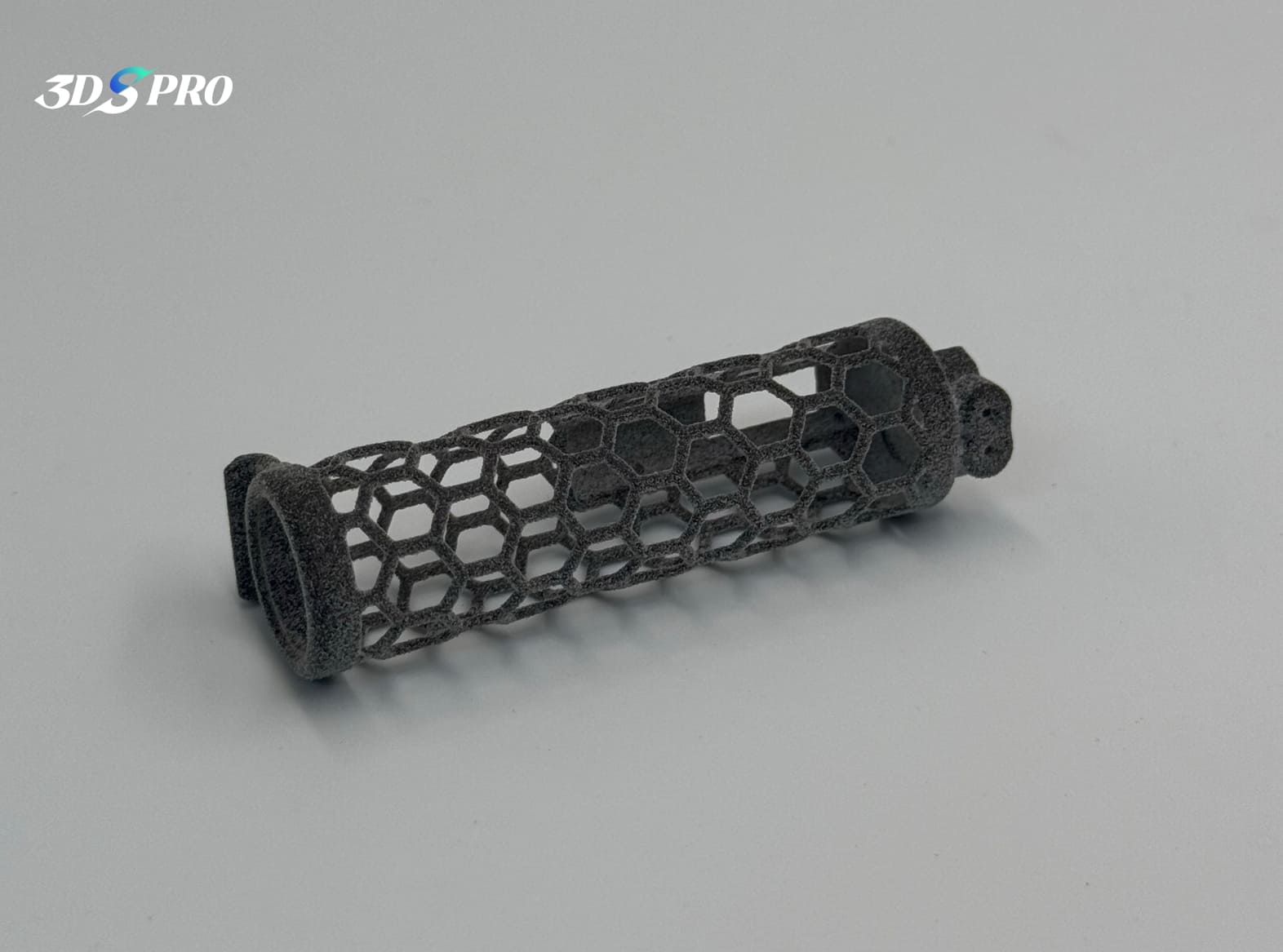
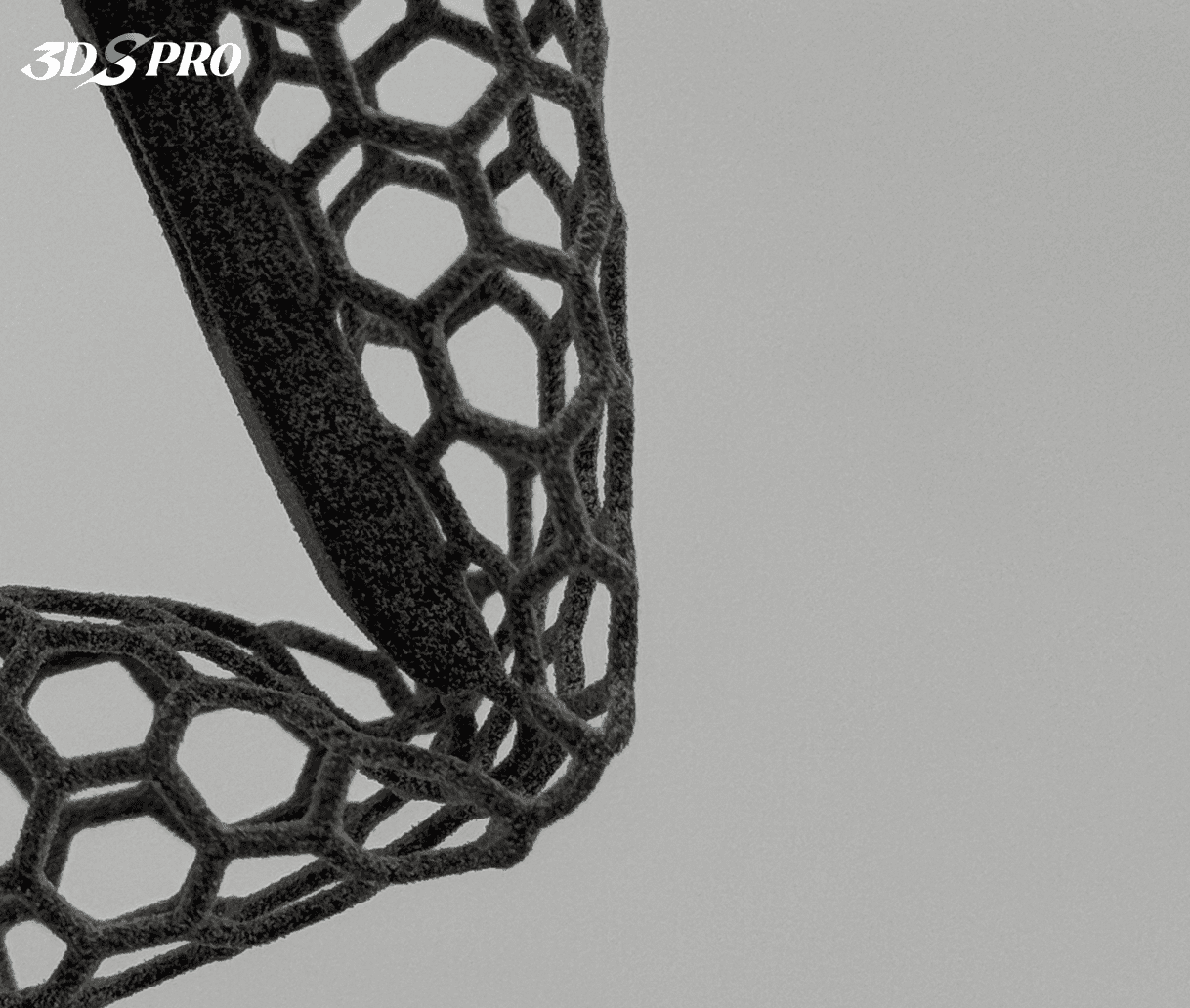
Honeycomb Tube |
MJF 3D Printing |
TPU |
88-90A |
Gray |
The MJF TPU printed tube with honeycomb structure:
1. Very light weight.
2. Surface is smooth, feels a bit powdery (but less than SLS TPU printed chainmail).
3. Soft and elastic, it can quickly return to its original shape after being pressed.
4. It is a functional prototype.
The MJF 3D printer lays a thin layer of TPU powder on the build platform. An inkjet head then deposits a fusing agent and detailing agent onto the powder layer. A heating unit passes over the powder bed, melting areas with the fusing agent, while the detailing agent defines the boundaries of the part. The process is repeated layer by layer until the entire TPU part is built. You get a TPU part with excellent mechanical properties. MJF TPU parts also do not require supports.
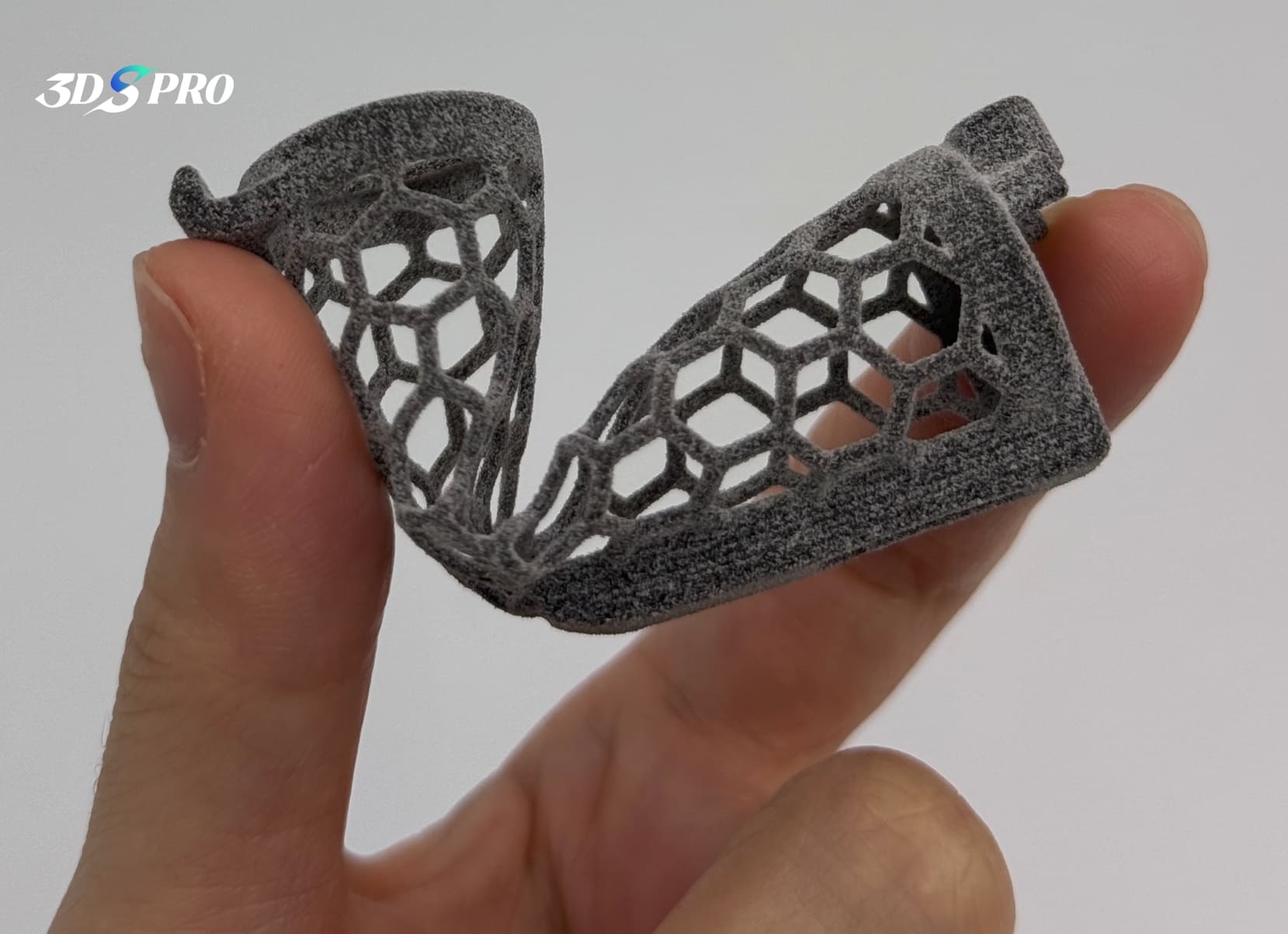
MJF printed TPU parts are highly flexible and tough, with excellent elongation and impact resistance. TPU parts produced using MJF typically have a smoother surface finish than FDM and SLS. MJF TPU parts also exhibit isotropic mechanical properties in all directions.

3. FDM 3D Printed TPU
FDM is a widely used 3D printing method where a continuous filament of TPU is fed through a heated extruder and deposited layer by layer to build the desired TPU 3D print.
The quality of FDM-printed TPU parts is highly dependent on print settings, such as temperature, speed, and layer height. FDM-printed TPU parts may have visible layer lines and a rougher surface finish compared to SLS and MJF TPUs. The FDM TPU printing process can be challenging, as TPU 3D printer filaments are difficult to handle due to their flexibility, requiring specific printer modifications or settings to avoid issues such as filament tangling.
Overall, FDM is one of the most convenient and cost-effective methods for printing TPUs, as FDM 3D printers are relatively inexpensive to purchase. Alternatively, you can opt for FDM 3D printing services on the market.
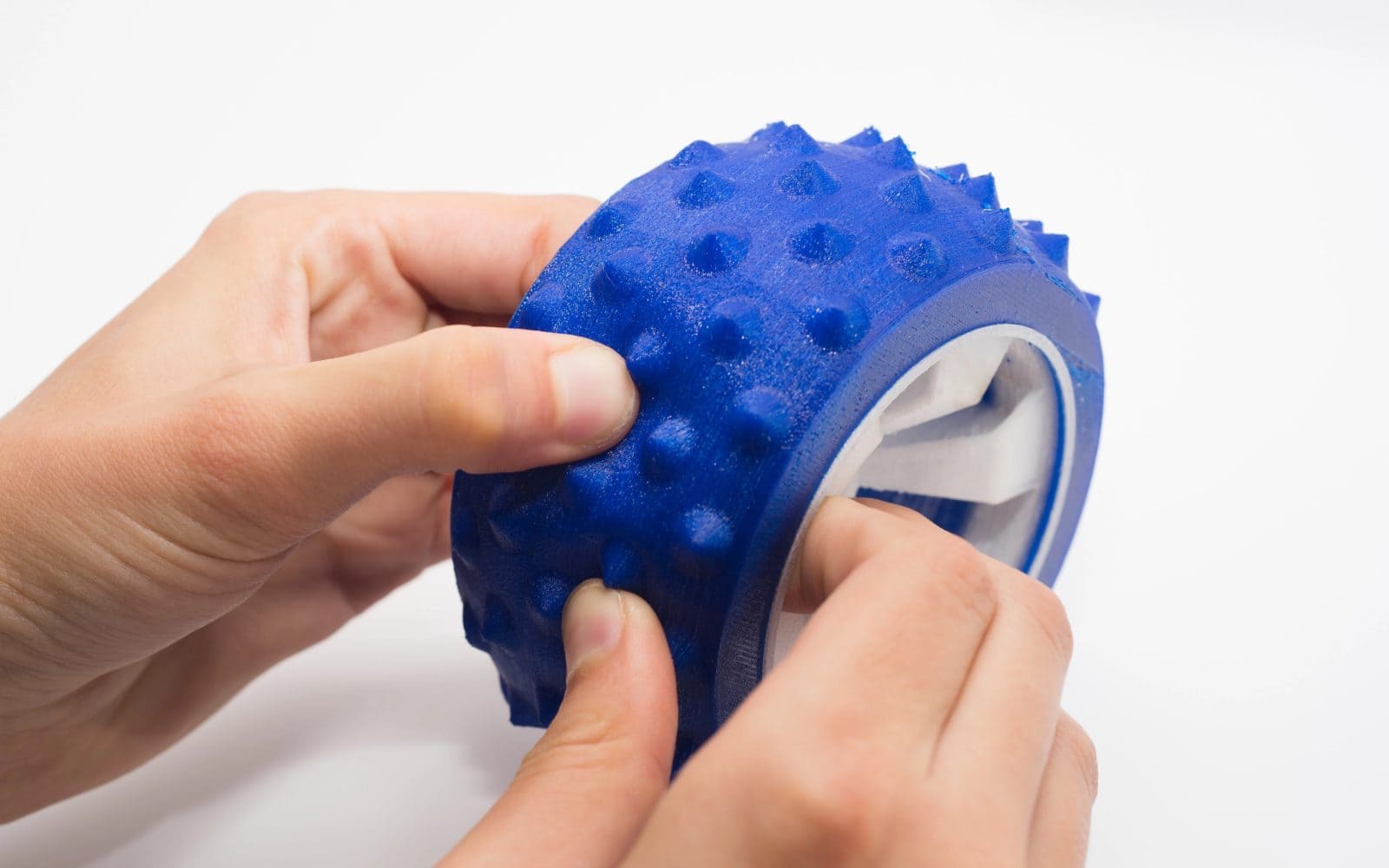

Image Source: Hubs
TPU Material for 3D Printing
TPU is a versatile and flexible material widely used in 3D printing. It is known for its excellent mechanical properties, including high elasticity, durability, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals.
3D Printer TPU Filaments
TPU filaments are used in FDM 3D printers. These filaments are flexible and can be extruded through a heated nozzle to build objects layer by layer.
TPU filaments are highly flexible, making them ideal for creating parts that need to bend or stretch without breaking. They offer excellent resistance to wear and tear, ensuring long-lasting performance.
TPU Plastic Powders
TPU plastic powders are used in SLS and MJF 3D printers. These powders are sintered or fused layer by layer to create detailed and durable TPU parts.
Parts produced with TPU powders typically have a smoother surface finish compared to FDM, reducing the need for post-processing. They are suitable for producing complex and intricate TPU parts for various industrial applications.
Shore Hardness
There is another key factor when choosing TPU material for your project: Shore hardness.
Shore hardness is a measure of a material's resistance to indentation and is commonly used to rate the hardness of polymers, elastomers, and rubbers. The Shore hardness scale ranges from 0 to 100, with higher numbers representing harder materials and lower numbers representing softer materials.
There are several Shore hardness scales, such as Shore A for softer materials like rubber and Shore D for harder materials like hard plastics. 3D printable TPU typically has a Shore hardness range of 85A to 95A, indicating its flexibility and softness. Some special types of TPU can have a Shore hardness as low as 40A, making it softer and more flexible.
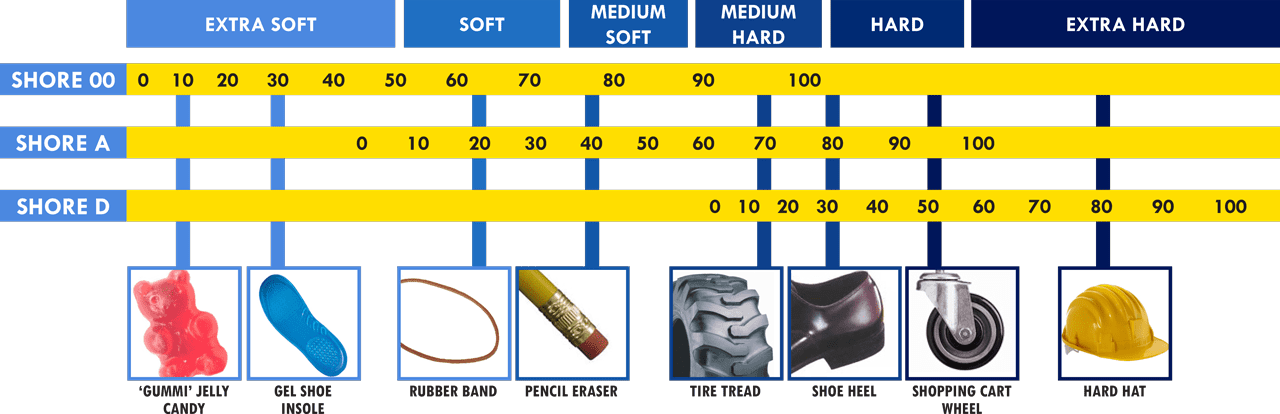
Image Source: Smooth-On Durometer Chart
3D Printing TPU at 3DSPRO
1. SLS 3D Printing Services
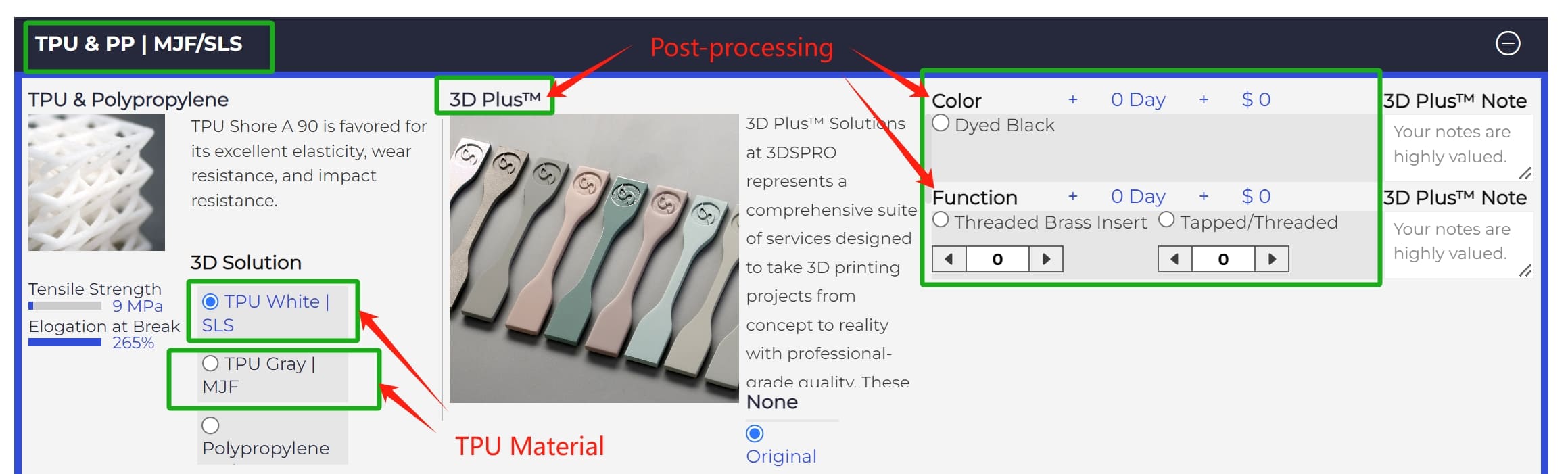
We offer SLS 3D printing with TPU for rapid prototyping and end-use production. Experienced in footwear, sports and medical applications. We also have specialized post-processing methods for SLS TPU parts called 3D Plus™ solutions, including dyeing, threading, tapping and more.
2. MJF 3D Printing Services
We offer high-quality MJF 3D printing services using TPU with outstanding flexibility, durability and precision. We are experienced in producing both functional and production parts with short turnaround times. We also have post-processing methods specifically for MJF TPU parts, including dyeing, threading, tapping and more.
Get the Costs of Your TPU 3D Printing Project Now
























