Earth Day 2024: Planet vs. Plastic
As Earth Day 2024 approaches, the world turns its attention to the escalating battle against plastic pollution. This year’s theme, “Planet vs. Plastic,” underscores a critical crossroads for environmental stewardship and sustainability.
The Plastic Predicament
Plastic, once hailed as a marvel of modern science, now blankets our planet with waste. Its durability and convenience have led to a throw-away culture, resulting in a staggering 448 million tons of plastic produced annually. Alarmingly, a significant portion of this plastic ends up as environmental pollutants, with an estimated 19-23 million tonnes leaking into aquatic ecosystems every year.
The Health Hazard
The ubiquity of plastic not only mars natural beauty but also poses a dire threat to wildlife and human health. Microplastics, the tiny fragments resulting from plastic degradation, have infiltrated our food chain and water sources. These particles carry toxic substances, raising concerns about their long-term effects on biological systems and human health.
A Call to Action
In response, EARTHDAY.ORG has set a bold agenda for Earth Day 2024, demanding a 60% reduction in plastic production by 2040 and advocating for a strong UN Treaty on Plastic Pollution. The campaign emphasizes the need for innovative solutions and a collective effort to phase out single-use plastics and mitigate the impact of fast fashion.
The Path Forward
As we commemorate Earth Day, we must reflect on our relationship with plastic. It’s a moment to rally, to innovate, and to forge a future where the planet no longer bears the burden of our plastic legacy. The fight against plastic is a fight for the health of our planet and all who call it home. Together, we can turn the tide on plastic pollution and pave the way for a cleaner, greener world.

Image Source: EARTHDAY.ORG
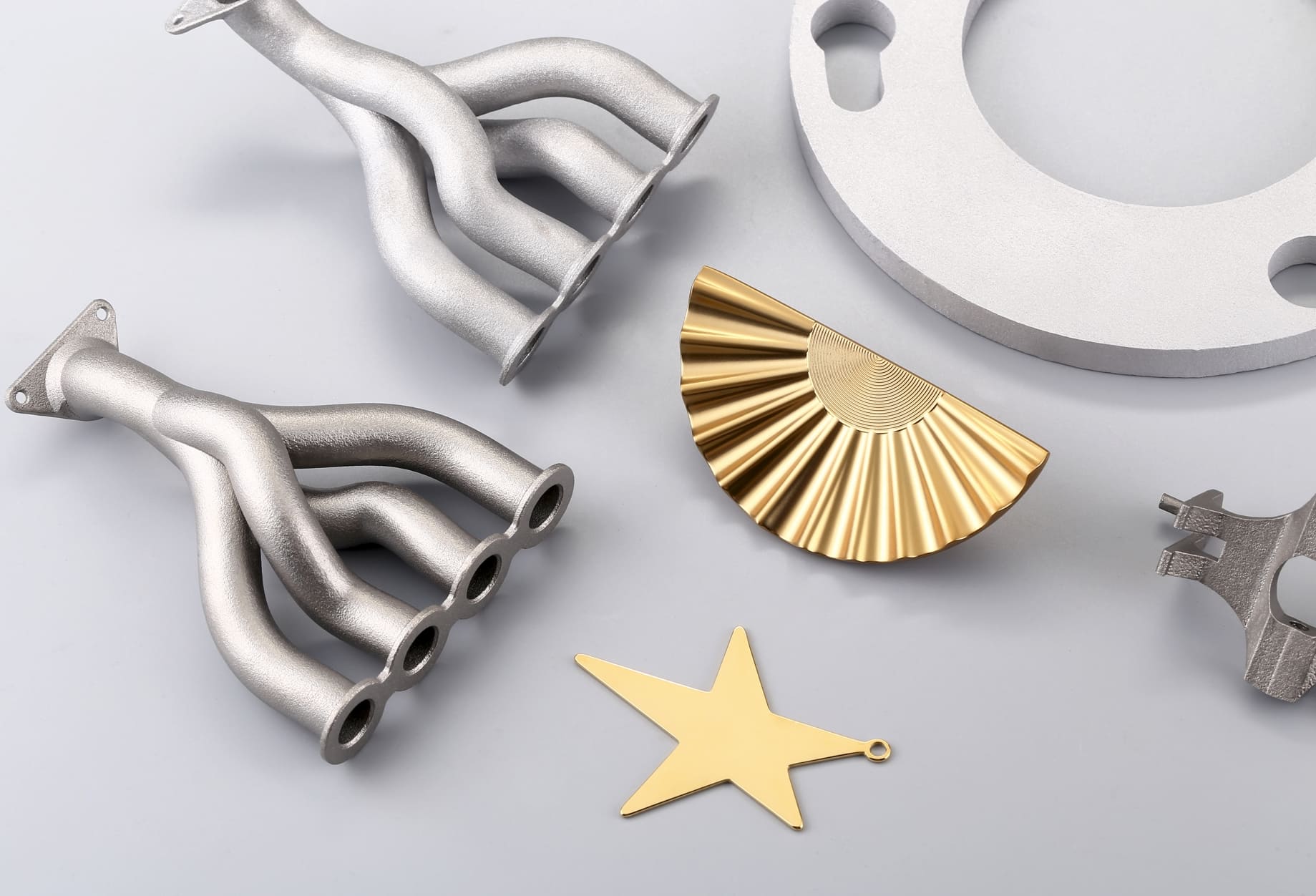
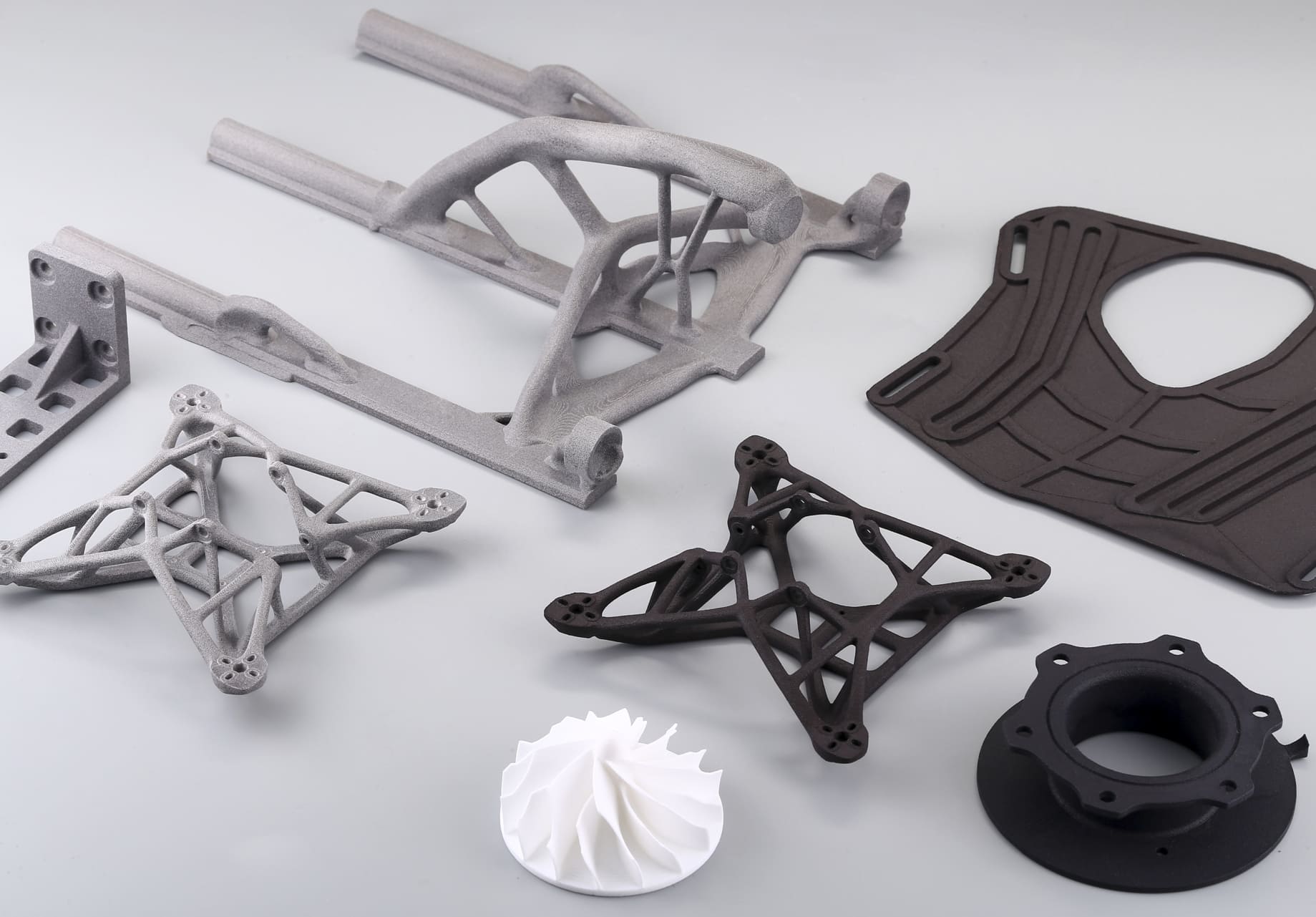
Can 3D Printing reduce plastic use?
Additive manufacturing (3D Printing) has a significant role to play in achieving net-zero emissions. By focusing on material efficiency, energy management, and sustainable practices, AM can help pave the way for a more environmentally friendly manufacturing sector. As industries and governments work towards carbon neutrality, AM offers a promising avenue for sustainable growth and innovation.
However, the intersection of 3D printing technology and environmental sustainability presents a paradox. On one hand, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is often associated with plastic materials, which are notorious for their environmental impact. On the other hand, this innovative technology holds the potential to revolutionize the way we think about and use plastics.
The Promise of 3D Printing
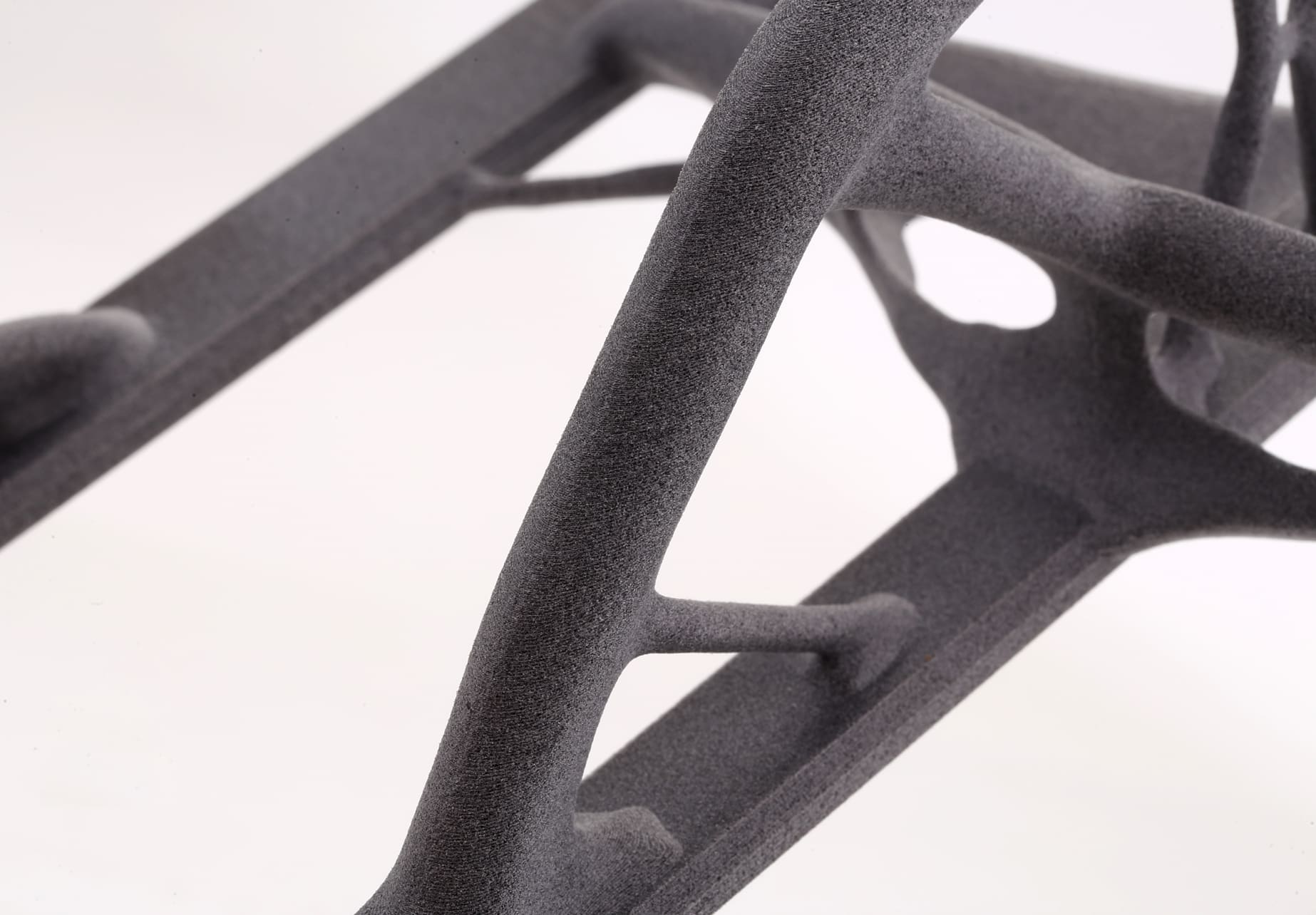
3D printing technology has the unique advantage of being an additive process, building objects layer by layer, which can significantly reduce material waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. The precise nature of the process ensures that only the required amount of plastic is utilized, potentially reducing the volume of plastic waste generated during production.
Moreover, 3D printing can breathe new life into plastic waste. Successful projects have showcased the utilization of post-consumer plastic waste as a primary material for 3D printing filaments. It not only aids in diverting plastic from landfills and oceans but also diminishes the need for virgin plastic production.
Challenges and Considerations
However, the environmental benefits of 3D printing are complex. 3D printers can consume substantial energy, and reliance on plastic materials remains a concern. Additionally, the process can produce fumes and toxic by-products that may require careful management to avoid environmental harm.
The Role of Bioplastics
One of the most interesting advancements in 3D printing is the use of biodegradable plastics. These materials can offer the same versatility and durability as conventional plastics but with the added benefit of being compostable at the end of their lifecycle. The adoption of bioplastics in 3D printing could significantly mitigate the long-term environmental impact of plastic products.
Towards a Circular Economy
3D printing is consistent with the principles of the circular economy, which emphasizes the reduction, reuse, and recycling of materials. By enabling the local production of goods, 3D printing can reduce transportation emissions and support decentralized recycling initiatives where waste plastic is turned into valuable products.
In conclusion, while 3D printing does involve the use of plastics, it offers a pathway to more sustainable material use. 3D printing could substantially lessen the ecological footprint of plastic manufacturing by optimizing the use of materials, encouraging the recycling of plastic waste, and investigating the use of biodegradable options. Realizing this potential requires many efforts, that is exactly what 3DSPRO's S Initiative means: continued innovation, responsible materials management, and integrating 3D printing into a comprehensive environmental strategy.