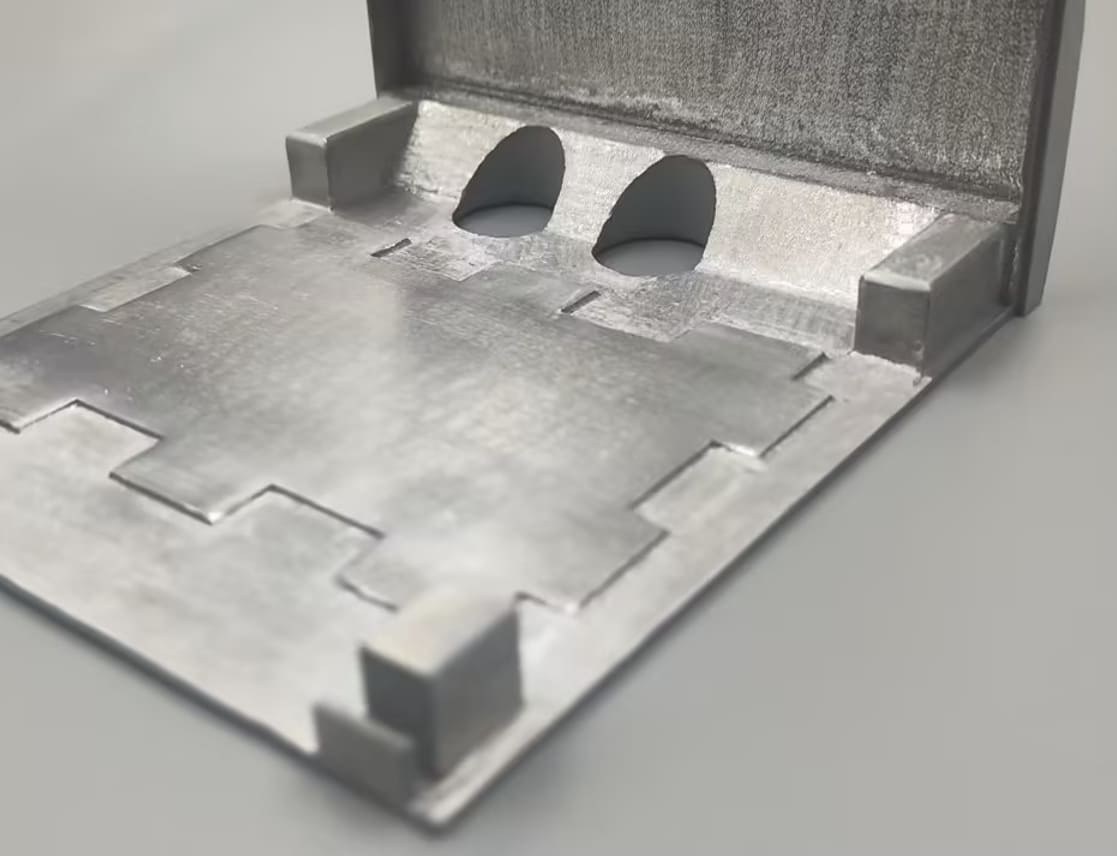
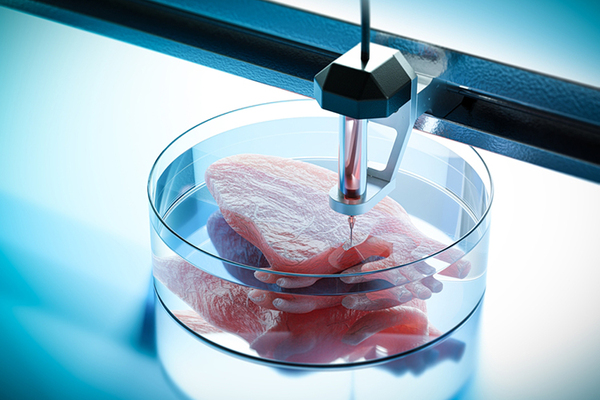
How does 3D printing help the medical industry?
3D printing is a force to change the landscape of medical manufacturing, patient care, and clinical procedures. Its ability to produce customized, complex, and cost-effective solutions is why 3D printing is redefining the medical industry.
Customization and Personalization
3D printing allows for the creation of medical devices tailored to the individual’s anatomy, which is particularly beneficial for implants and prosthetics, ensuring a perfect fit and improved comfort for patients.
Rapid Prototyping
The technology enables quick production of prototypes, allowing for faster design iterations and development, accelerating the innovation cycle for new medical devices.
Complex Geometries
With 3D printing, complex structures that are difficult or impossible to create with traditional manufacturing methods can be produced. It is crucial for intricate devices like internal bone structures or detailed dental work.
Cost-Effectiveness
It reduces the need for expensive tooling and molds, making it a cost-effective solution for manufacturing medical devices, especially in low volumes or for highly specialized applications.
Educational Models
Accurate anatomical models derived from patient imaging data can be printed, providing a valuable tool for medical education and pre-surgical planning.
In-House Production
Hospitals are increasingly adopting in-house 3D printing facilities, which allow for on-demand production of medical tools and devices, reducing dependency on external suppliers and improving response times in critical situations.
Research and Innovation
Ongoing research is exploring the potential of 3D printing for bioprinting tissues and organs, which could lead to breakthroughs in transplants and treatments for various diseases.
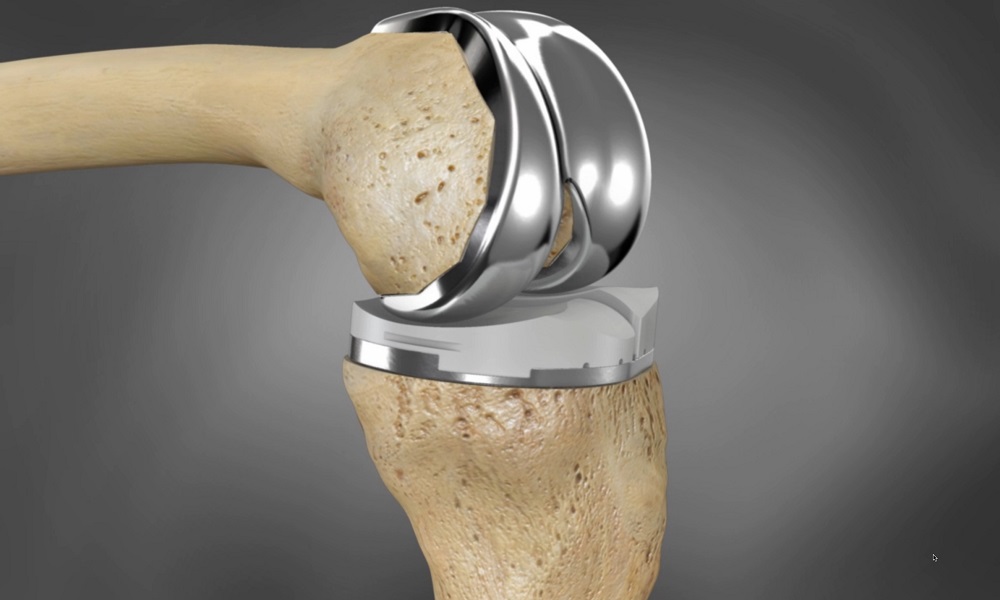
Image Source: Advanced Chiropractic Spine & Sports Medicine
3D Printing Applications in Medical Industry
Customized Prosthetics and Orthopedics
One of the most profound impacts of 3D printing is the creation of custom-fit prosthetic limbs and orthopedic implants. These devices are tailored to the patient’s exact body measurements, providing better functionality and comfort.
Surgical Instruments
The technology is used to produce precise and specialized surgical tools that cater to the specific needs of operations and surgeons’ preferences. This customization can lead to more successful outcomes and quicker recovery times for patients.
Bioprinting and Tissue Engineering
Although still in the experimental phase, 3D printing holds the promise of printing living tissues and organs. 3D printing could revolutionize organ transplants and the treatment of various diseases in the future.
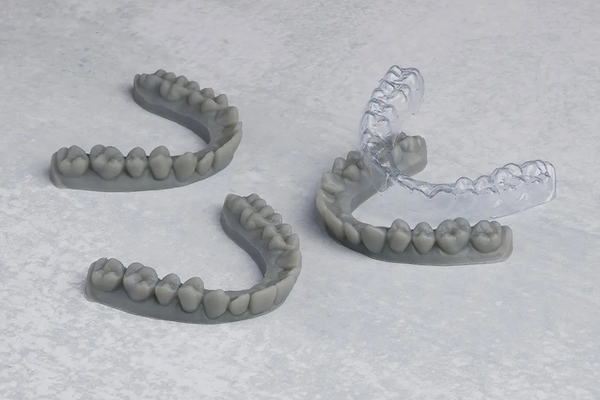
Dental Applications
In dentistry, 3D printing is used to create crowns, bridges, stone models, and a range of orthodontic appliances, all with remarkable speed and precision.
Personalized Medical Devices
Beyond implants and prosthetics, 3D printing allows for the production of personalized medical devices, such as hearing aids, which can be designed to fit the unique contours of a patient’s ear.
Anatomical Models
Accurate models of patient-specific anatomy can be printed for educational purposes or to plan complex surgical procedures. These models help surgeons to practice and strategize before the actual operation.
Instrumentation
3D printers manufacture various medical instruments, including guides that assist with the correct placement of a device during surgery, which improves the accuracy and efficiency of surgical procedures.
Implants
From cranial plates to hip joints, 3D printing is used to create implants that can be customized to fit the patient’s anatomy, leading to better integration and longevity of the implant.
External Prostheses
The technology is also applied in creating external prostheses like hands, which are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing, helping to improve the quality of life for amputees.
Research and Development
3D printing is a powerful tool for R&D, enabling the rapid prototyping of medical devices. It allows for quick iteration and testing, which is essential for innovation in medical technology.
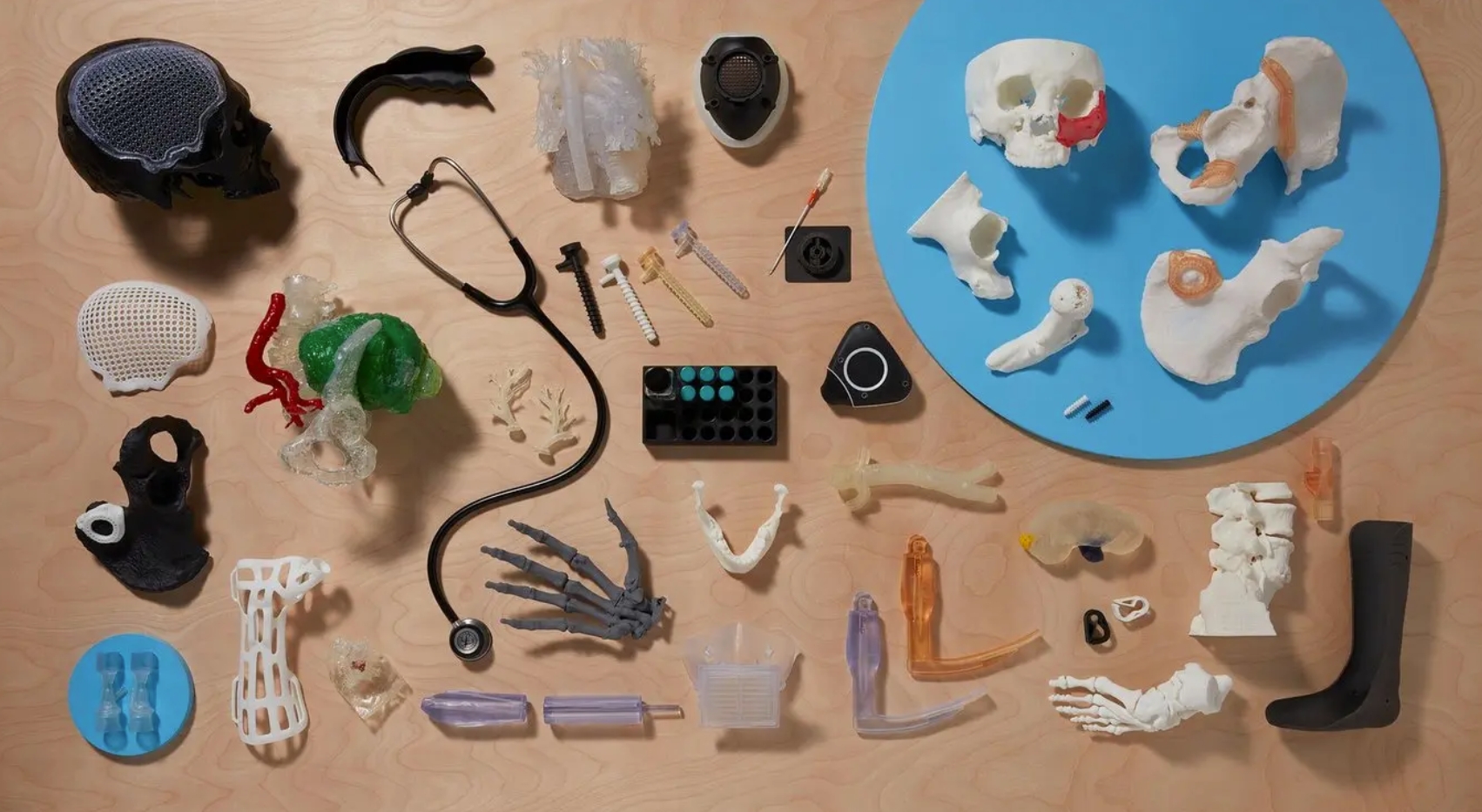

Image Source: Formlabs
Are 3D printed implants safe for the human body?
The safety of 3D printed implants has been a topic of extensive research and discussion within the medical community. 3D printed implants are often made from biocompatible materials, meaning they are designed to be safe when in contact with human tissue. Metals like titanium, which are commonly used in these implants, have a long history of safe use in the body. Besides, bioresorbable polymers can gradually break down and are absorbed by the body, eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove the implant.
As 3D printed implants can be customized to fit the patient’s anatomy precisely, they often require less adjustment during surgery, which can reduce the risk of complications.
Before being approved for use, 3D printed implants undergo rigorous clinical testing to ensure they perform as intended and do not cause adverse reactions. Tests with human cells have shown that bioscaffolds built using 3D printing are safe and non-toxic.
While the benefits are significant, it’s important to acknowledge that, as with any medical device, there are potential risks. These can include allergic reactions, chronic inflammation, or greater susceptibility to infection. However, such risks are not unique to 3D printed implants and can occur with any type of implant.
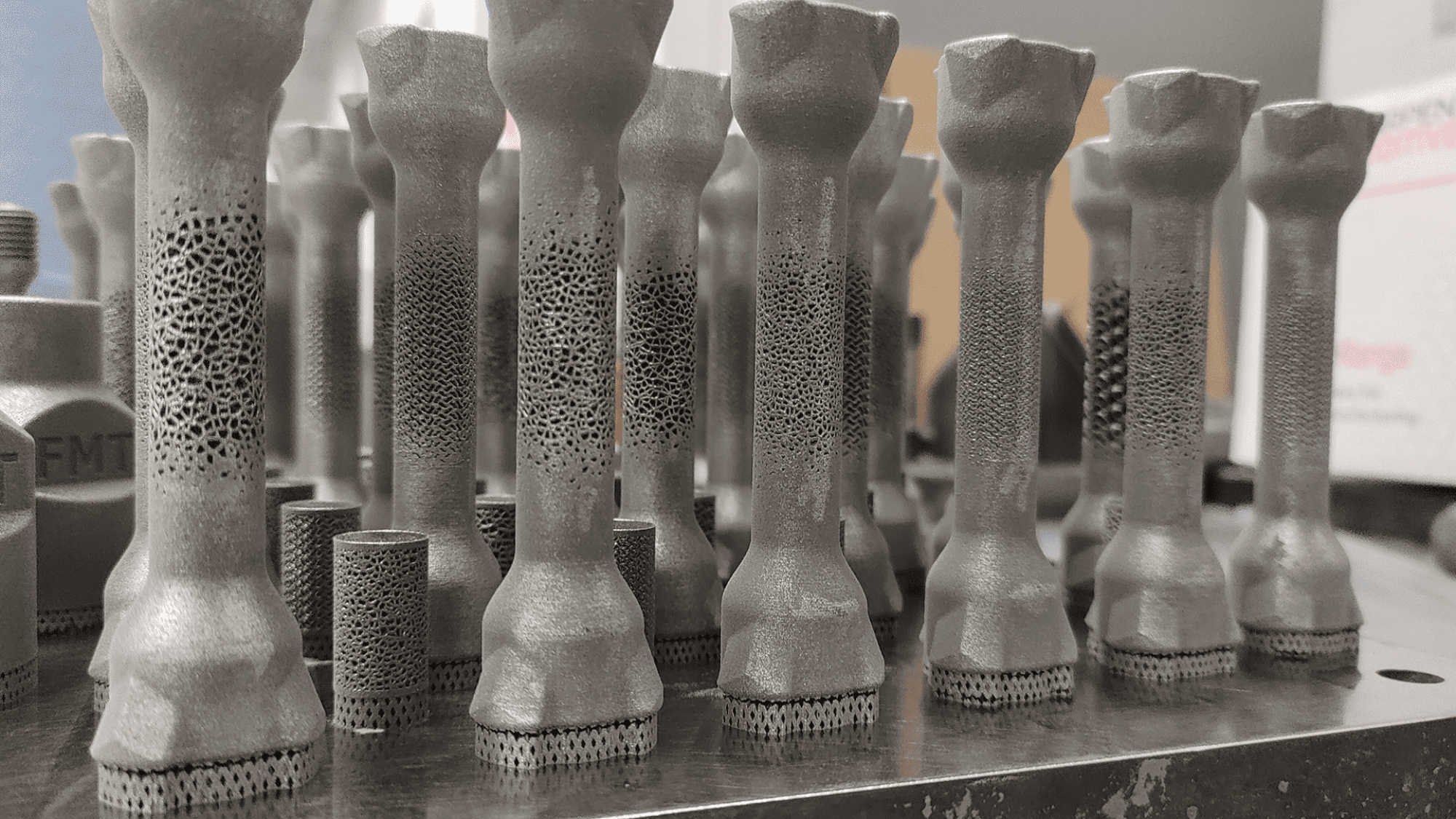

Image Source: UNIVERSITY OF OULU
How to regulate 3D printed healthcare products?
Regulating 3D printed healthcare products is crucial to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality. The regulation of 3D printed healthcare products involves a comprehensive framework that addresses the entire lifecycle of a device, from design and manufacturing to post-market monitoring. By adhering to these regulations, manufacturers can ensure that their products are safe and effective for medical use.
Establishing Standards
Regulatory bodies like the FDA have set guidelines for 3D printing in healthcare, covering device design, manufacturing, and testing. These standards ensure that products are safe for patient use and meet the same quality criteria as traditionally manufactured devices.
Quality Systems Regulations
Manufacturers must comply with existing quality systems regulations, which include requirements for the design, production, and distribution of medical devices. Quality systems ensure that 3D printed devices are consistently produced to high standards.
Material Safety
The materials used in 3D printing must be biocompatible and safe for patient contact. Regulators require thorough testing to ensure that these materials do not cause adverse reactions.
Technical Considerations
The FDA provides specific technical considerations for additive-manufactured devices, which include recommendations for device design, manufacturing processes, and device testing.
Point-of-Care Manufacturing
With the rise of point-of-care (PoC) 3D printing at hospitals and medical centers, there’s a need for clear regulatory frameworks to address the unique challenges posed by in-house device production.
Post-Market Surveillance
After a 3D printed medical device is approved and in use, manufacturers must engage in post-market surveillance to monitor the device’s performance and report any adverse events.
Collaboration with Standards Organizations
Agencies like the FDA collaborate with standards organizations such as ASTM International to develop and publish standards and test methods for additive manufacturing technologies.
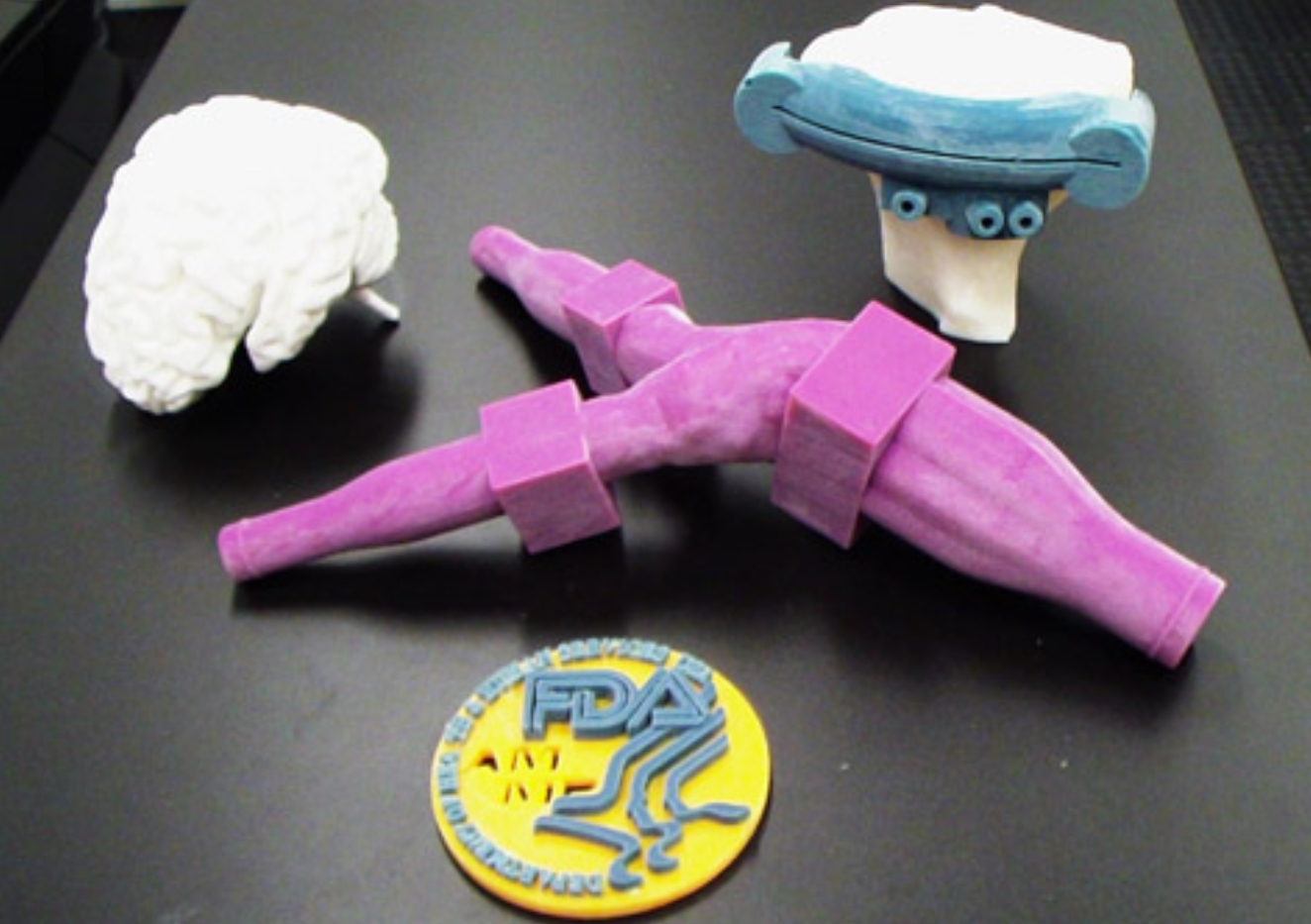

Image Source: FDA
3DSPRO Delivers 3D Printing Services for Various Industries
3DSPRO offers a suite of comprehensive solutions that cater to a wide range of industries. With a variety of technologies like Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), and Selective Laser Melting (SLM), we can produce prototypes and end-use parts with precision and efficiency.
● SLA Printing: Known for its high resolution and smooth surface finish, SLA is ideal for creating detailed prototypes and end-use parts.
● SLS Printing: SLS is known for its ability to produce strong, durable parts without the need for support structures, which makes it perfect for complex geometries and moving parts.
● MJF Printing: MJF stands out for its speed and precision, producing parts with fine details and consistent mechanical properties.
● SLM Printing: Specializing in metal parts, SLM can create high-strength and complex metal components that are impossible to manufacture through traditional methods.
● Material Versatility: 3DSPRO provides a wide range of materials, from durable plastics to premium metals, ensuring that clients can find the perfect fit for their projects.
● 3D Plus™ Solutions: 3DSPRO provides comprehensive post-processing solutions for different types of 3D printing, ensuring aesthetics and functionality.
● Industry-Specific Solutions: 3DSPRO offers tailored solutions for industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer products.
● Rapid Turnaround: Understanding the importance of time in innovation, we have a quick production lead time, which ensures that clients can move swiftly from design to deployment.

COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!