The process of 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, consists of layering materials based on digital models in order to produce three-dimensional objects. Dental professionals and patients benefit greatly from 3D printing, which has transformed traditional dental practices.
A major advantage of 3D printing in dentistry is its ability to produce high-precision and customized instruments. Traditional methods of creating dental implants, crowns, bridges, and orthodontic devices involve multiple steps, manual labor, and significant time. However, with 3D printing, these processes are streamlined, and faster production and greater precision are feasible.
Dental professionals can use intraoral scanners to capture detailed images of a patient’s teeth and gums, which are then converted into digital models. These models are used to design and print dental appliances that perfectly fit the patient’s unique anatomy.
Moreover, 3D printing reduces the time required to produce dental parts. Now, what used to take weeks can be completed in a matter of hours or days.
Applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry
Dental Implants
3D printing has changed the creation of dental implants. Using an intraoral scanner, dentists can capture detailed images of a patient’s teeth and gums. A digital model is then created from these images to design implants that are exactly sized for the patient. The high resolution and accuracy of 3D printers, such as those using stereolithography (SLA) or digital light processing (DLP), are capable of making implants with complex geometries and fine details.
Crowns and Bridges
With 3D printing, dentists can design crowns and bridges based on digital scans of the patient’s teeth, ensuring a perfect fit. The use of biocompatible materials, such as dental resins and ceramics, ensures that the printed crowns and bridges are durable and accurate.
Orthodontics
In orthodontics, 3D printing is widely used to create clear aligners and other orthodontic devices. Clear aligners, such as those used in Invisalign treatments, are custom-made to fit a patient’s teeth and gradually move them into the desired position. Start with a digital scan of the patient’s teeth, then a series of aligners are designed that apply gentle pressure to the teeth over time. 3D printing makes these aligners rapidly; the treatment process thus becomes more efficient and comfortable for patients. Additionally, 3D printing is used to create other orthodontic appliances, including retainers and space maintainers, etc.
Surgical Guides
3D printing can be used to produce surgical guides for dental implants and other surgical procedures. Surgical guides help dentists and oral surgeons place implants and perform other procedures more accurately and confidently, reducing the risk of complications and improving treatment outcomes. The use of 3D-printed surgical guides can also shorten the duration of surgeries and enhance the overall efficiency of dental practices.
Prosthetics
With 3D printing, dentists can design and produce dentures that fit perfectly based on digital scans of the patient’s mouth. Using biocompatible materials ensures that printed prostheses are comfortable, durable, and aesthetically pleasing. Additionally, 3D printing can produce prostheses quickly, reducing wait times for patients and improving their overall experience.
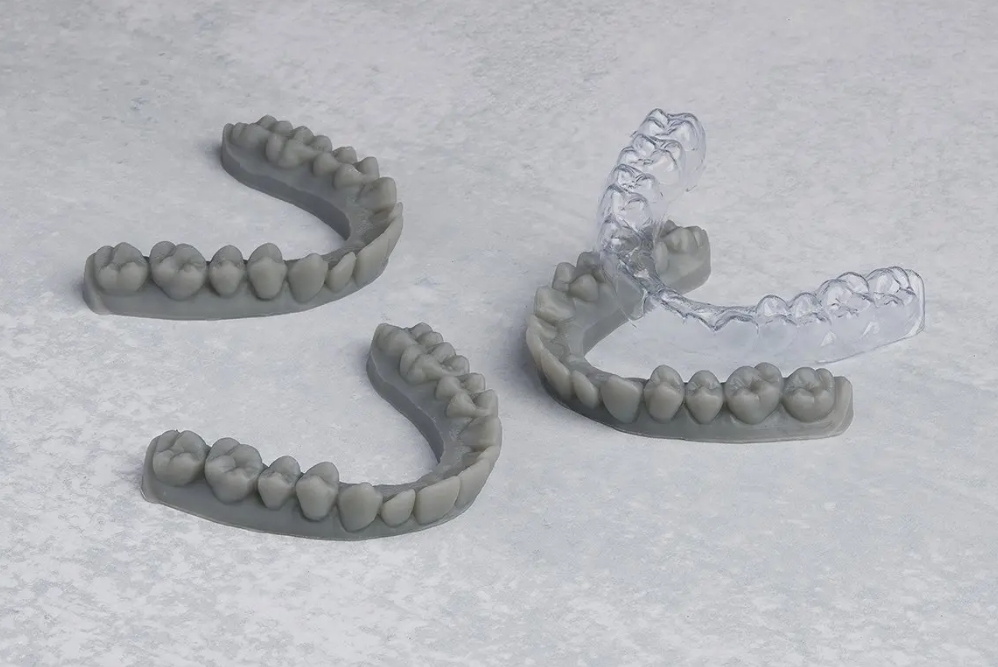

Image Source: Formlabs
Technologies Used in Dental 3D Printing
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography (SLA) is one of the earliest and most widely used 3D printing technologies in dentistry. SLA can produce high-precision dental parts with smooth surfaces. It is ideal for making dental models, crowns, bridges, and surgical guides. The accuracy of SLA printers ensures that dental appliances fit perfectly, reducing the need for adjustments.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is similar to SLA, but uses a digital light projector to cure the resin. DLP 3D printing can produce highly detailed and accurate dental parts quickly. It is particularly useful for creating clear aligners, dental models, and temporary restorations. DLP is a popular choice for dental labs and clinics aiming to enhance their workflow efficiency.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses a laser to fuse powdered thermoplastics into solid objects. SLS is known for its ability to create strong and durable parts with complex geometries. In dentistry, SLS is used to produce frameworks for removable partial dentures, orthodontic appliances, and custom implants. The strength and biocompatibility of SLS printed parts are suitable for long-term use in the mouth.
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is similar to SLS but uses a laser to fully melt metal powders, resulting in dense and strong metal parts. SLM is used in dentistry to create custom metal implants, crowns, and bridges with excellent mechanical properties. SLM can produce complex metal structures with high strength.
Bioprinting
In dentistry, bioprinting holds promise for creating tissue-engineered constructs, such as gingival tissues and bone grafts. While still in the experimental stage, bioprinting has the potential to innovate regenerative dentistry by enabling the creation of personalized, biologically compatible dental tissues.
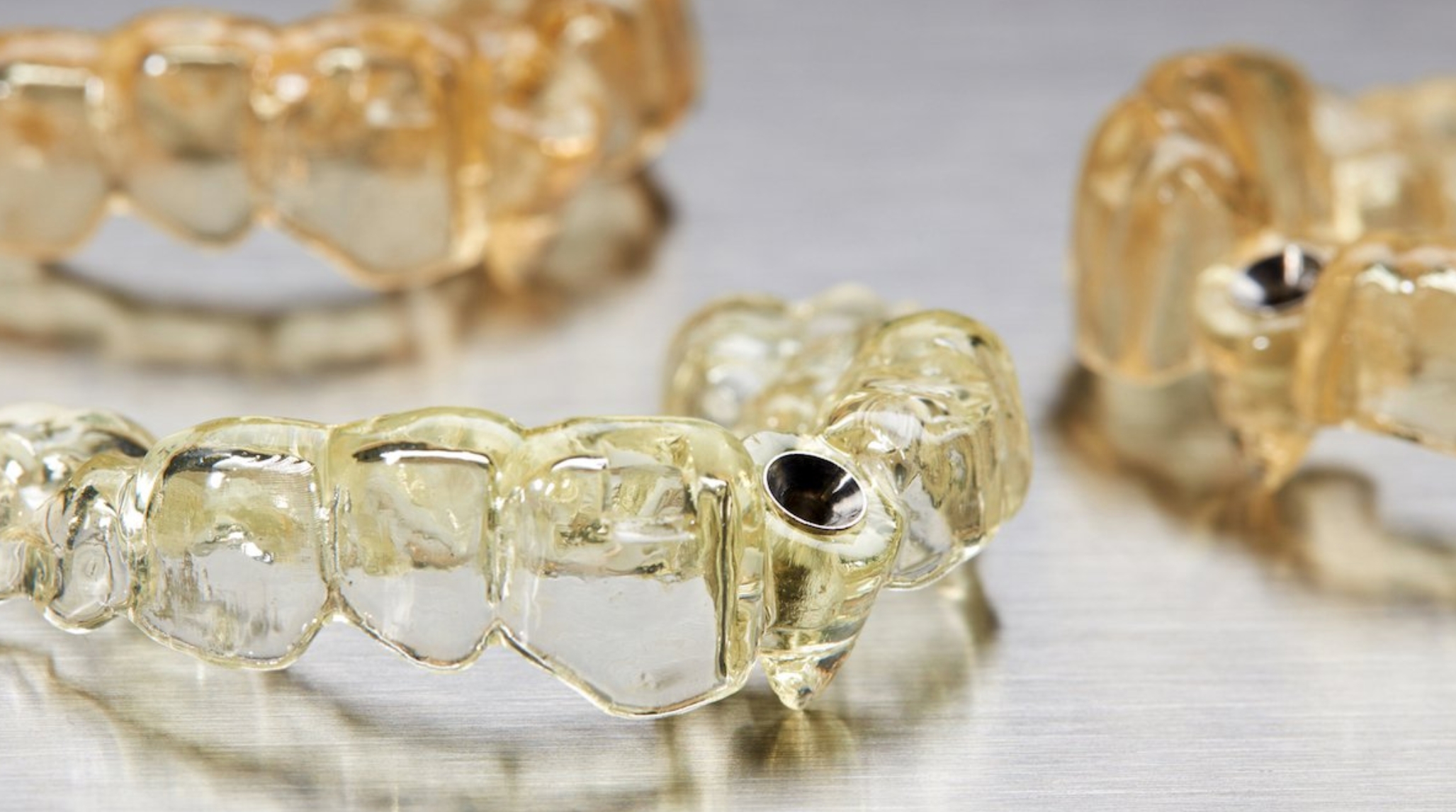

Image Source: Formlabs
Materials Used in Dental 3D Printing
Polymers
● Resins: Dental resins are used in stereolithography (SLA) and digital light processing (DLP) printers. These materials are ideal for creating detailed dental models, crowns, bridges, and surgical guides. Resins can be formulated to have different properties, such as high strength, flexibility, or transparency, making them suitable for various dental applications.
● Acrylics: Acrylic-based materials are often used for fabricating dentures and other removable prosthetics. They offer good mechanical properties and can be easily colored to match the natural appearance of teeth and gums.
● Thermoplastics: Thermoplastics like polylactic acid (PLA) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) are used in fused deposition modeling (FDM) printers. While not as commonly used in high-precision dental applications, they are useful for creating dental models and prototypes.
Metals
● Titanium: Titanium is widely used for dental implants due to its excellent biocompatibility, strength, and resistance to corrosion. 3D printing with titanium allows for the creation of custom implants that fit precisely into a patient’s jawbone.
● Cobalt-Chromium: This alloy is used for creating metal frameworks for removable partial dentures and other dental prosthetics. It offers high strength and durability, which is suitable for long-term use in the mouth.
● Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is used for orthodontic appliances, such as brackets and wires. It provides the necessary strength and flexibility for effective orthodontic treatments.
Ceramics
● Zirconia: Zirconia is a popular material for crowns, bridges, and implants due to its high strength, durability, and natural tooth-like appearance. 3D printing with zirconia allows for the creation of highly precise and aesthetically pleasing dental restorations.
● Alumina: Alumina ceramics are used in some dental applications where high wear resistance and biocompatibility are required. They are less commonly used than zirconia but still play a role in certain dental restorations.
Composites
● Fiber-Reinforced Composites: These materials combine polymers with fibers, such as glass or carbon fibers. They are used for creating dental prosthetics and other applications that require enhanced strength and durability.
● Hybrid Composites: Hybrid composites combine ceramics and polymers to achieve a balance of strength, flexibility, and aesthetics. They are used for crowns, bridges, and other dental restorations that require both durability and a natural appearance.
Image Source: Formlabs
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!