Drones, once a niche technology reserved for military applications, have soared into the public consciousness, becoming popular in various sectors, including photography, agriculture, and even delivery services.
3D printing enables the creation of complex, lightweight structures that are perfect for the aerial demands of drones. It also allows for a level of customization previously unattainable, giving drone enthusiasts the power to tailor their machines to specific needs and preferences. Moreover, the ability to print replacement parts on demand significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs, making drone flying more accessible to a broader audience.
The Advantages of 3D Printed Drones
Customization Possibilities
Enthusiasts and professionals can design and print drones tailored to specific tasks, whether it’s a lightweight frame for racing drones or specialized mounts for photography equipment.
Ease of Repairs and Replacement of Parts
Drones are prone to accidents and damage, especially when navigating challenging environments. 3D printing simplifies the repair process by enabling the quick production of replacement parts. Instead of waiting for parts to be shipped from a manufacturer, drone operators can print a new propeller, gear, or even an entire frame right at home or in the field, reducing downtime and keeping their drones airborne.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility for Hobbyists
The cost of entering the drone hobby has traditionally been high, with pre-assembled drones and proprietary parts carrying hefty price tags. 3D printing makes it more accessible to hobbyists with a tighter budget. By printing their drones, individuals can significantly cut costs, experiment with different designs, and learn valuable skills in drone piloting and 3D printing.
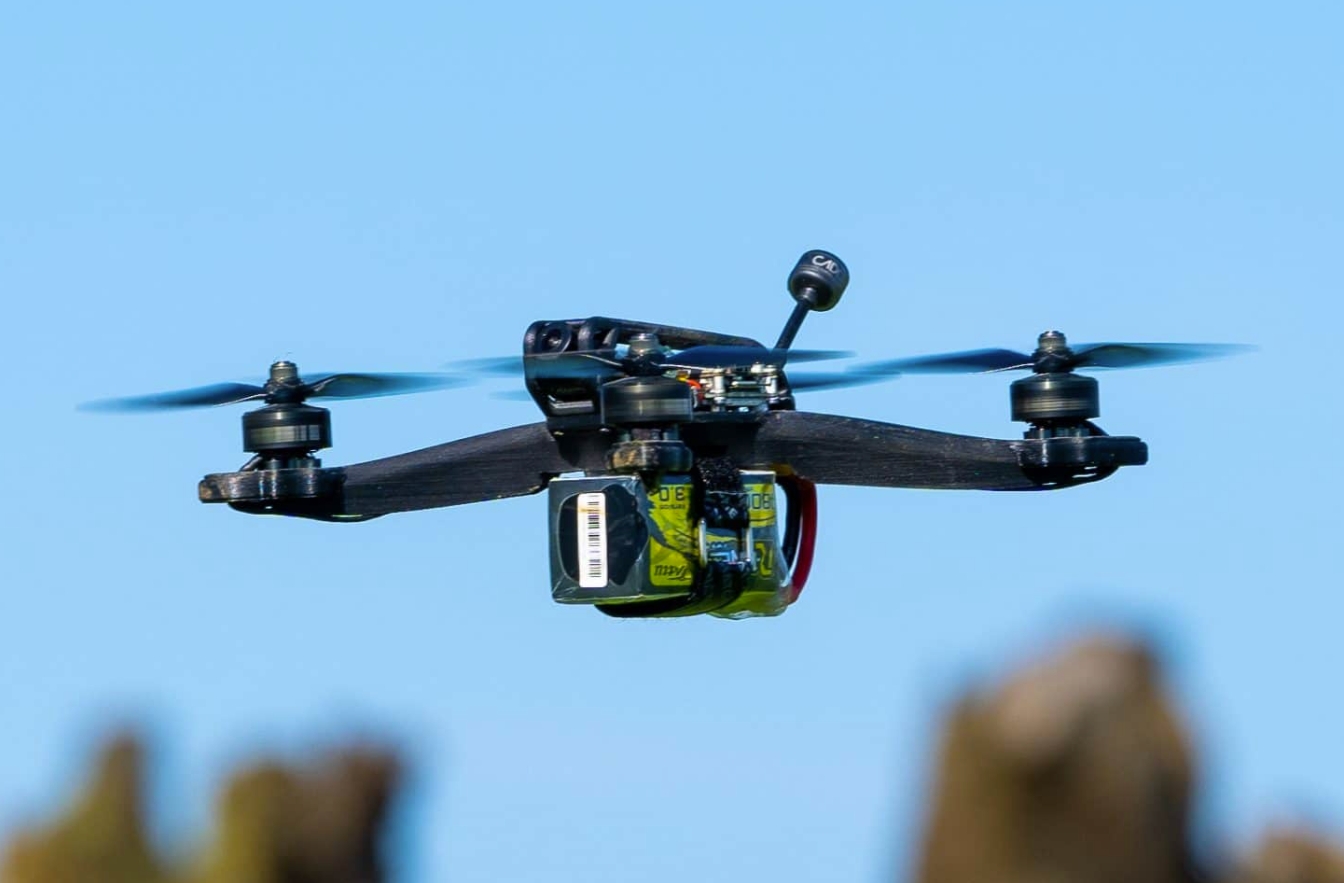

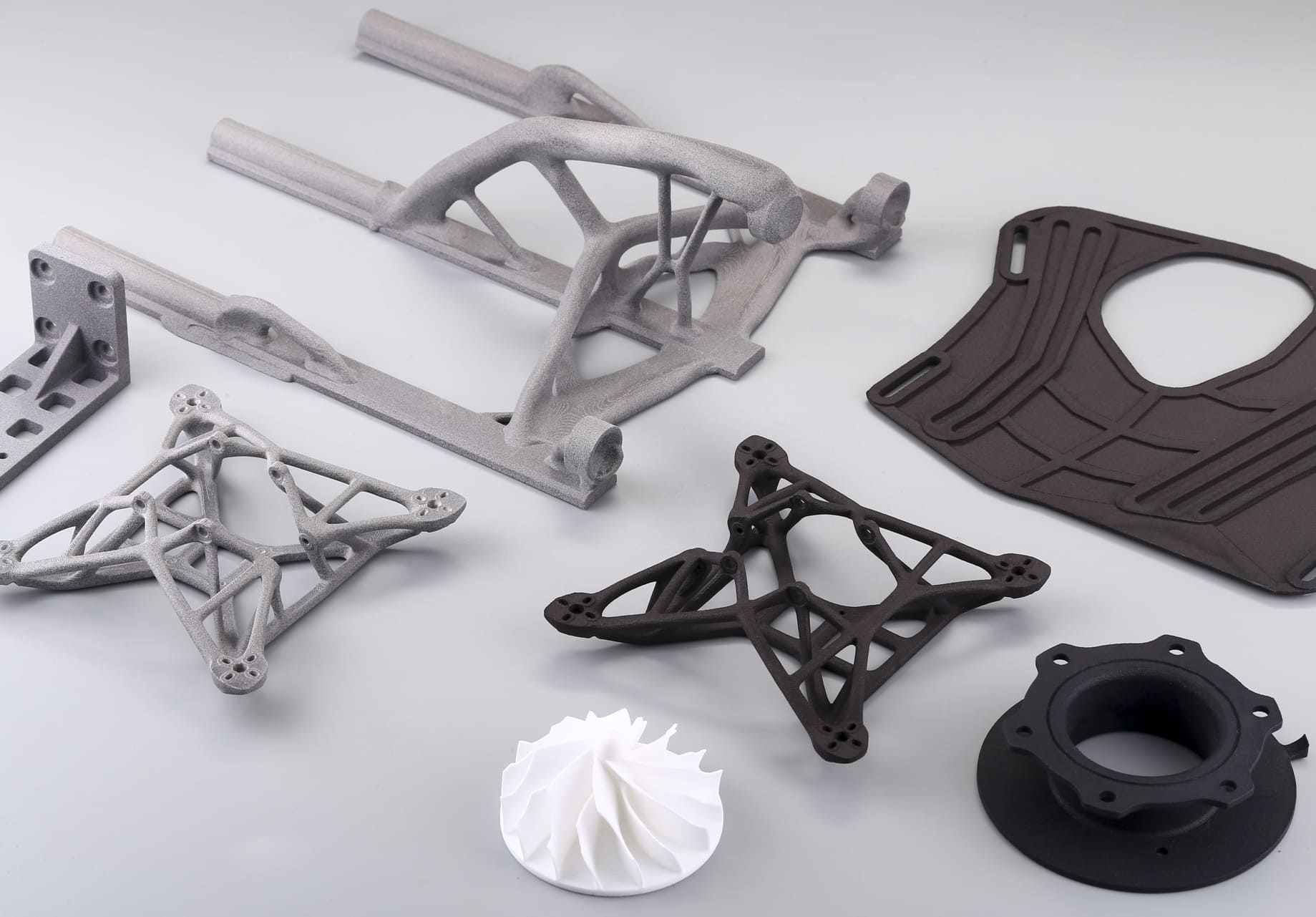
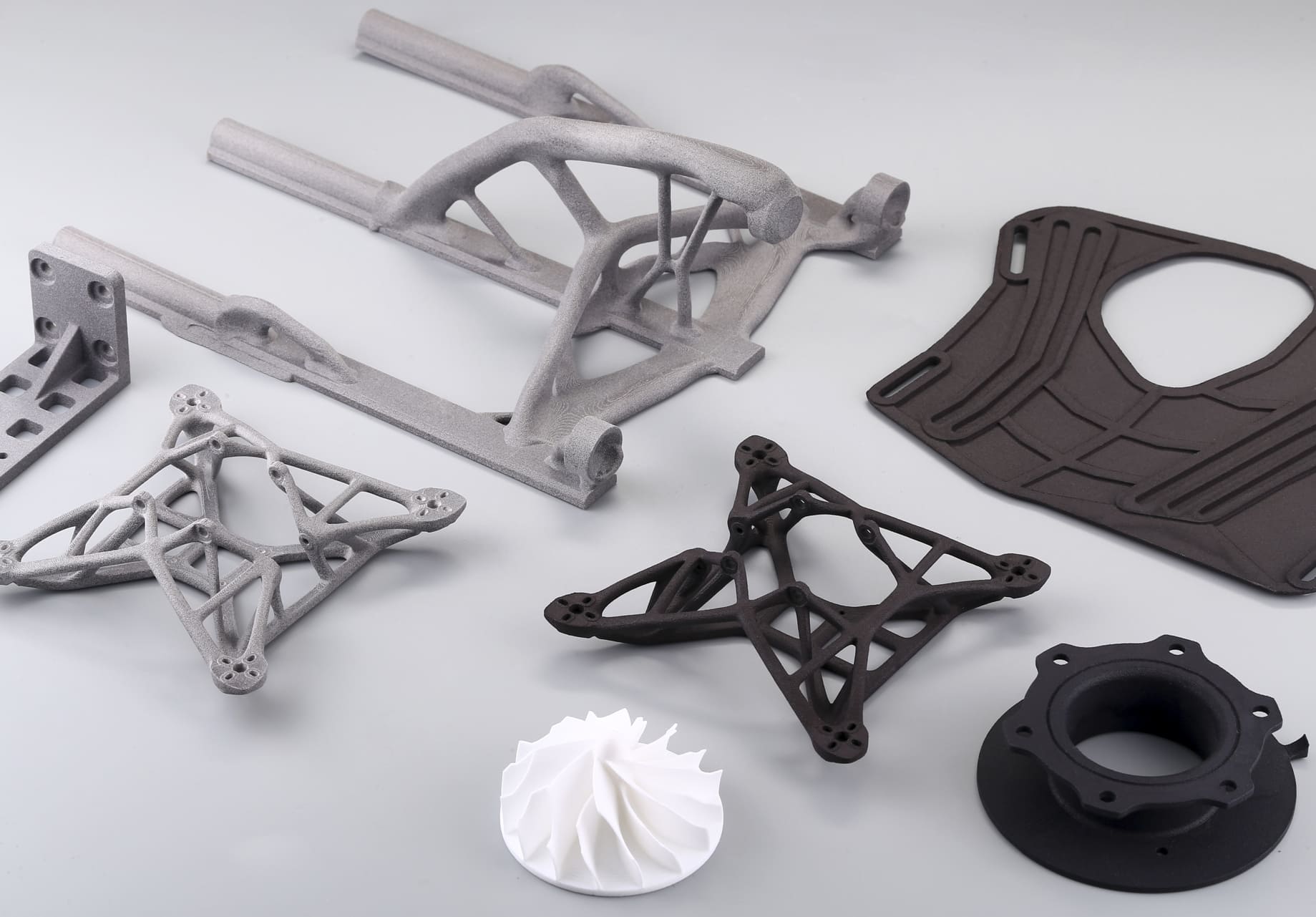
Image Source: Mark3D
Components of a 3D Printed Drone
Frame and Housing Structures
The frame is the skeleton of the drone, providing structural integrity and shape. In 3D printed drones, the frame is often made from lightweight yet durable materials like ABS or PLA plastic. The design of the frame can vary greatly depending on the intended use of the drone, from simple and sturdy for beginners to complex and aerodynamic for advanced applications. The housing structures protect the internal components and can also be customized to accommodate additional equipment or to improve aerodynamics.
Propellers and Their Design Variations
Propellers are critical for the lift and maneuverability of the drone. While typically not 3D printed due to the need for precision and balance, the design of propellers can be optimized using 3D modeling software before being manufactured. Variations in propeller design can affect the drone’s speed, stability, and noise level, allowing for a tailored flying experience.
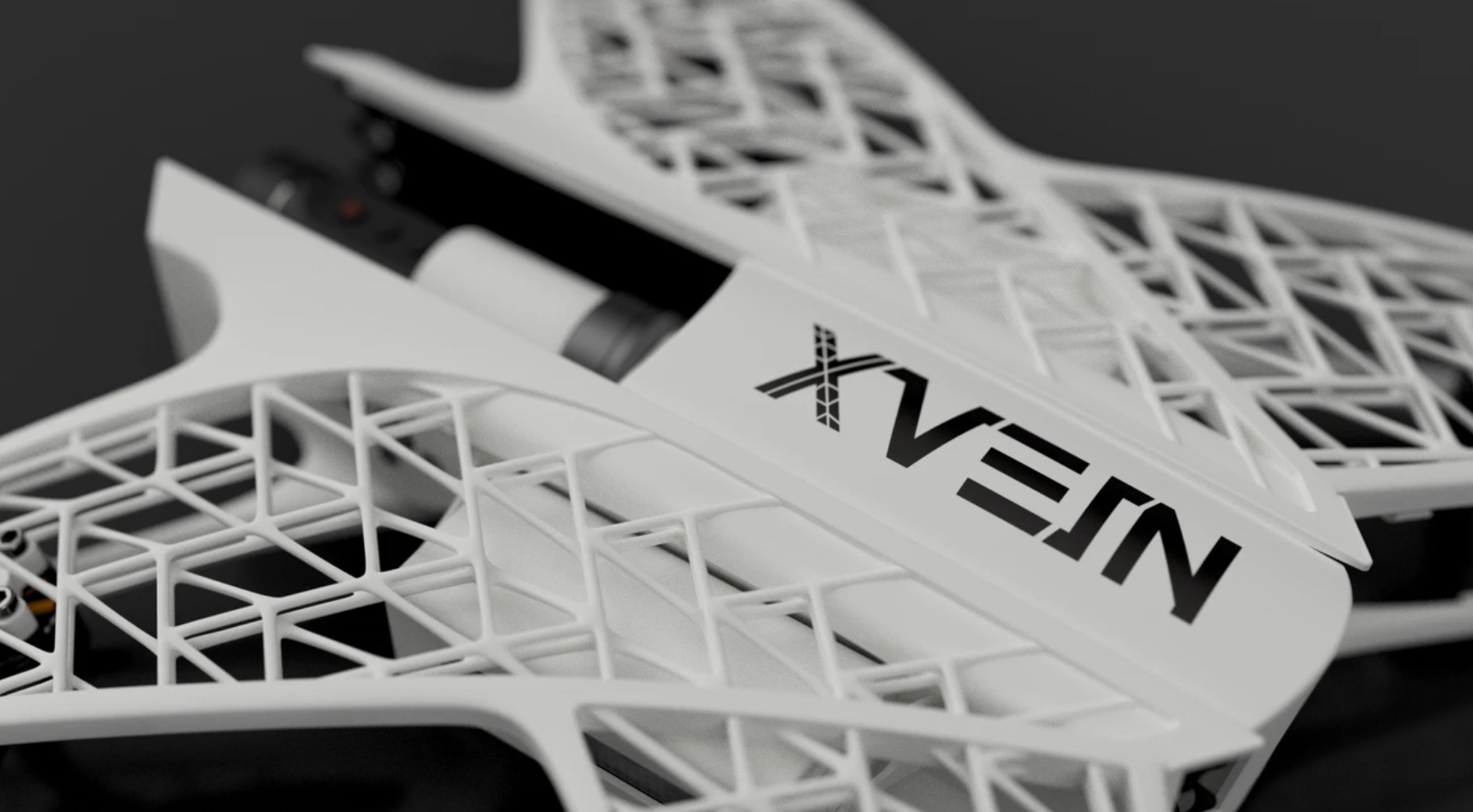

Image Source: Autodesk
Building Your Own 3D Printed Drone
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Basic Quadcopter
1. Design or Download the Frame: Start by either designing your frame or downloading a pre-made model from a 3D printing resource site.
2. Print the Frame: Using a 3D printer, print the frame components. PLA or ABS filament is recommended for its balance of strength and weight.
3. Gather Non-printed Parts: Purchase the motors, ESCs, flight controller, battery, and propellers from a trusted supplier.
4. Assemble the Motors and ESCs: Attach the motors to the frame and connect them to the ESCs, which in turn will be connected to the flight controller.
5. Install the Flight Controller: Secure the flight controller to the frame, ensuring it’s properly oriented.
6. Attach the Battery: Place the battery in a position that helps balance the drone and connect it to the power distribution board or ESCs.
7. Mount the Propellers: Install the propellers on the motors, making sure they are in the correct orientation for their respective positions.
8. Final Checks: Double-check all connections and ensure everything is secure.
Resources for Finding Models and Parts
● Websites like Thingiverse, MyMiniFactory, Cults3D, and Thangs offer a wide range of 3D models specifically for drones. You can download the STL files directly, and some are free!
● CAD software such as AutoCAD, Blender, and SolidWorks can be great tools to help you in the design progress.
● Online hobby shops and forums are great places to find recommendations for electronic components.
Tips for Assembling and Testing the Drone
● Balancing: Make sure the drone is balanced; an unbalanced drone can be difficult to control.
● Firmware: Update the flight controller’s firmware to the latest version before your first flight.
● Calibration: Calibrate the ESCs and the flight controller’s sensors according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
● Test Flight: Conduct a test flight in an open area, free from obstacles and people, to ensure the drone operates correctly.
● Troubleshooting: If the drone behaves erratically, check for common issues like loose connections or incorrect propeller placement.
Remember, safety first. Always follow local regulations regarding drone flying, and never fly near airports or in restricted zones.

Image Source: Autodesk
Challenges and Considerations
Technical Challenges in Design and Printing
● Material Selection: Finding the right balance between weight and strength is crucial. Materials must be light enough for flight but strong enough to withstand crashes and environmental factors.
● Precision: Drones require high precision in their parts, especially in components like propellers, where even minor imbalances can affect performance.
● Thermal Management: Electronic components generate heat. The design must allow for adequate cooling to prevent overheating.
● Aerodynamics: The frame and housing must be designed to minimize drag and maximize lift for efficient flight.
Legal and Safety Considerations of Flying Drones
● Regulations: Many countries have regulations governing drone flights, such as altitude limits, no-fly zones, and registration requirements.
● Privacy: Drones equipped with cameras must respect privacy laws and avoid recording in areas where individuals expect privacy.
● Liability: In the event of an accident, drone operators may be held liable for damages or injuries caused by their drones.
● Insurance: Some regions require drone operators to carry insurance, especially for commercial use.
Drone enthusiasts need to stay informed about the latest regulations and best practices to ensure safe and legal flying.
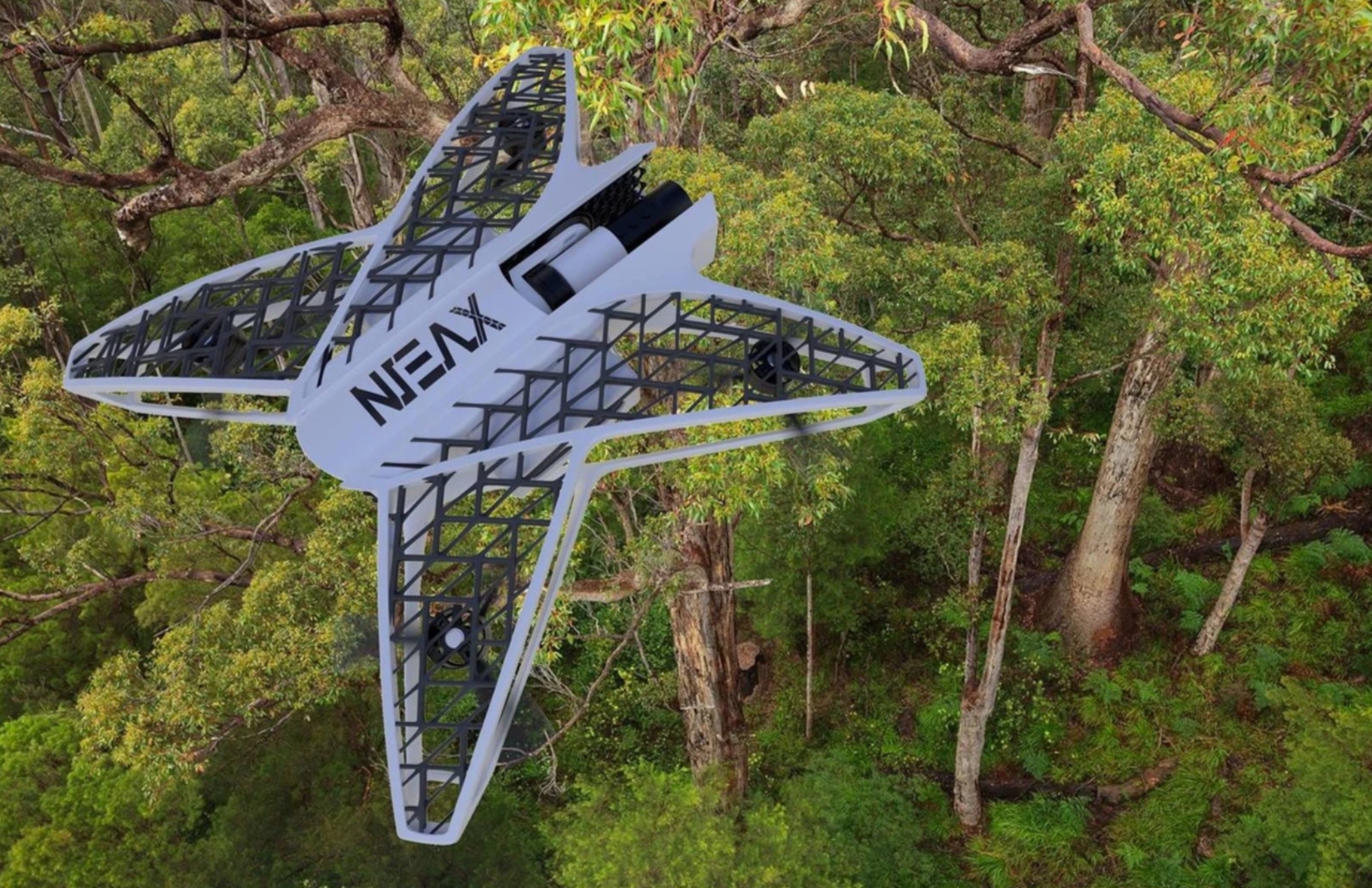

Image Source: AutoDesk
3D Printing Drone Parts at 3DSPRO
At 3DSPRO, we specialize in turning your drone dreams into reality with our 3D printing services. Our offerings are specifically designed to cater to the unique needs of drone enthusiasts and professionals who seek precision, durability, and innovation in their drone parts.
SLA Printing for Detailed Components
Our SLA printing service is perfect for creating intricate drone parts that require smooth finishes and high detail, such as camera mounts and decorative elements. The precision of SLA printing ensures that every curve and contour is replicated perfectly, which is essential for the aerodynamics and functionality of drone components.
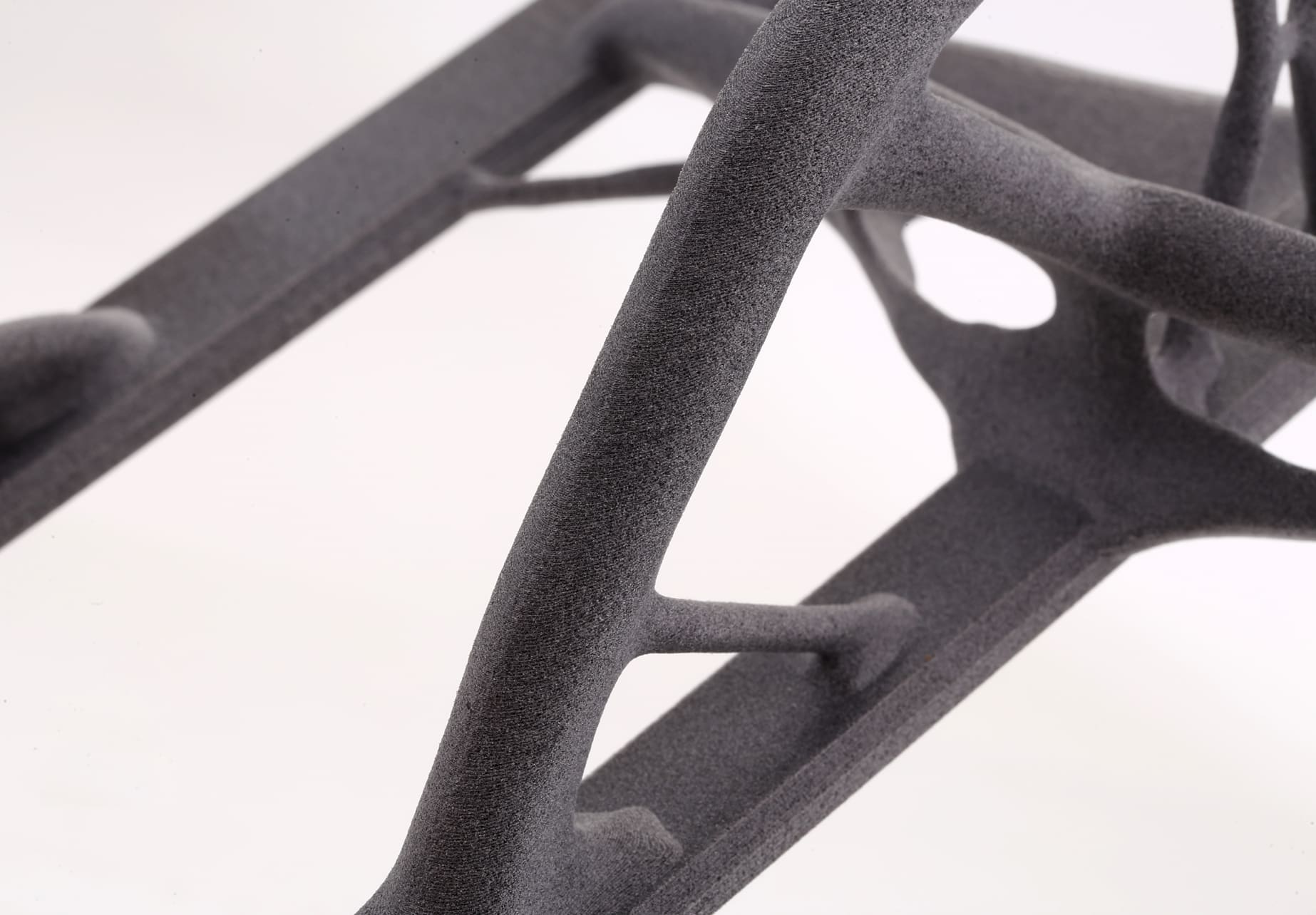
SLS and MJF for Robust Functional Parts
For parts that need to withstand the rigors of flight, our SLS and MJF printing services provide the robustness required. These technologies are ideal for producing durable frames, landing gear, and protective guards that are lightweight yet strong enough to protect the drone’s vital components during rough landings or unexpected impacts.
SLM for High-Performance Metal Parts
When the application demands it, our SLM printing service allows for the creation of metal parts that offer superior strength and thermal resistance. It is particularly useful for creating custom motor mounts or heat sinks that can handle the high-power demands of advanced drones.
3D Plus™ Services for Better Surface Finish
Beyond printing, 3DSPRO’s 3D Plus™ services ensure that each part fits perfectly and looks good! From painting to polishing, we provide a variety of surface finishing techniques to enhance the appearance and performance of your drone parts.
Instant Quoting for Streamlined Ordering Process
Our instant quoting system simplifies the process of ordering your custom drone parts. With just a few clicks, you can get a detailed quote that includes pricing and estimated delivery times, making it easier than ever to plan your drone project.
At 3DSPRO, we are committed to providing you with the highest quality 3D printed drone parts tailored to your specifications and delivered with efficiency. Whether you are building a drone from scratch or upgrading an existing model, our services are designed to elevate your drone experience.
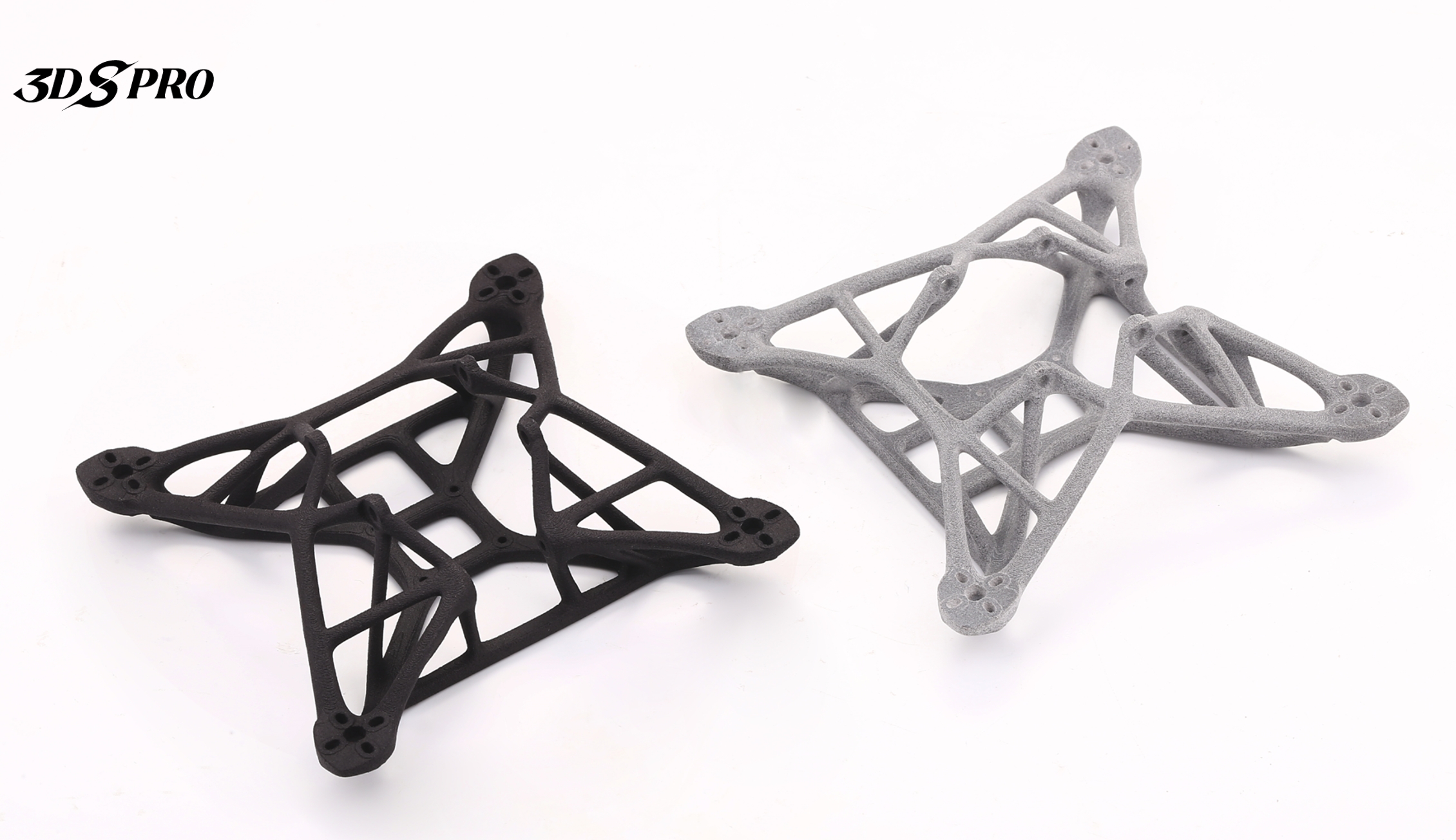

3DSPRO 3D Printed Drone Parts (MJF and SLS 3D Printed)
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!