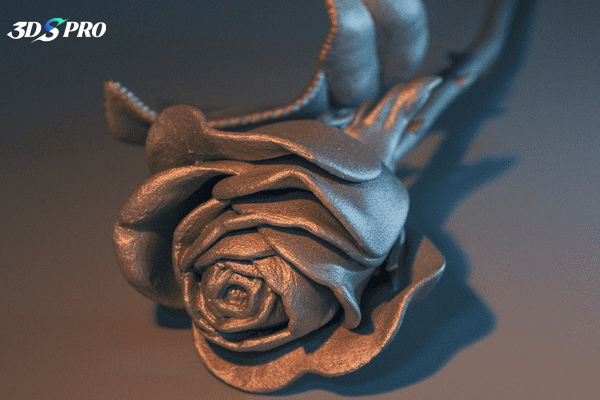
Popular 3D Printing Methods to Make 3D Printed Art
The art and design industry benefits from 3D printing as it provides artists with innovative tools and materials to make their creative visions a reality. Which 3D printing method will they choose to create 3D printed art? Here are some popular choices:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM is one of the most widely used 3D printing techniques due to its accessibility and affordability. FDM 3D printing involves extruding thermoplastic filaments layer by layer to build an object. Artists favor FDM for its versatility and the wide range of (colorful) materials available, including PLA, ABS, and PETG. It’s ideal for creating large sculptures, prototypes, and functional art pieces.
Stereolithography (SLA)
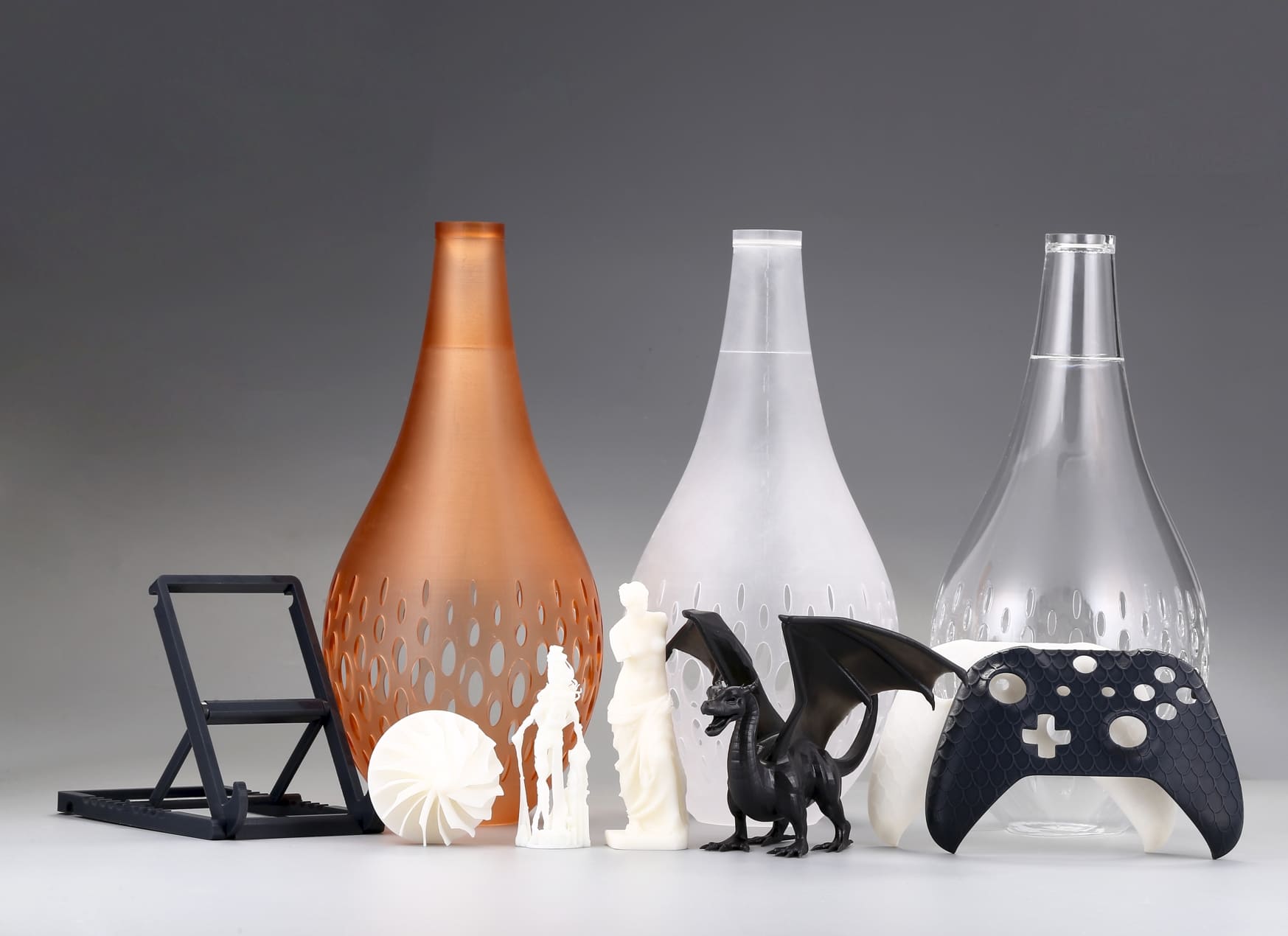
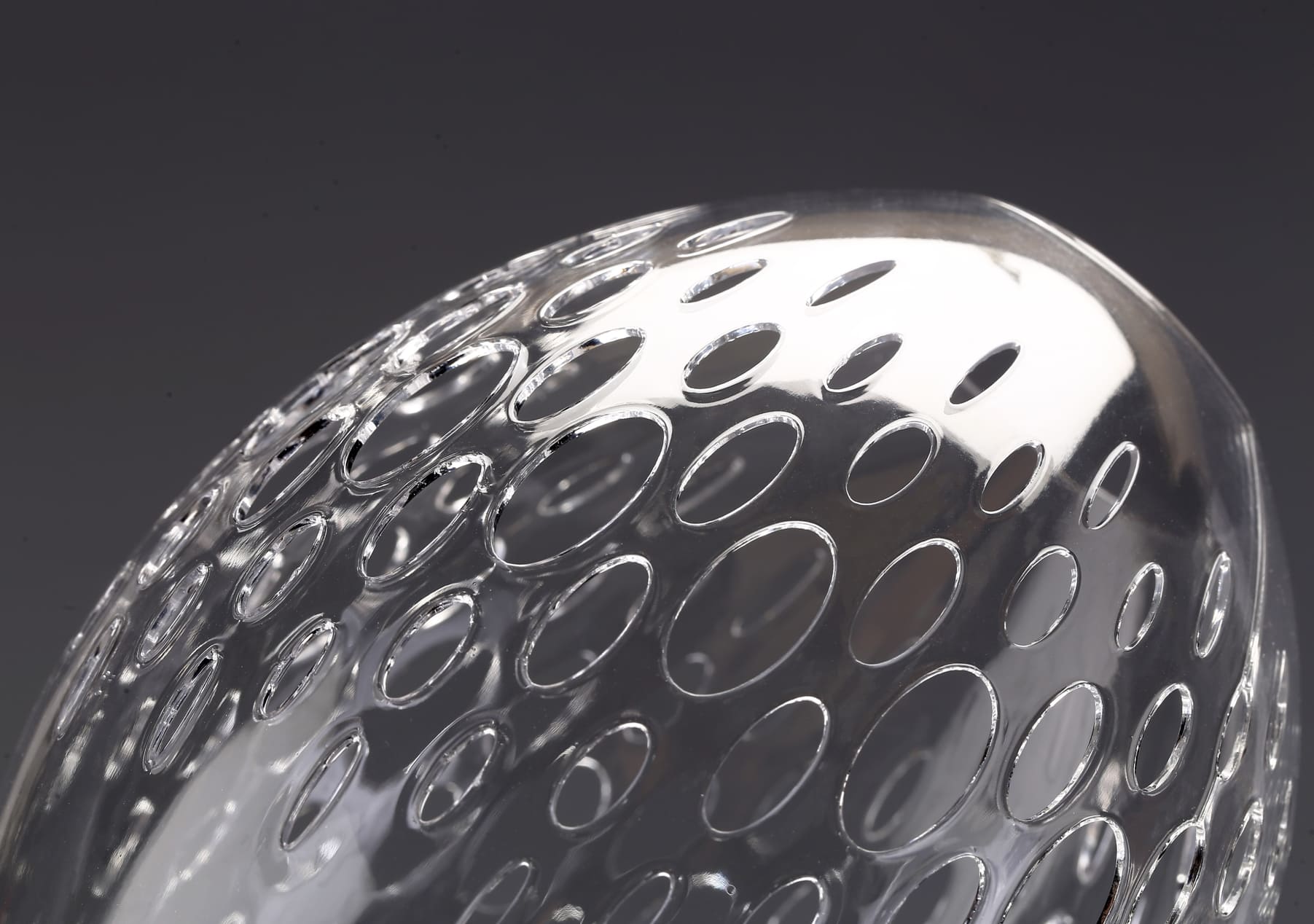
SLA uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers, producing highly detailed and smooth prints. SLA 3D printing is perfect for intricate designs and fine art pieces that require a high level of precision. Artists often use SLA for jewelry, miniatures, and detailed sculptures. The ability to achieve fine details makes SLA a favorite for creating lifelike and delicate art. Some artists prefer to use airbrush painting to enhance the beauty and quality of their resin artwork.
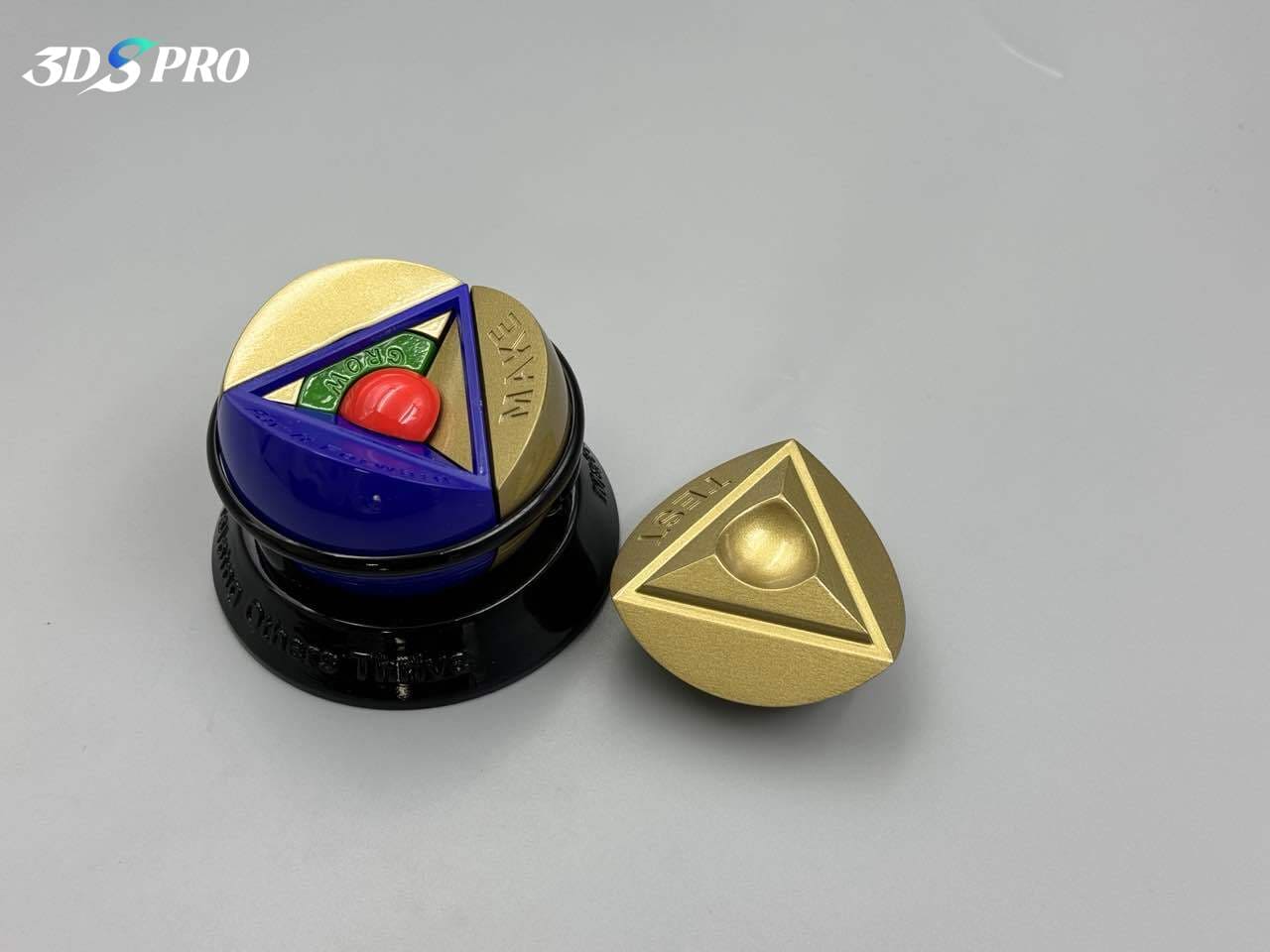

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
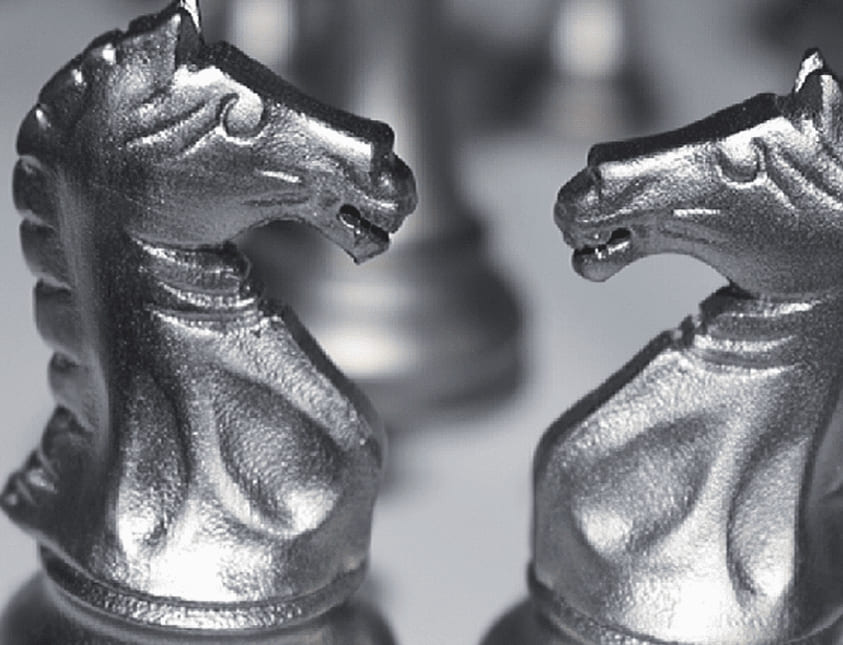
SLS involves using a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or polyamide, into solid objects. SLS 3D printing is known for its strength and durability, making it suitable for functional art and complex geometries. Artists use SLS to create robust sculptures, wearable art, and intricate installations that require high strength and flexibility.
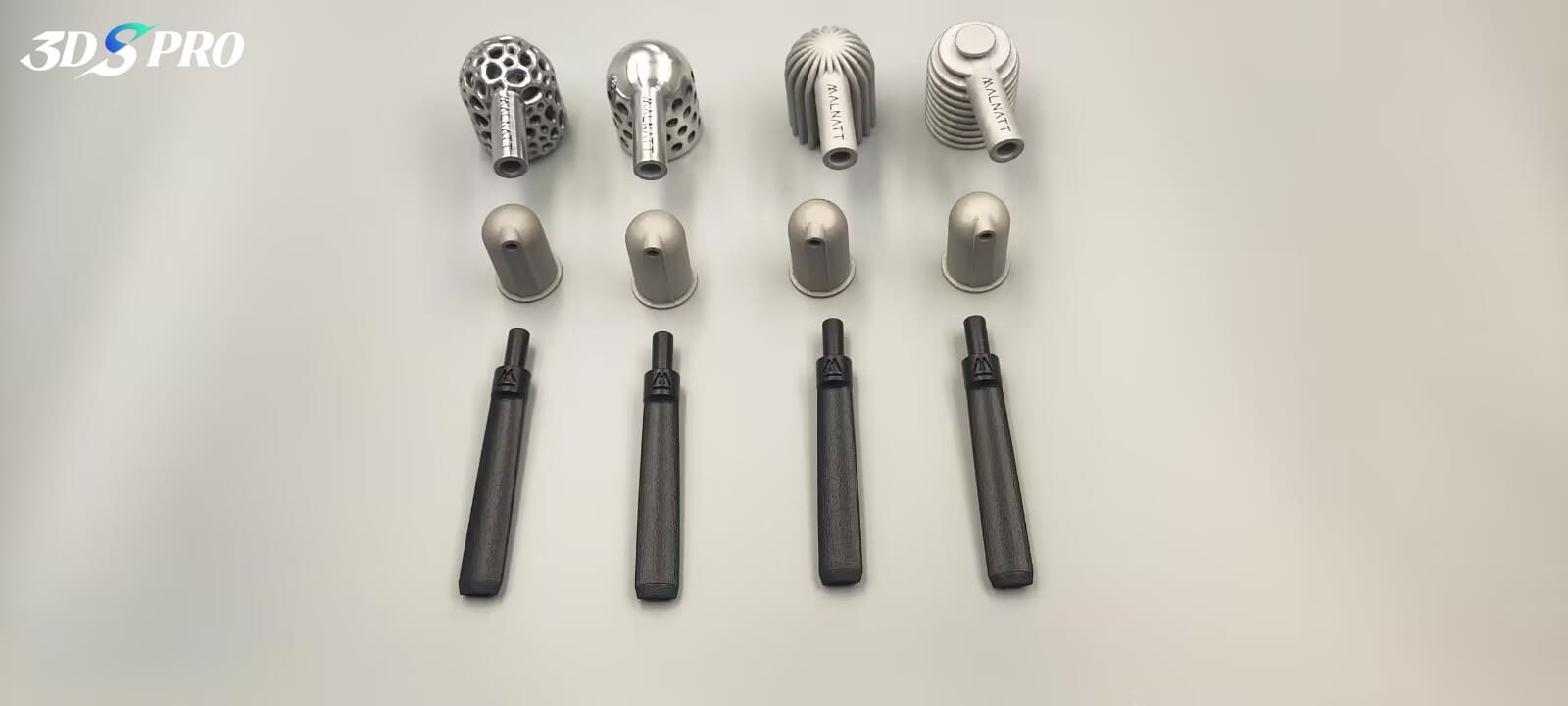
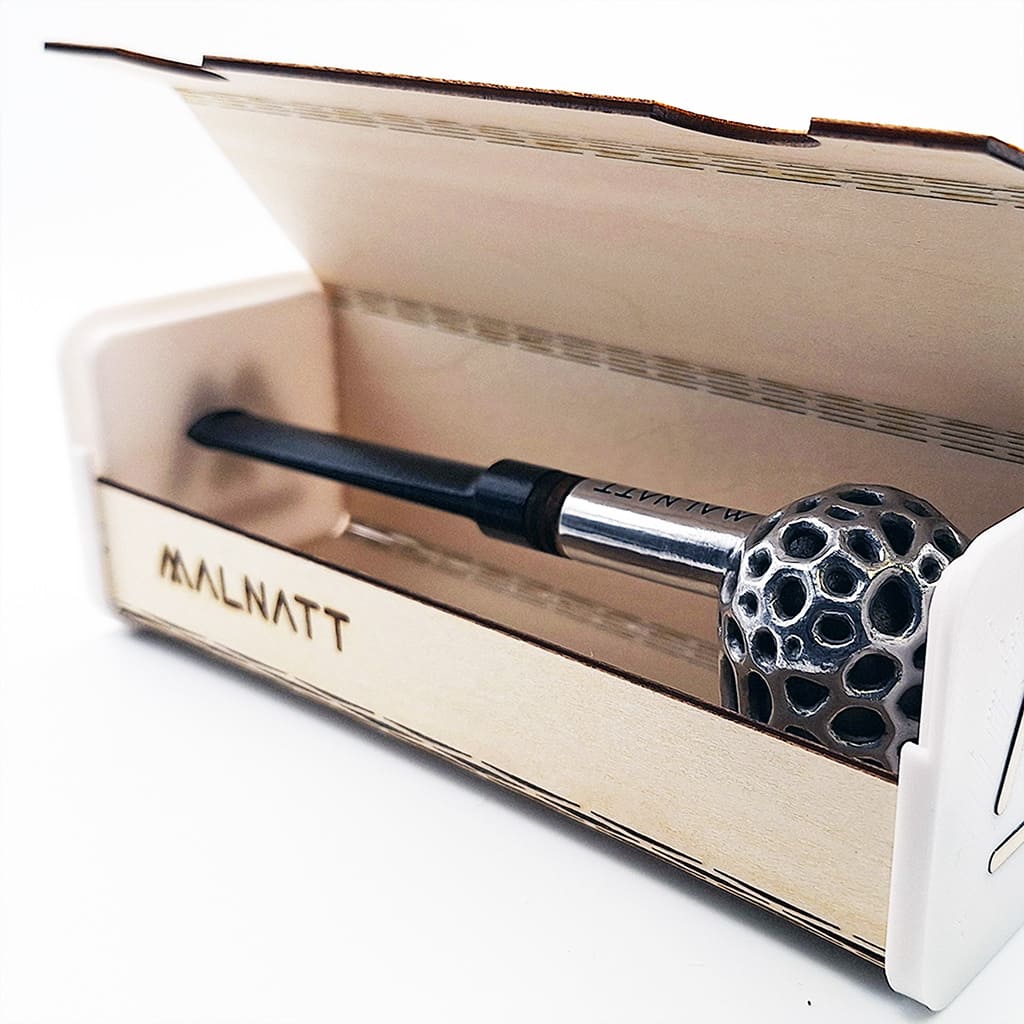


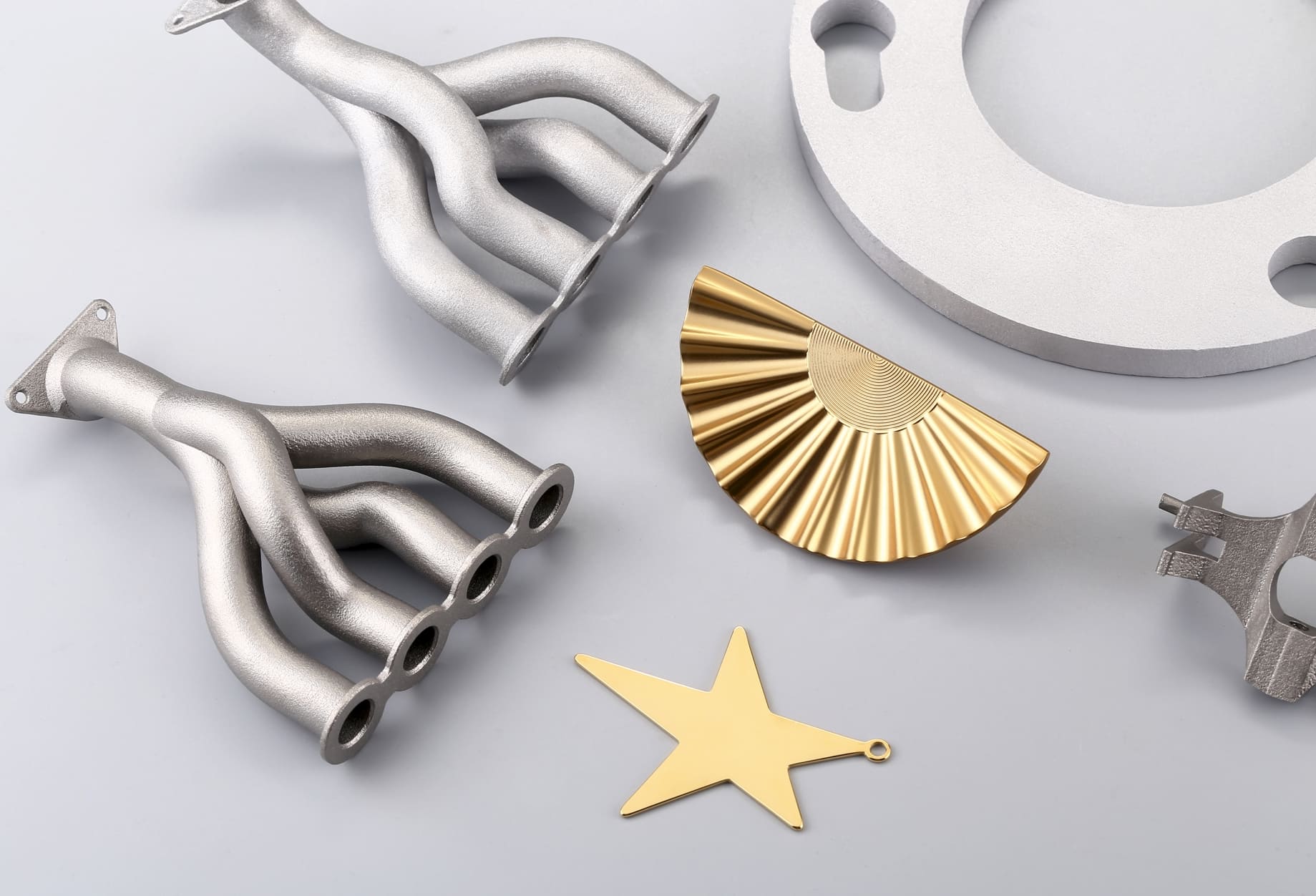
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
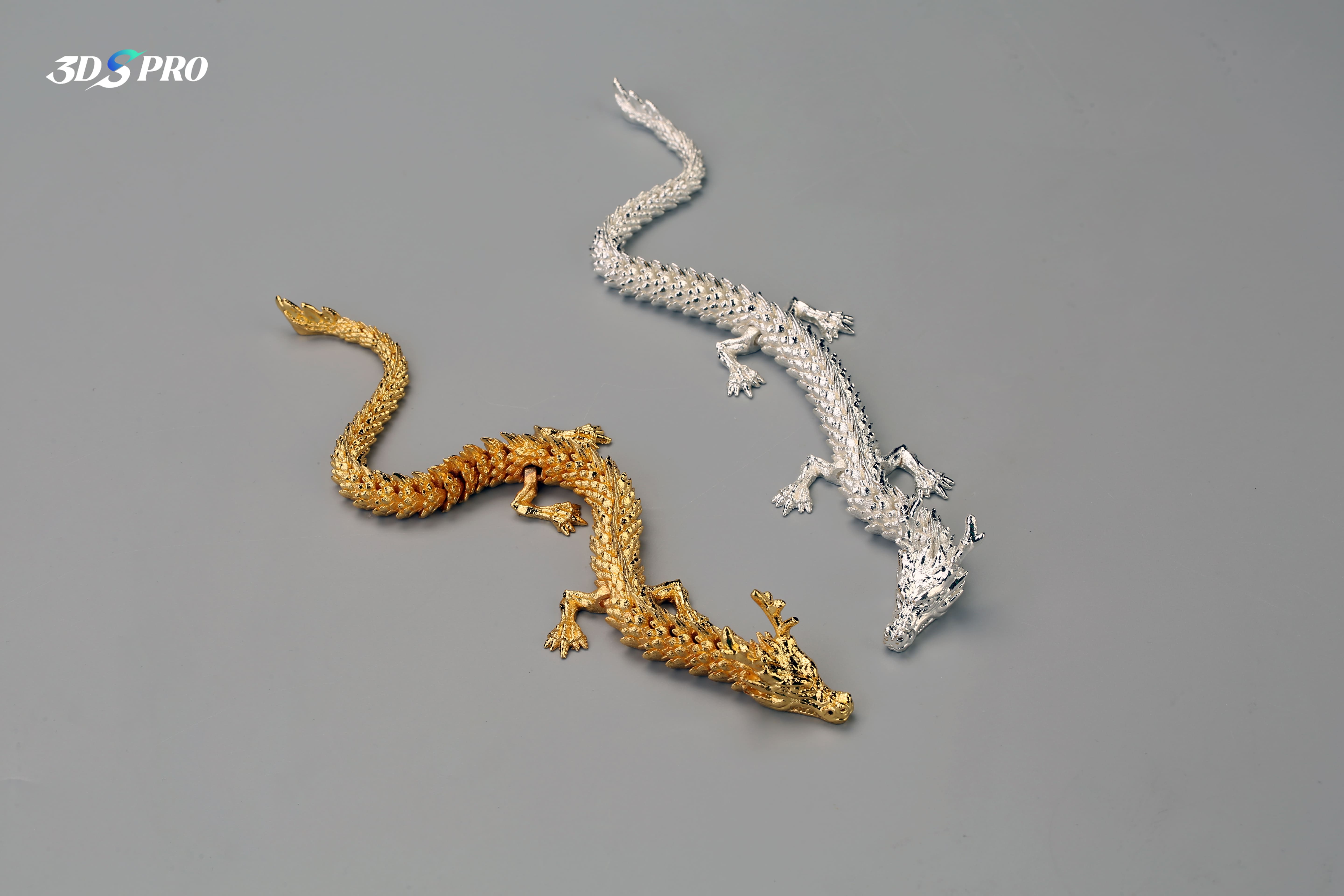
SLM is a technique that uses a laser to melt powdered metal selectively into solid objects. SLM 3D printing is perfect for creating metal art pieces with intricate details and high strength. Artists use SLM to produce metal sculptures, jewelry, and functional art that require the durability and aesthetic appeal of metal. Post-processing, such as polishing, anodizing, and electroplating, can make 3D printed metal artworks stunning.

PolyJet Printing
PolyJet works by jetting layers of liquid photopolymer onto a build platform and curing them with UV light. PolyJet allows for multi-material and multi-color printing, enabling artists to create vibrant and complex pieces with varying textures. PolyJet is ideal for producing realistic prototypes, detailed models, and colorful art installations.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Art and Design
Enhanced Creativity and Customization
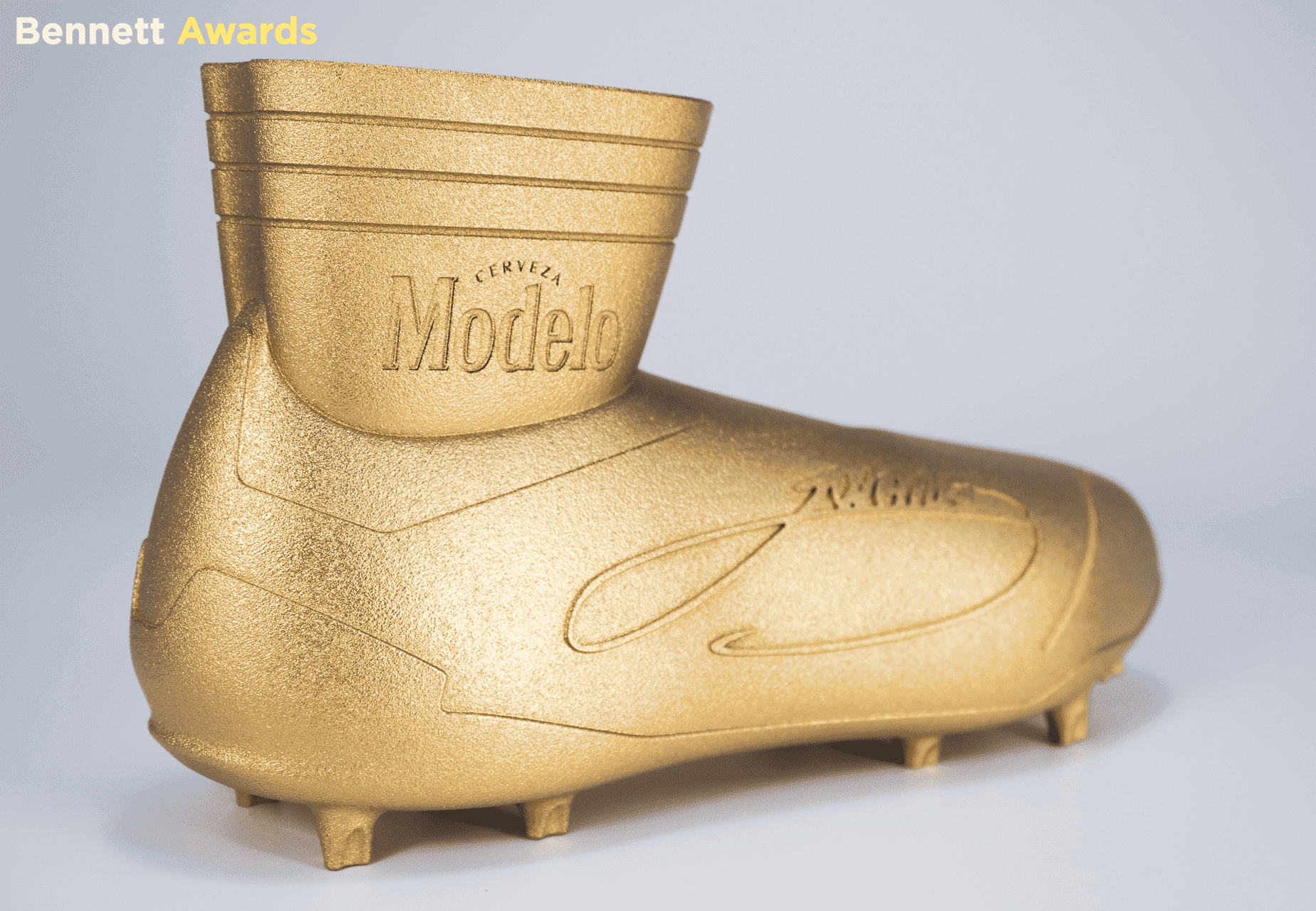
3D printing allows artists and designers to push the boundaries of their creativity. With the ability to create complex geometries and intricate details, artists can bring their most imaginative ideas to life. The customization capabilities of 3D printing allow for one-of-a-kind pieces tailored to individual preferences, which is particularly valuable in fields such as fashion, jewelry, and custom art installations.

Cost-Effective Prototyping and Production
Traditional prototyping and production methods can be time-consuming and costly. 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and low-volume production, reducing the time and cost required. Artists can quickly iterate on their designs and make adjustments without expensive molds or tooling. The efficiency of 3D printing saves money and speeds up the creative process, reducing turnaround time on projects.
Accessibility and Democratization of Art
Independent artists, small studios, and hobbyists can now create high-quality work without expensive equipment or large-scale production facilities. This accessibility fosters a more inclusive creative community where anyone with a vision can turn their ideas into reality.

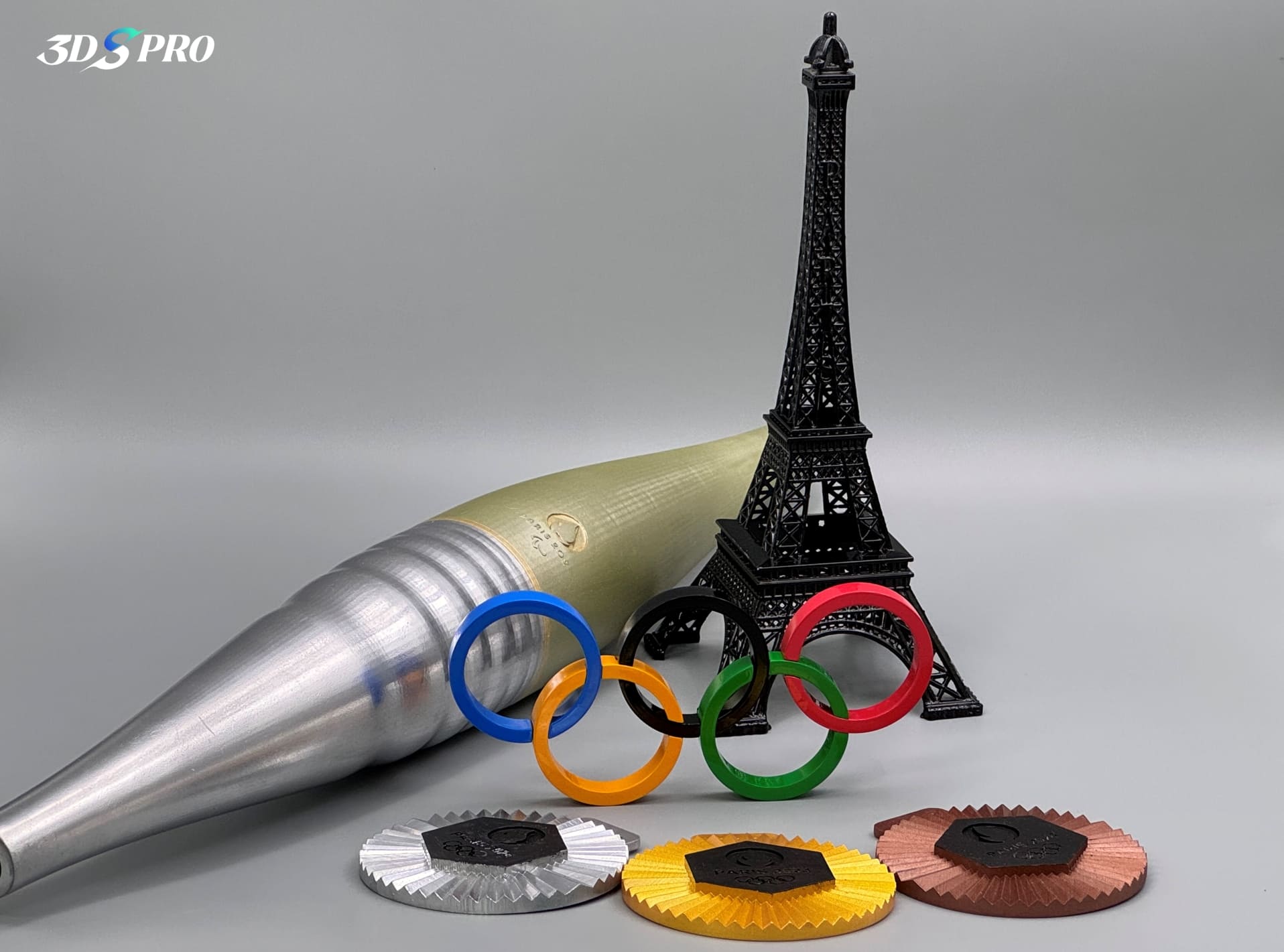
Sustainability and Reduced Waste
3D printing builds objects layer by layer, using only the material needed for the final product, significantly reducing material waste compared to subtractive manufacturing methods such as carving or machining. In addition, many 3D printing materials are recyclable or biodegradable, contributing to more sustainable art and design practices.
Preservation and Restoration
3D printing can help artists and conservators create exact replicas of historical artifacts and works of art, ensuring that cultural heritage is preserved for future generations. 3D printing can also repair damaged works, recreating missing parts with high accuracy and preserving the integrity of the original work.

Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Artists can collaborate with engineers, architects and scientists to explore new possibilities and create innovative works that merge art and technology. This interdisciplinary approach results in groundbreaking projects that challenge traditional boundaries and open up new avenues for creative expression.
Innovation in Art Forms
3D printing introduces new art forms and techniques that were previously impossible or impractical. Artists can experiment with materials such as metals, ceramics, and even biomaterials, expanding the range of textures and finishes available to create dynamic, interactive, and multi-dimensional artworks that engage audiences and redefine the art experience.
Applications of 3D Printed Art
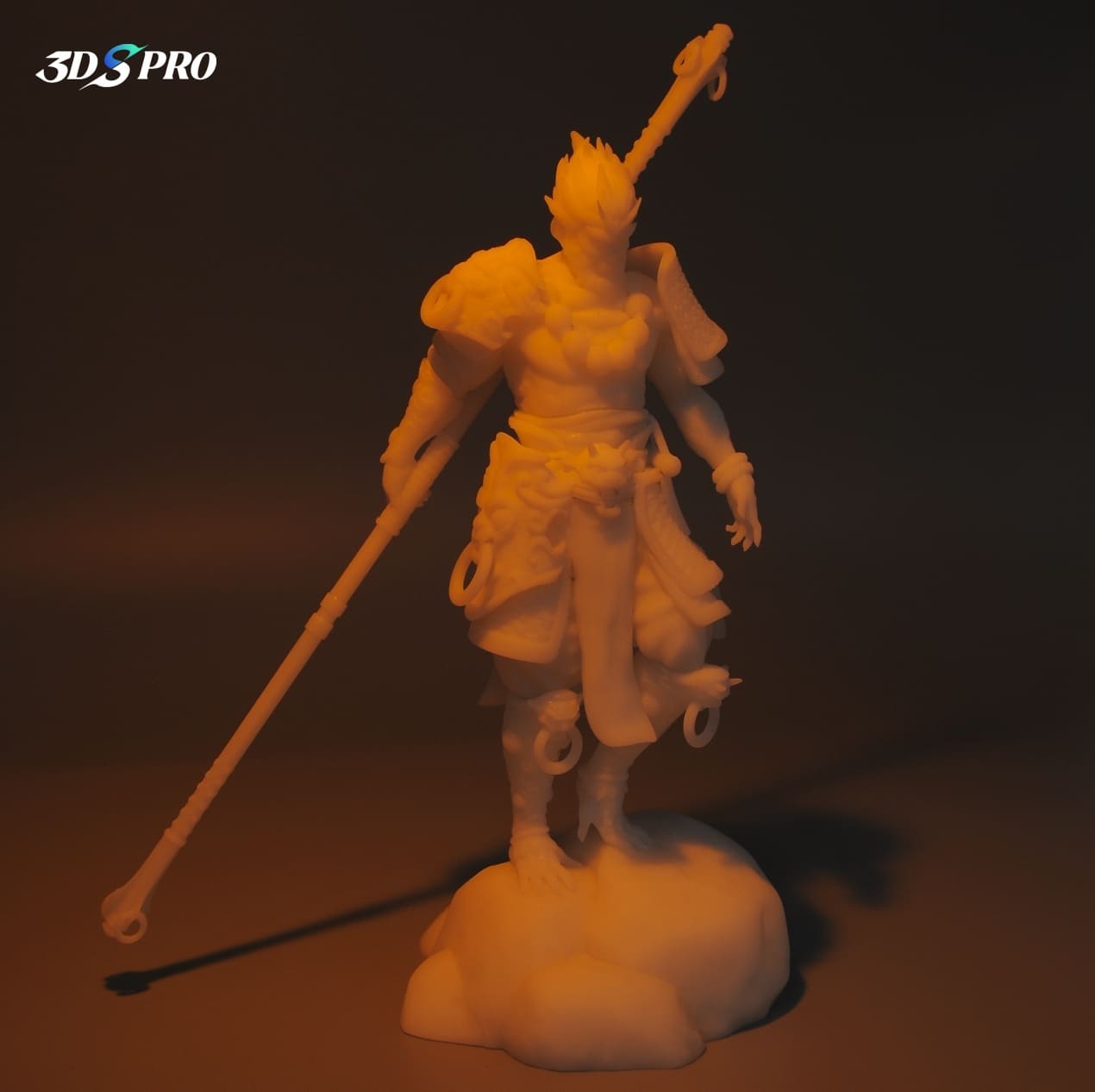
Sculpture and Installations
Artists can experiment with different shapes, textures, and materials to create unique pieces. For example, large installations can be assembled from multiple 3D printed components to create monumental works that engage viewers.
Fashion and Jewelry
Designers use 3D printing to create avant-garde clothing, accessories, and jewelry that push the boundaries of traditional fashion. 3D printing can create complex patterns and structures, resulting in wearable art that is both functional and beautiful.
Visual Arts and Mixed Media
Artists can create mixed media works that incorporate 3D printed elements, adding depth and dimension to their work. This fusion of old and new technologies results in dynamic and engaging artworks that challenge traditional notions of art.
Architectural Models
Architects and designers use 3D printing to create detailed and accurate architectural models. These models help visualize complex structures and provide a tangible representation of design concepts. 3D printed models are valuable for presentations, allowing clients and stakeholders to better understand and appreciate the proposed design.
Film and Animation
In the film and animation industries, 3D printing is used to create props, costumes, and sets. The technology enables rapid prototyping and production, allowing filmmakers to bring their creative visions to life quickly and efficiently. 3D printed models are also used in stop-motion animation, providing detailed and customizable characters and scenes.
Restoration and Replication
Museums and conservators use 3D printing to create exact replicas of fragile or damaged artifacts, ensuring that cultural heritage is preserved for future generations. 3D printing can also create detailed replicas that can be displayed and studied without damaging the originals.
Interactive and Kinetic Art
Artists are using 3D printing to create interactive, kinetic artworks that engage audiences in new and exciting ways. These artworks often incorporate moving parts, sensors, and other interactive elements to create an immersive experience for the viewer. 3D printing can precisely manufacture complex mechanisms, allowing artists to explore new forms of expression.

Challenges and Considerations
Material Limitations
Compared to traditional art materials, the choice of materials is limited, and some materials may be expensive and difficult to find.
Learning Curve
Mastering 3D printing requires proficiency in 3D modeling software, understanding printer capabilities, and troubleshooting common problems, which can be time-consuming.
Ethical and Copyright Issues
Artists must have intellectual property rights to protect their work from unauthorized copying, and using 3D printing to replicate existing artworks can spark debates about authenticity.
Cost and Accessibility
High-quality 3D printers and materials are expensive, and access to advanced 3D printing facilities can be limited, especially in areas without an established maker community.
Post-Processing Requirements
Many 3D printed objects require additional steps such as sanding, painting, or assembling multiple parts.
Use Our 3D Printing Services to Make 3D Printed Art
3DSPRO can eliminate all of the challenges that mentioned above by providing comprehensive 3D printing services and 3D Plus™ solutions.
We offer a wide range of 3D printing services, including DLP, SLA, SLS, MJF, and SLM 3D printing tailored to meet the unique needs of artists and designers. Whether you’re creating intricate sculptures, custom jewelry, or large-scale installations, our team is equipped to handle projects of any complexity.
Our exclusive 3D Plus™ solutions go beyond standard 3D printing to provide a holistic approach to your creative projects. Our experienced designers can help refine your 3D models, optimize them for printing, and suggest improvements to enhance the final product. More importantly, we offer 20 types of post-processing services, such as spray painting, anodizing, electroplating, etc.
With our comprehensive 3D printing services and 3D Plus™ solutions, you can focus on what you do best—creating stunning art—while we handle the rest.
Get the Costs of 3D Printed Art

COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!