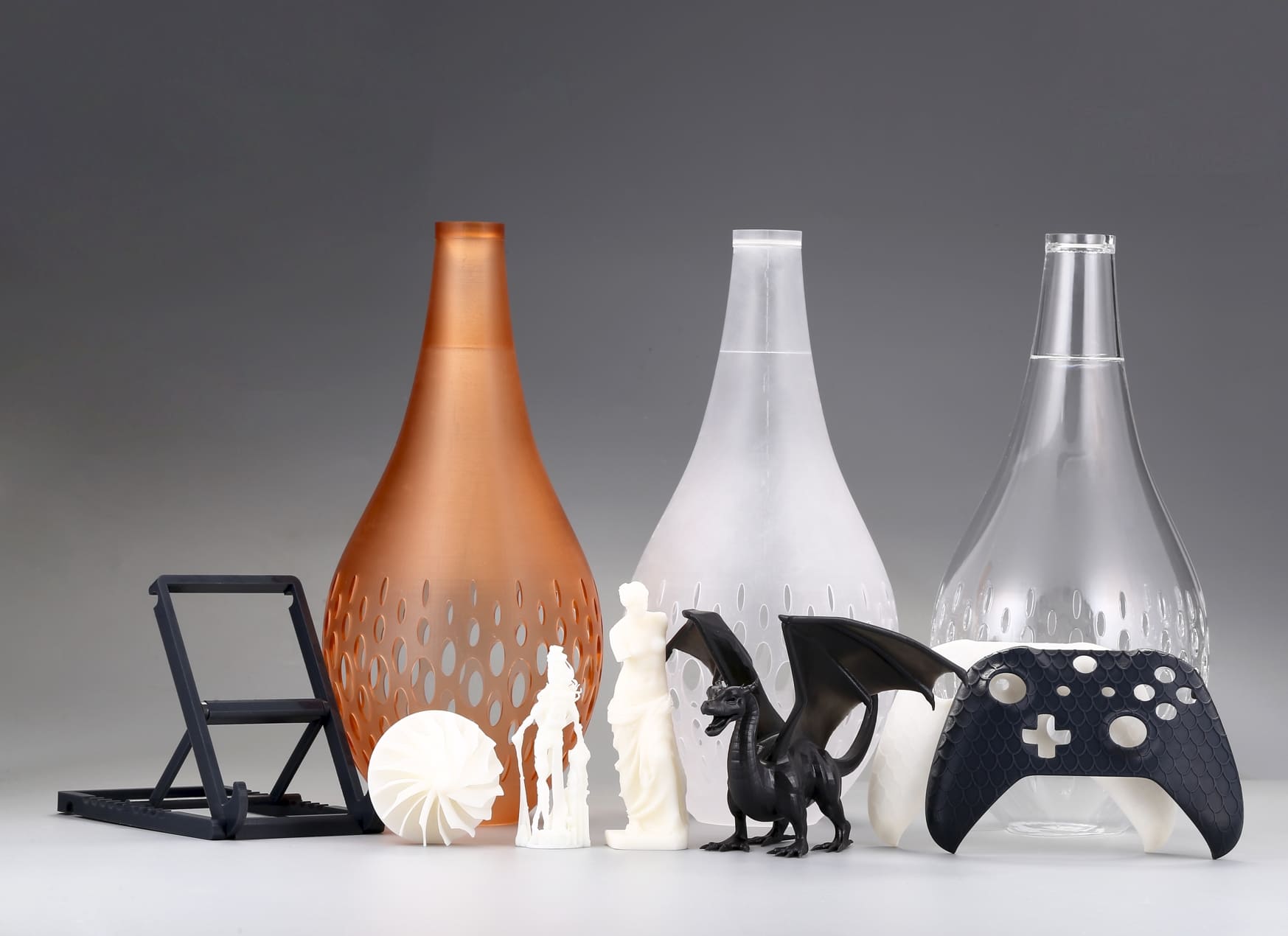
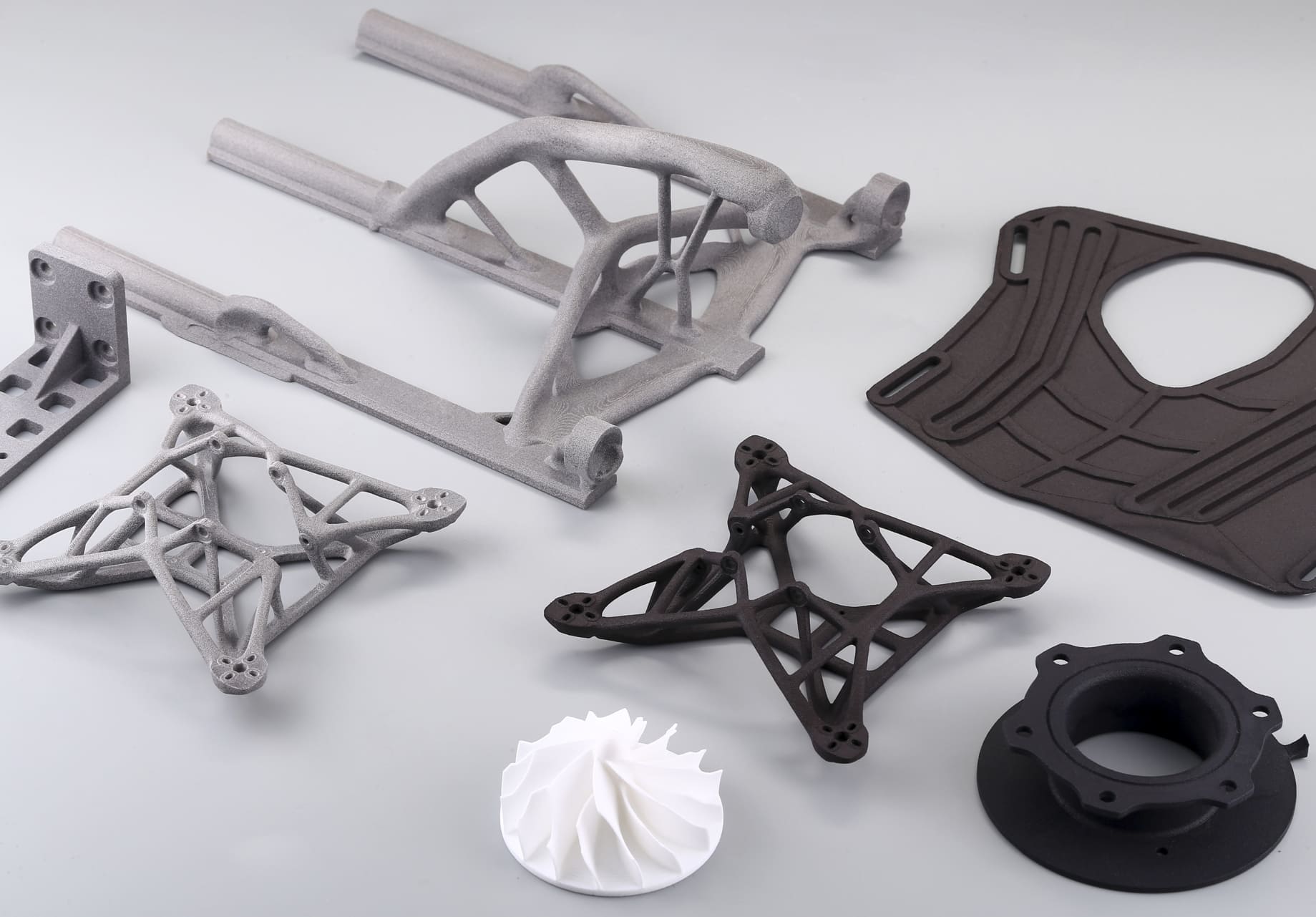
Not sure if 3D printing is right for your project? In this guide, we’ll walk through the pros and cons of 3D printing, compare them at a glance, and help you decide if it’s the right solution for your project.
If you’re ready to make 3D printing your go-to manufacturing solution, explore 3DSPRO’s expert 3D printing and precision surface-finishing services—let us help you bring your most innovative ideas to life!
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing—also known as additive manufacturing—is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital model by laying down successive layers of material. Common technologies include:
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Extrudes thermoplastic filament layer by layer.
SLA (Stereolithography): Uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin in precise patterns. 3DSPRO SLA 3D Printing Services >>
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Fuses powdered materials (nylon, metals) with a laser. 3DSPRO SLS 3D Printing Services >>
MJF (Multi Jet Fusion): Jets a binding agent onto a powder bed and fuses it with infrared heat, producing highly detailed nylon parts with consistent mechanical properties. 3DSPRO MJF 3D Printing Services >>
SLM (Selective Laser Melting): Fully melts metal powder with a high-powered laser, enabling the production of dense, load-bearing metal components. 3DSPRO SLM 3D Printing Services >>

Image copyright © 3DSPRO. All rights reserved.
Top 7 Pros of 3D Printing
1. Rapid Prototyping & Time-to-Market
You can go from CAD file to physical prototype in hours—dramatically speeding up product development cycles.
2. Cost-Effective for Low-Volume Runs
For small batches (dozens to hundreds), tooling costs are minimal compared to injection molding or CNC machining.
3. Design Freedom & Complex Geometries
Internal channels, lattice structures, and organic shapes that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive with traditional manufacturing are easily produced.
4. On-Demand Manufacturing
Avoid inventory carrying costs. Produce parts only when you need them, reducing warehouse space and obsolete stock.
5. Material Versatility
From PLA and ABS plastics to high-performance nylons, resins, elastomers, and even metal alloys, you can choose the best material for strength, flexibility, or heat resistance.
6. Reduced Waste
Additive processes build only what’s needed, unlike subtractive methods that cut away material—helping companies or individuals meet sustainability goals.
7. Customization & Personalization
Easily adjust a digital design to fit unique specifications, whether it’s a custom medical implant or a one-of-a-kind consumer product.
Image copyright © 3DSPRO. All rights reserved.
Top 5 Cons of 3D Printing
1. Limited Build Size
Most desktop and industrial machines have maximum dimensions—large parts may need to be printed in sections and assembled.
2. Surface Finish & Mechanical Strength
Layer lines can lead to anisotropic strength (weaker between layers), and post-processing (sanding, polishing) is often required for smooth surfaces.
3. Material Limitations & Costs
High-performance materials (PEEK, carbon-fiber composites, specialty resins) can be expensive, and their properties may not match those of traditional materials.
4. Post-Processing Requirements
Supports removal, cleaning, curing (for resins), and surface finishing add time and labor to the overall process.
5. Intellectual Property & Regulatory Risks
Digital file sharing can lead to unauthorized copies, and certain industries (medical and aerospace) have strict certification requirements.
Pros vs. Cons at a Glance
|
Pros |
Cons |
Mitigation Tips |
|
Rapid prototyping (hours vs. weeks) |
Limited build volume |
Print in modules; use large-format printers |
|
Low tooling cost for small batches |
Anisotropic strength & visible layers |
Orient parts optimally; apply coatings or infiltration |
|
Complex geometries & design freedom |
Requires post-processing |
Factor in finishing time; automate where possible |
|
On-demand manufacturing (no inventory) |
Material cost for specialty polymers |
Bulk-buy materials; optimize part design to use less |
|
Wide material selection |
Regulatory hurdles in some industries |
Work with certified service providers |
|
Reduced material waste |
File security & IP concerns |
Use encrypted file transfer and digital rights management |
|
Easy customization & personalization |
Longer per-piece print time at scale |
Reserve printing for high-value or custom items |
How to Decide if It’s Right for You
Use this simple checklist before choosing 3D printing services:
√ Production Volume: Are you producing low to medium quantities?
√ Budget Constraints: Does your budget allow for higher per-unit cost but lower upfront tooling?
√ Design Complexity: Do you need shapes or internal features impossible with molding or machining?
√ Material Requirements: Can available printable materials meet your strength, temperature, or biocompatibility needs?
√ Lead Time: Do you need parts in hours or days instead of weeks?
√ Post-Processing Capacity: Are you equipped—or willing to outsource—for finishing tasks?
If most answers are “yes,” 3D printing is likely a strong fit. Otherwise, consider hybrid approaches (e.g., 3D printed molds for injection molding) or traditional manufacturing.

Image copyright © 3DSPRO. All rights reserved.
FAQs
Q: Is 3D printing cheaper than injection molding?
A: For small runs (typically under 1,000 units), 3D printing often wins due to no mold costs. Beyond that, injection molding’s per-piece cost drops significantly.
Q: Can I print in metal?
A: Yes—technologies like Selective Laser Melting and Binder Jetting enable metal printing. At 3DSPRO, we deliver professional metal 3D printing services.
Q: What materials are food-safe for 3D printing?
A: Look for FDA-approved filaments like certain PLA blends and PETG. Always verify the manufacturer’s certification and apply a food-safe coating if needed.
Q: How long does a typical 3D print take?
A: Print time varies with part size, layer height, and machine speed. Small prototypes might take 30 minutes; larger, detailed parts can run 10+ hours.
Q: Do I need special software for 3D printing?
A: You’ll need CAD software (e.g., Fusion 360, SolidWorks) for design and slicing software (e.g., Cura, PrusaSlicer) to convert models into printer instructions (G-code).
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!



























