Process
3D Printing Process
3D Printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, is a process that creates objects by building them up layer by layer. It starts with a digital model, usually designed in CAD software, which is then sliced into thin layers by slicing software. These layers are printed one on top of the other, using materials such as thermoplastics, resins, or metals until the object is fully formed.

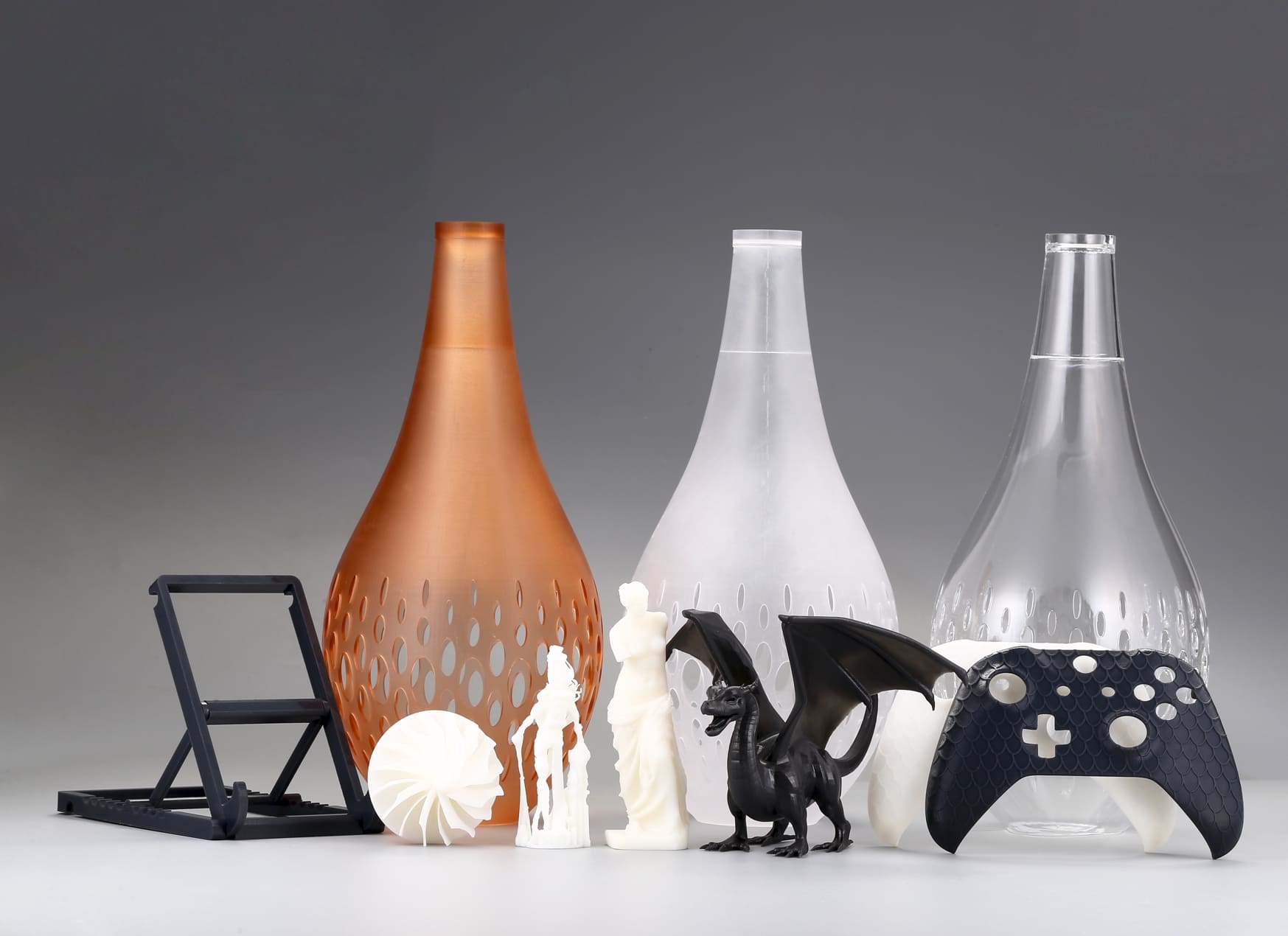
3DSPRO 3D Printed Samples (Spray Painted)
Injection Molding Process
Injection Molding involves injecting molten material into a pre-made mold, where it cools and solidifies into the shape of the mold cavity. The materials used are typically thermoplastics or thermosetting polymers.
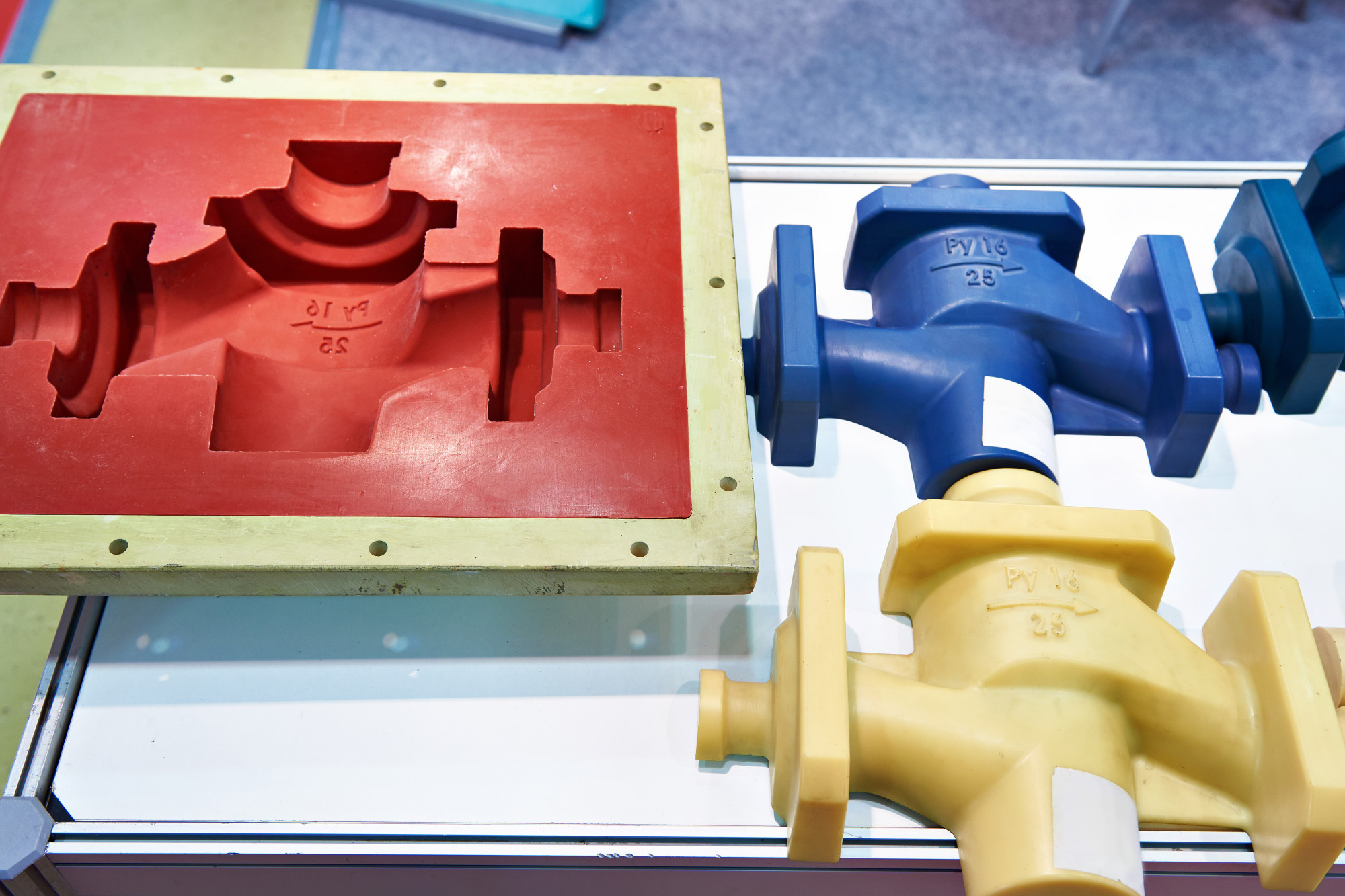
Image Source: PrototechAsia
Cost
3D Printing Costs
● Printer Price: The cost of 3D printers varies widely, from affordable hobbyist models starting around $200 to professional FDM and SLA printers that can start from $2,500 and go up to $11,000 or more.
● Material Costs: Materials for 3D printing, such as filament and resin, can range from $20 to $100 per kilogram. The choice of material affects both the quality and cost of the printed object.
● Operational Costs: Running a 3D printer includes the cost of electricity, which is relatively low, and the cost of replacing parts like nozzles. An active 3D printer costs roughly $0.35 per hour to operate.
● Labor Costs: Depending on the complexity of the design and post-processing required, labor costs can vary. Skilled labor for design and finishing can add to the overall cost.
Injection Molding Costs
● Mold Cost: The cost of the mold, or tooling, is the most significant upfront cost in injection molding. Simple molds can start as low as $100 for low-volume 3D printed molds, while complex multi-cavity steel molds for high-volume production can exceed $100,000.
● Machine Costs: The price of an injection molding machine is influenced by its injection capacity, automation features, and energy efficiency. Additional auxiliary equipment may also be required.
● Material Costs: Thermoplastics materials used in injection molding are generally inexpensive, contributing to lower variable costs.
● Volume: Injection molding becomes more cost-effective at higher volumes due to economies of scale. The cost per part decreases significantly as the number of parts produced increases.
Material
3D Printing Materials
● Thermoplastics: Such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PLA (Polylactic Acid), are popular for their ease of printing and good mechanical properties.
● Resins: Offer smooth finishes and are used in processes like SLA (Stereolithography).
● Metals: Including stainless steel and titanium, are used for durable and heat-resistant items.
● Composites: Such as carbon-fiber or glass-filled materials, provide enhanced strength and rigidity.
● Specialty Materials: Like wood-based or flexible filaments, they cater to niche applications with unique aesthetic or functional requirements.

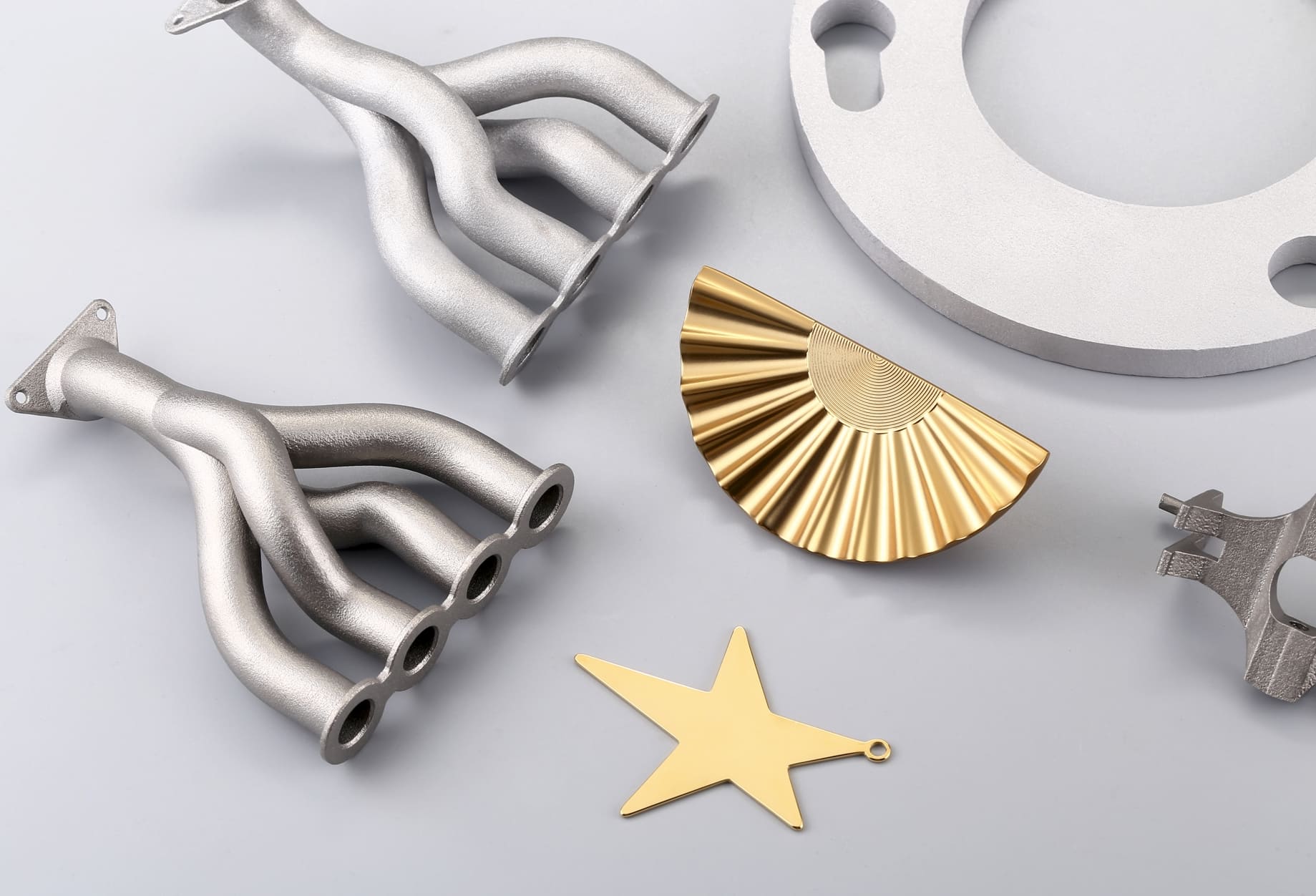
SLS Printed Sample
Injection Molding Materials
● Polypropylene (PP): Known for its fatigue resistance and flexibility.
● Polyethylene (PE): Offers good chemical resistance and is widely used for consumer products.
● ABS: Provides a balance of toughness and rigidity, suitable for automotive parts and consumer goods.
● Nylon: Renowned for its strength and thermal resistance, ideal for mechanical components.
● Polycarbonate (PC): Distinguished by its transparency and impact resistance, used in applications requiring clarity and durability.

Injection Molded ABS Part (Image Source: HLH Rapid)
Speed
3D Printing Speed
3D printing is capable of producing highly customized, complex designs. However, this comes at the expense of speed. The process requires building an object layer by layer, which can be time-consuming, especially for larger or more complex items. The overall speed of 3D printing depends on the size and complexity of the object, the type of printer, and the materials used. The entire process includes pre-processing, printing, and post-processing stages.
Injection Molding Speed
Injection molding is a high-speed process suitable for mass production. The speed at which molten material is injected into the mold and the time it takes to cool and solidify are key factors that determine the overall cycle time. The design of the mold, the type of material, and the injection parameters all play a role in the speed of the injection molding process. Adjusting the injection speed can impact the quality and efficiency of production.
Volume
3D Printing Volume
3D printing, with its production flexibility, is a cost-efficient solution for low to medium-production volumes. It is perfect for creating prototypes or small batches of parts where each item can be unique or customized. While there are no upfront tooling costs, the time it takes to print each part means that there are more efficient methods for producing large quantities than 3D printing.
Injection Molding Volume
On the other hand, injection molding is the gold standard for high-volume production. It is ideal for manufacturing large quantities of identical parts. The more parts produced, the more cost-effective the process becomes, spreading the initial tooling cost over a larger number of units.
Precision
3D Printing Precision
In 3D printing, precision is determined by the printer’s resolution and the control over the printing process. Typically, the layer height ranges from 0.05 to 0.3 mm, and the XY resolution is around 0.1 to 0.4 mm. Proper calibration of the printer is essential for achieving high precision, including the alignment of the print bed, the accuracy of the extruder, and the consistency of the filament.

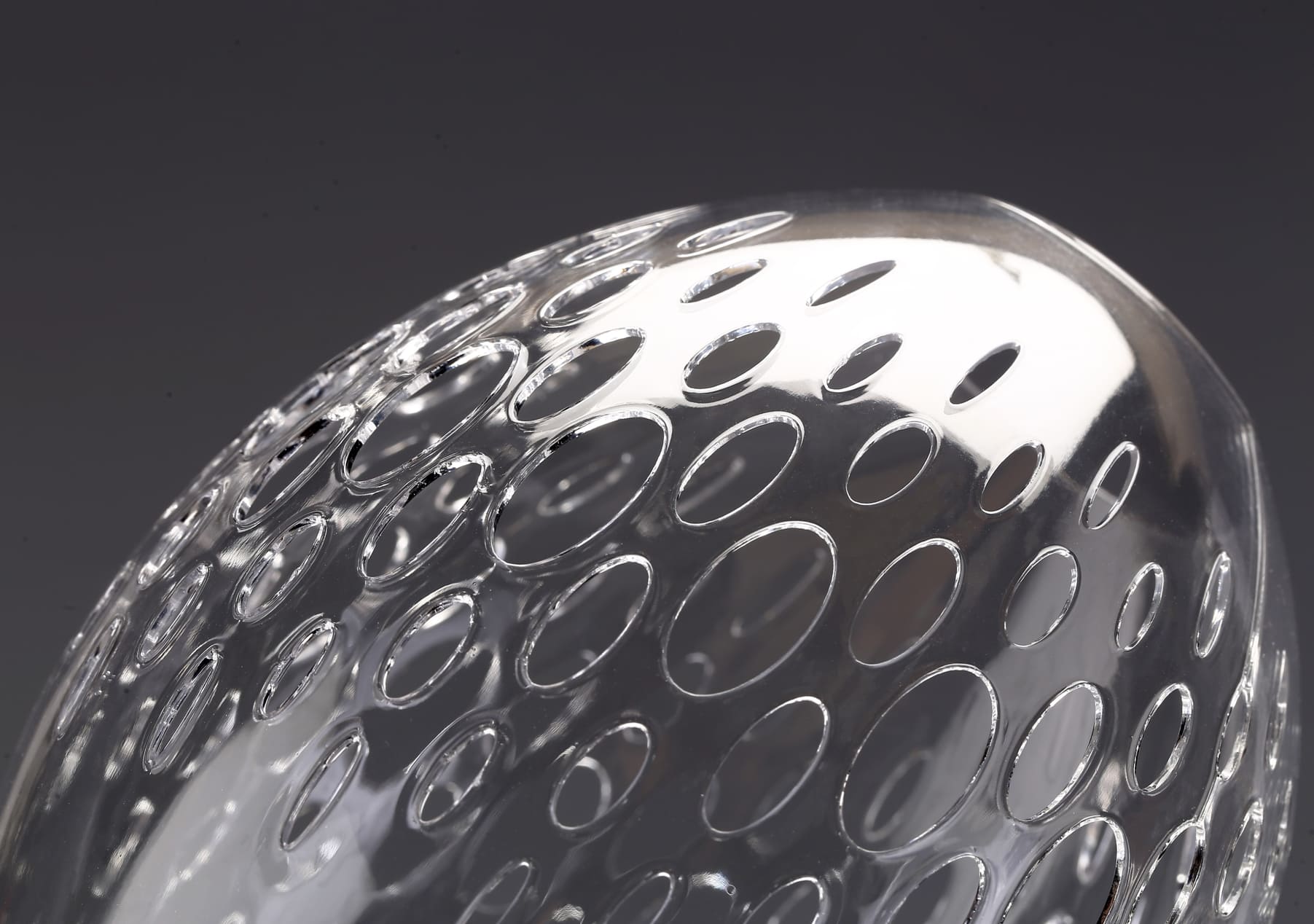
3DSPRO 3D Printed Delaunay Cup Replica
Injection Molding Precision
Injection molding can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm, depending on the material, part design, and molding conditions. The precision of the mold directly affects the precision of the part. High-quality molds with fine details ensure that the parts produced are accurate and consistent.
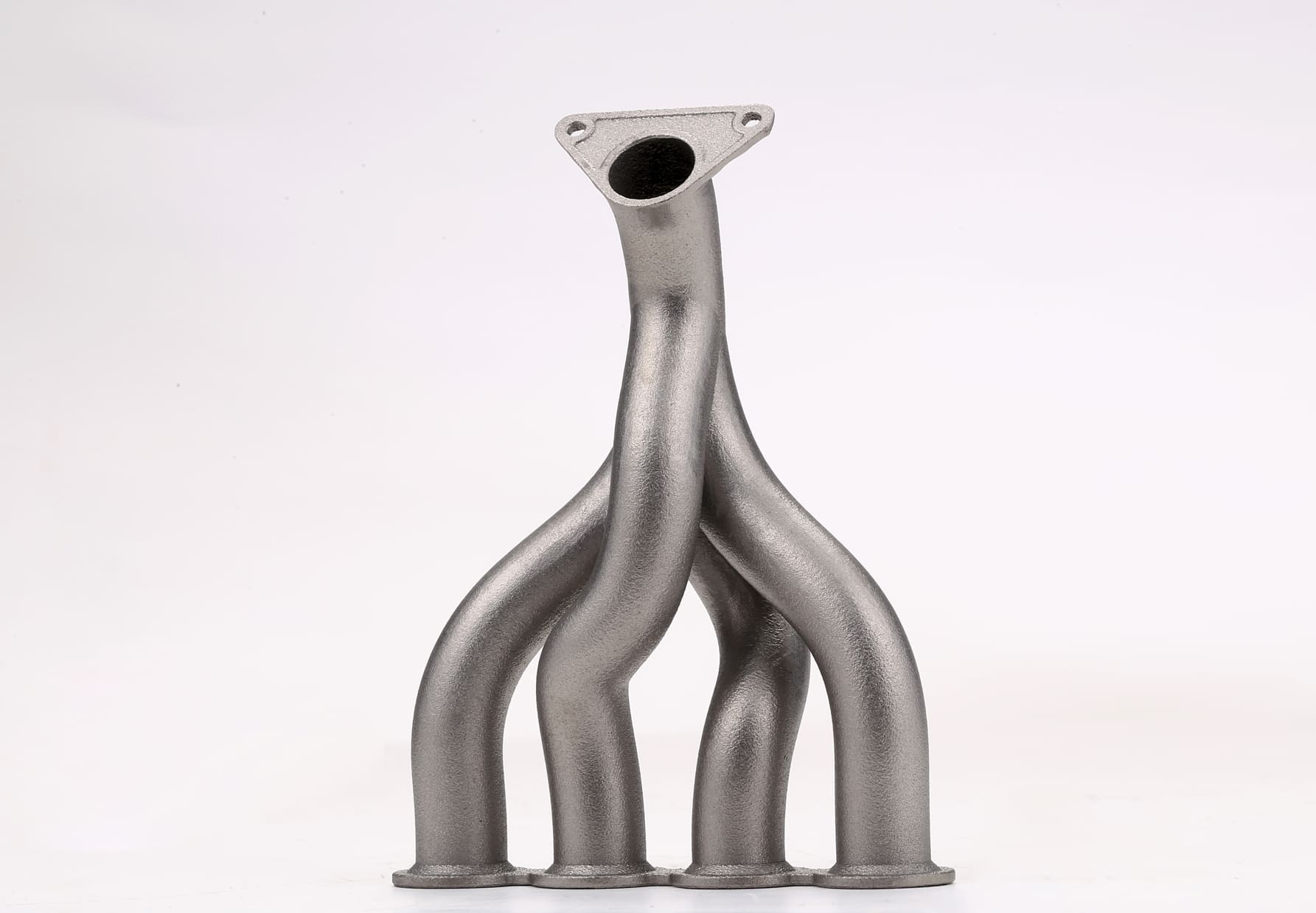
Image Source: Fictiv
Applications
3D Printing Applications
● Medical: Custom prosthetics, implants, and surgical planning models are revolutionizing patient care.
● Aerospace: Lightweight and strong components are essential for the demands of space travel.
● Automotive: Prototyping and end-use parts are created with speed and precision.
● Consumer Goods: Personalized products and home decor items cater to individual preferences.
● Education: Teaching aids and models enhance learning experiences.
● Food Industry: Edible materials are being experimented with for custom food creation.
Injection Molding Applications
● Packaging: Everything from bottle caps to storage containers.
● Automotive: Durable parts like dashboards and bumpers.
● Electronics: Enclosures and chassis for devices.
● Construction: Components that require strength and durability.
● Consumer Goods: Toys, household items, and everyday products.
3DSPRO Online 3D Printing Services
3DSPRO offers an online 3D printing platform that empowers innovators and creators to make their ideas into tangible objects. Established with the vision to accelerate innovation, 3DSPRO offers a seamless experience from idea to product, integrating SLA, SLS, MJF, and SLM 3D printing technologies and a wide range of materials to match every stage of product development.
Whether you’re looking to prototype a new concept or produce end-use parts, upload your 3D designs on our instant quoting system Squote. We ensure the lowest general cost and highest efficiency.

3DSPRO 3D Printed Airplane (Red Gloss Painted)
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!



























