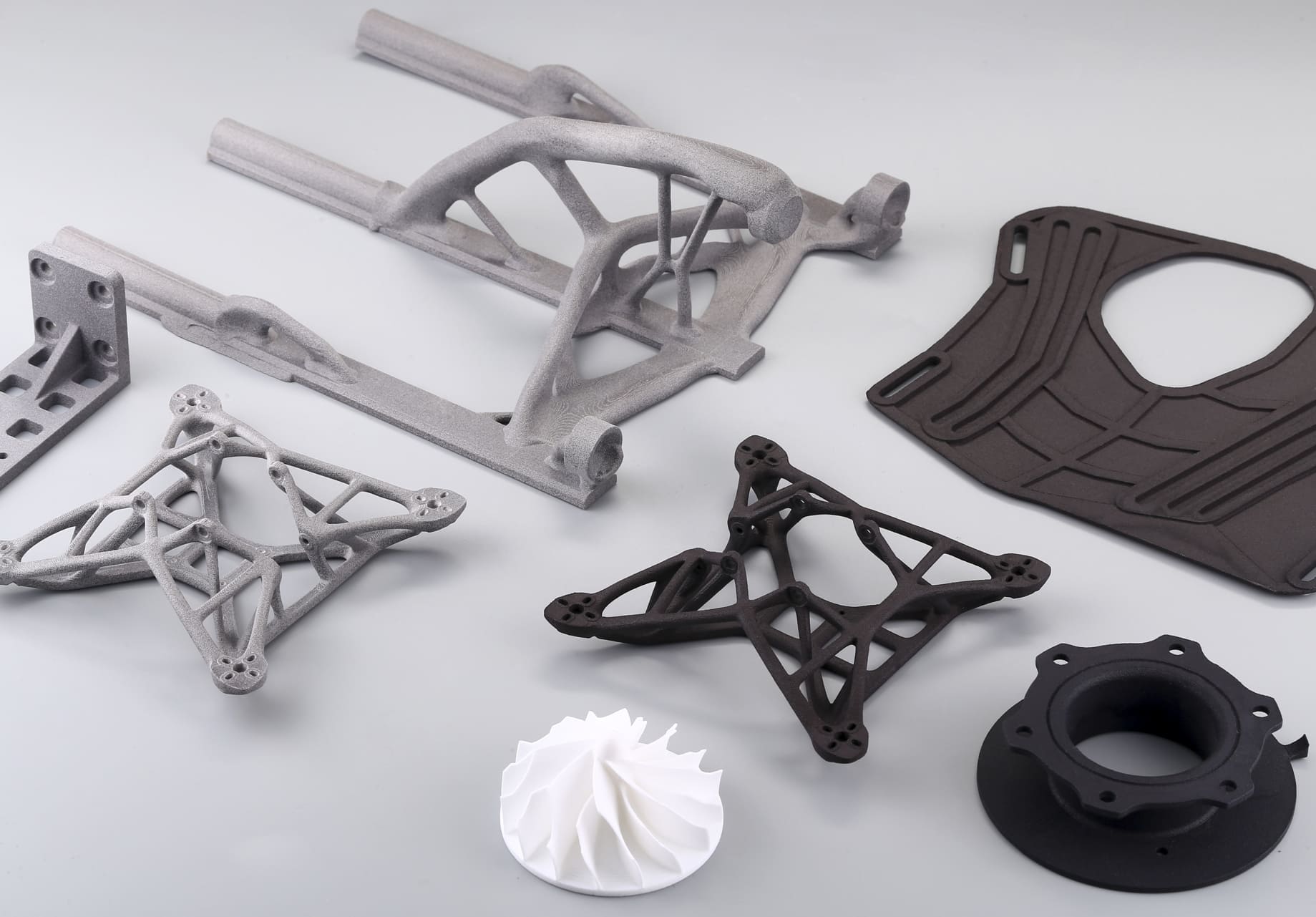
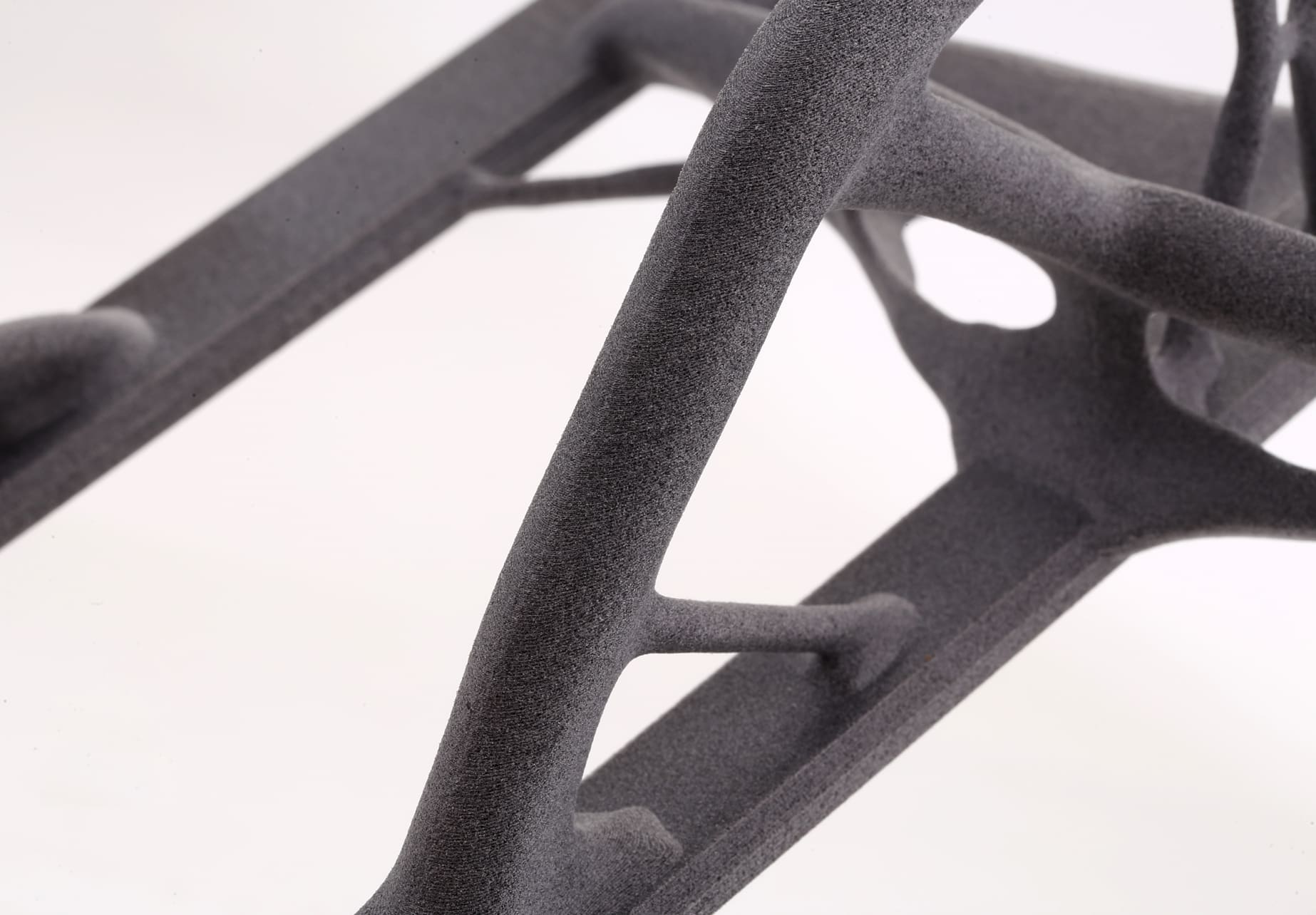
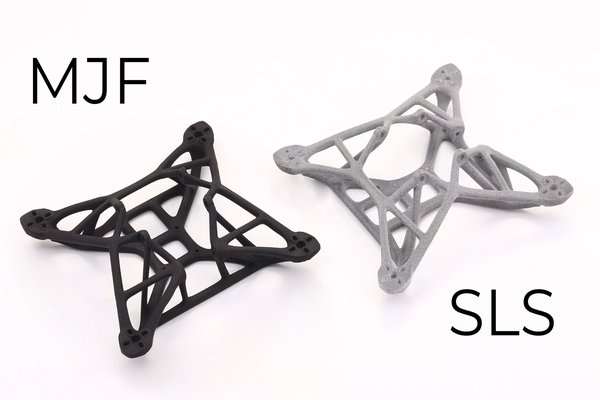
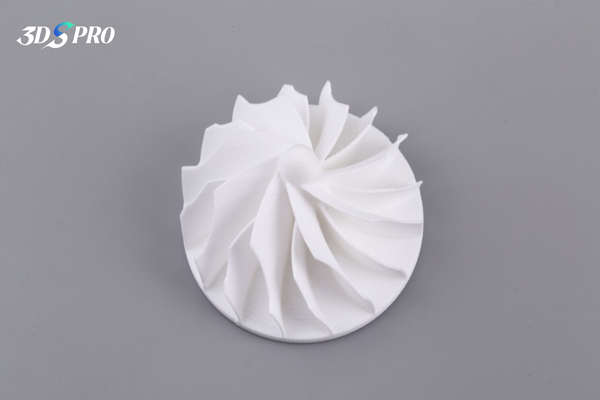
What is SLS nylon 3D printing?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an advanced additive manufacturing technology that uses a high-powered laser to fuse small particles of polymer powder into a solid, three-dimensional object. SLS 3D printing is particularly effective with nylon, a versatile and durable thermoplastic, making it a popular choice for creating functional prototypes and end-use parts.
The SLS process begins with a thin layer of nylon powder being evenly spread across the build platform. A high-powered laser then scans the powder bed, selectively sintering (fusing) the powder particles together based on the cross-sectional data from a 3D digital model. After each layer is sintered, the build platform lowers slightly, and a new layer of powder is spread over the previous layer. This process repeats layer by layer until the entire object is formed.
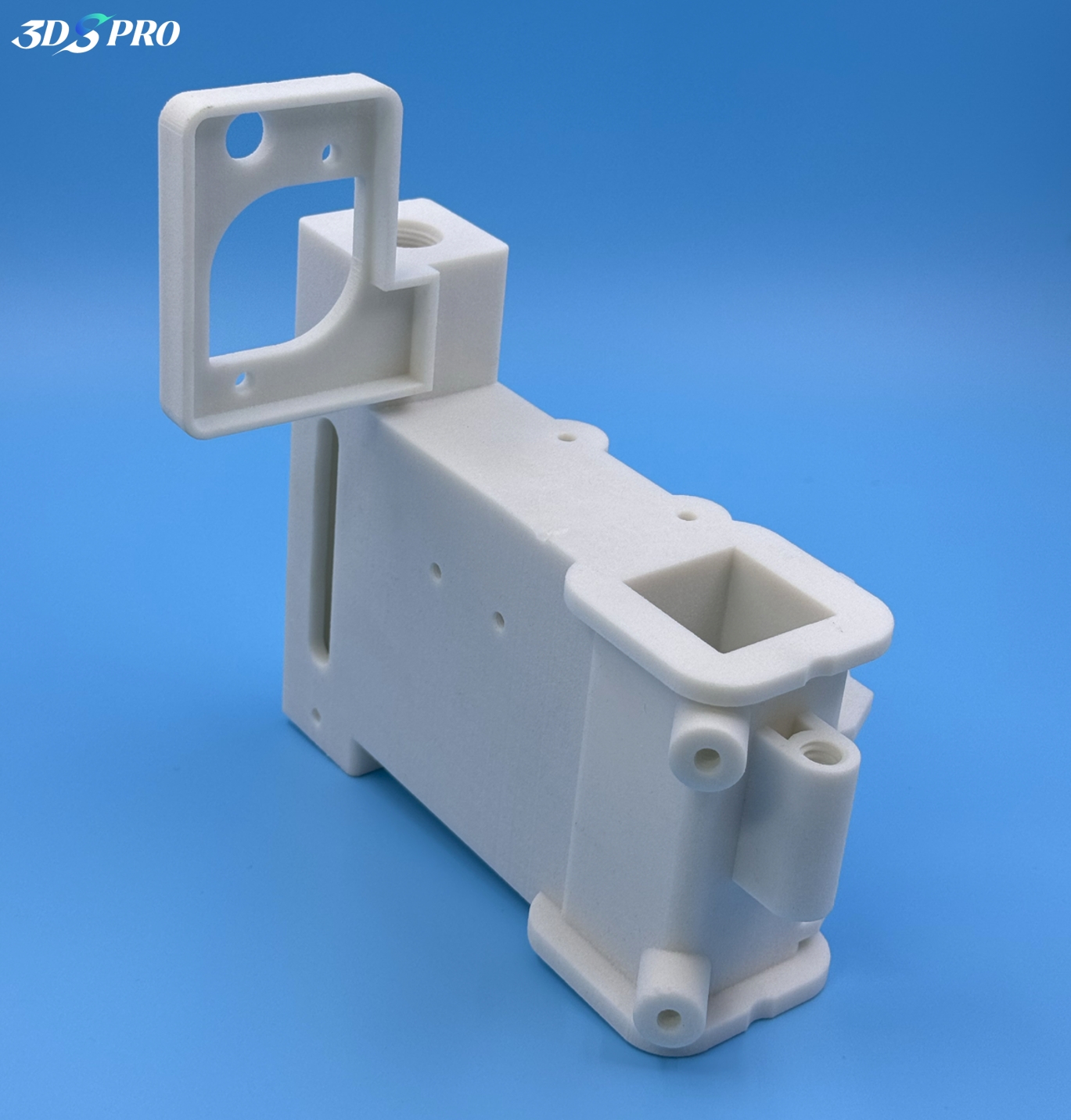

Nylon for 3D Printing
Nylon, a synthetic thermoplastic polymer, is a popular material for Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing due to its excellent mechanical properties and versatility. Let's explore the types of nylon materials used in SLS 3D printing and their specific characteristics.
Types of Nylon Used in SLS 3D Printing
● Nylon 12 (PA 12): Nylon 12 is known for its high performance, dimensional accuracy, and versatility. It offers good tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility. It is widely used for high-performance prototyping, small-batch manufacturing, permanent jigs, fixtures, and general SLS parts.
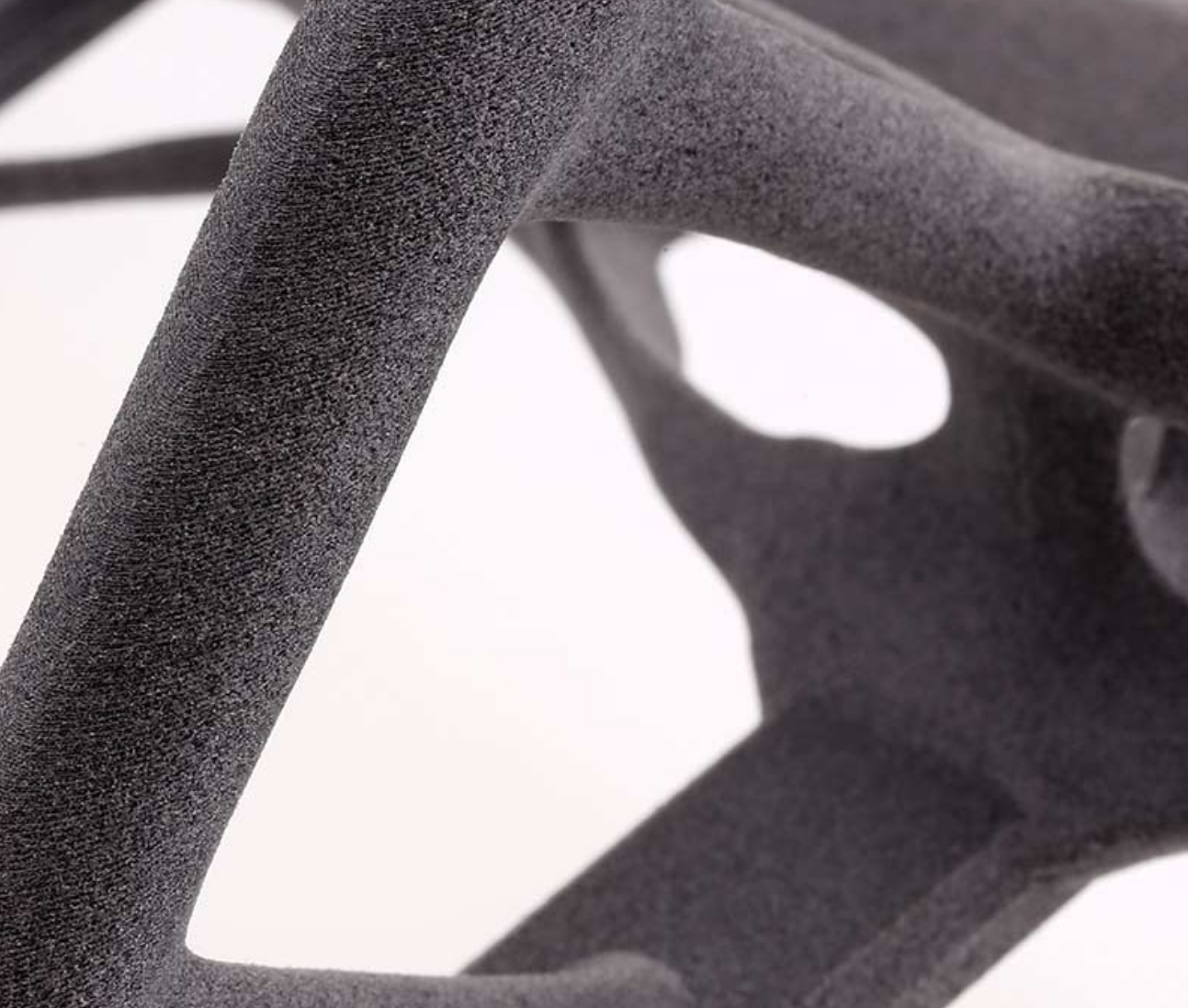

● Nylon 11 (PA 11): Nylon 11 is a ductile, strong, and flexible material, making it ideal for parts that require durability and performance. It has excellent impact resistance and can withstand repeated stress. PA 11 is suitable for impact-resistant prototypes, thin-walled ducts and enclosures, snaps, clips, hinges, orthotics, and prosthetics.
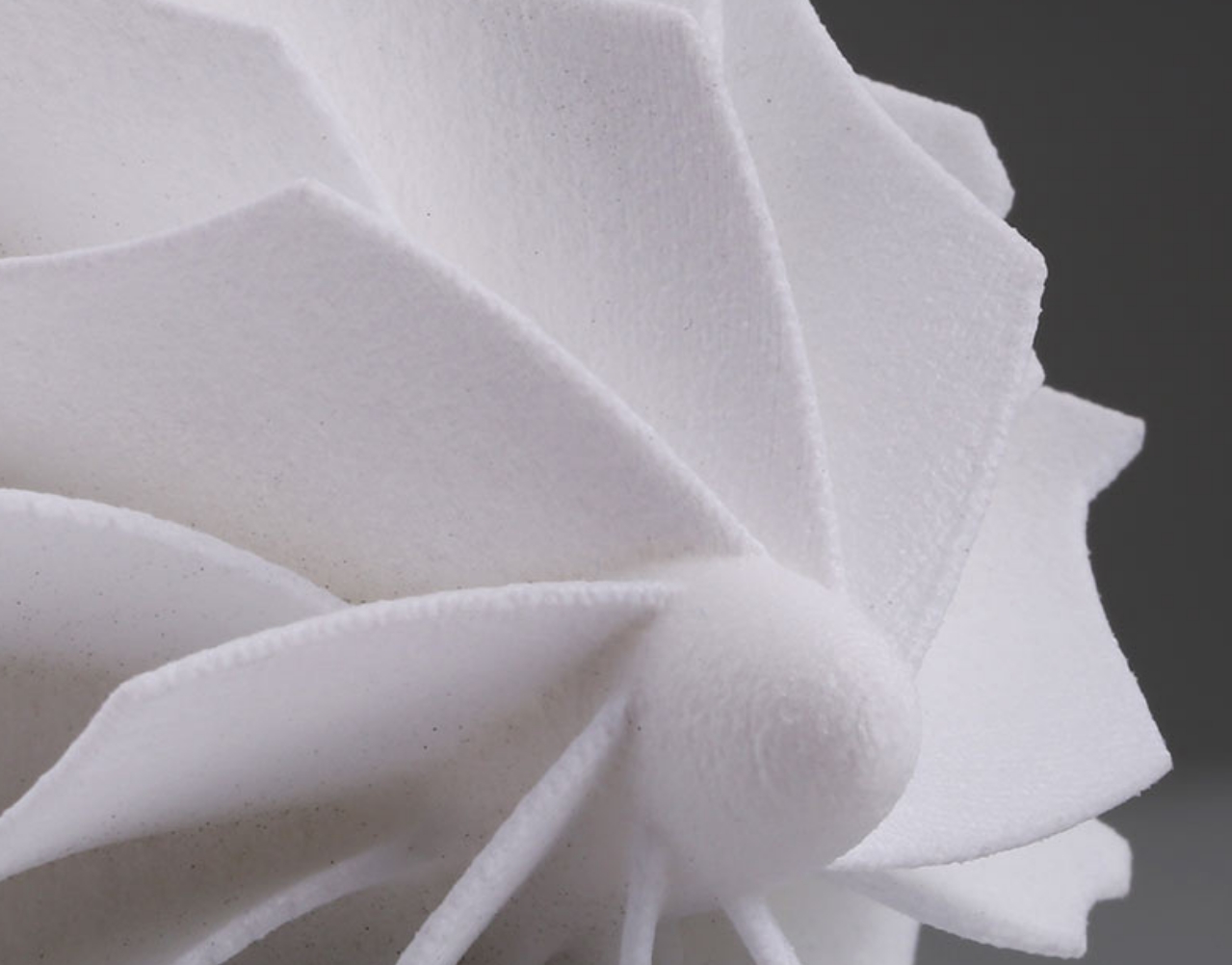

● Nylon 12 GF (Glass-Filled): This variant is reinforced with glass fibers, enhancing its stiffness and thermal stability. It is suitable for demanding industrial environments. It is used for robust jigs and fixtures, replacement parts, parts undergoing sustained loading, threads, sockets, and high-temperature applications.
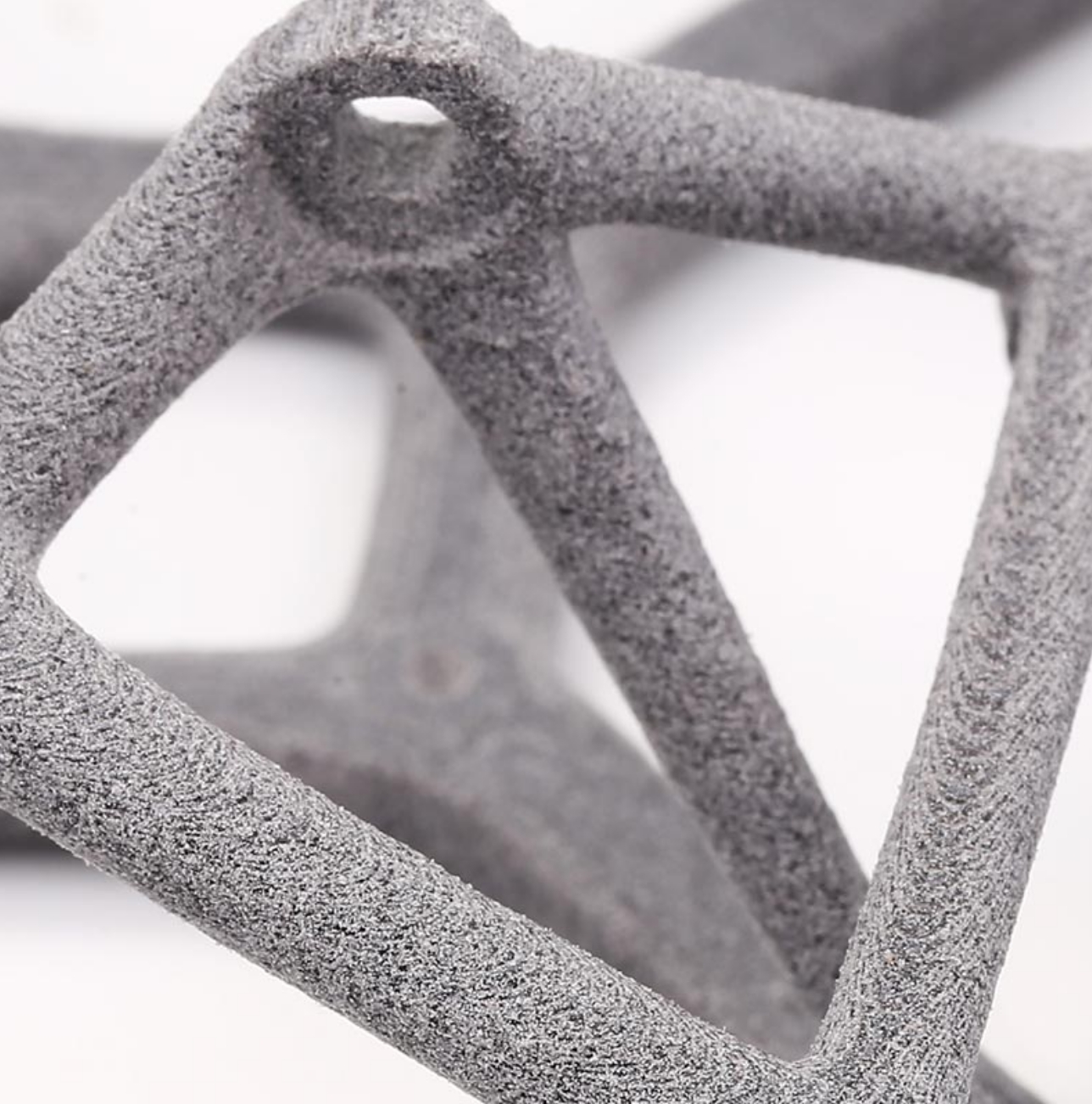

● Nylon 11 CF (Carbon-Filled): Carbon-filled nylon 11 offers increased strength and rigidity, making it suitable for high-performance applications. It is used in parts that require high strength and rigidity, such as structural components and high-stress parts.
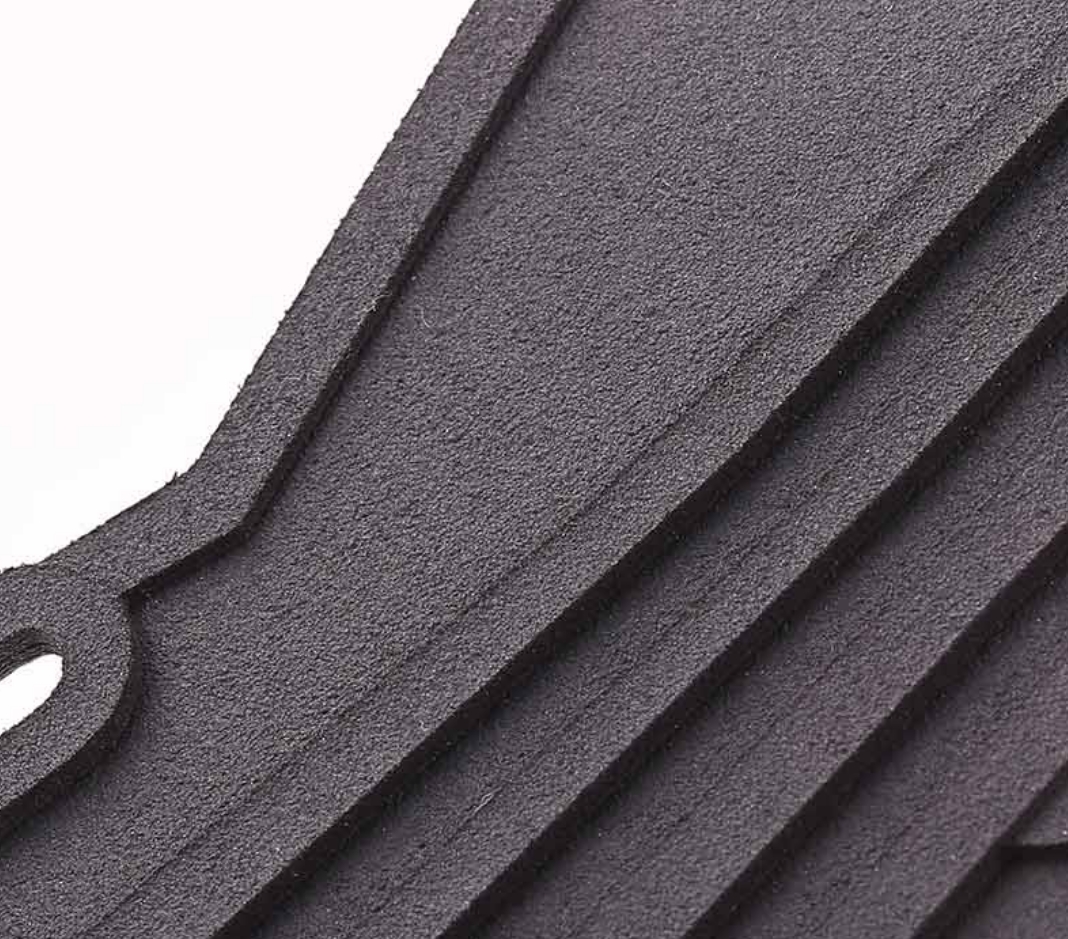

Advantages of Nylon for SLS 3D Printing
● Durability: Nylon parts produced through SLS are strong, impact-resistant, and can endure repeated wear and tear.
● Versatility: Nylon can be used in a wide range of applications, from functional prototypes to end-use parts.
● Environmental Stability: Nylon is resistant to UV light, heat, moisture, solvents, and temperature variations, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
● Recyclability: The unsintered nylon powder can be recycled and reused in subsequent builds, reducing material waste and cost.
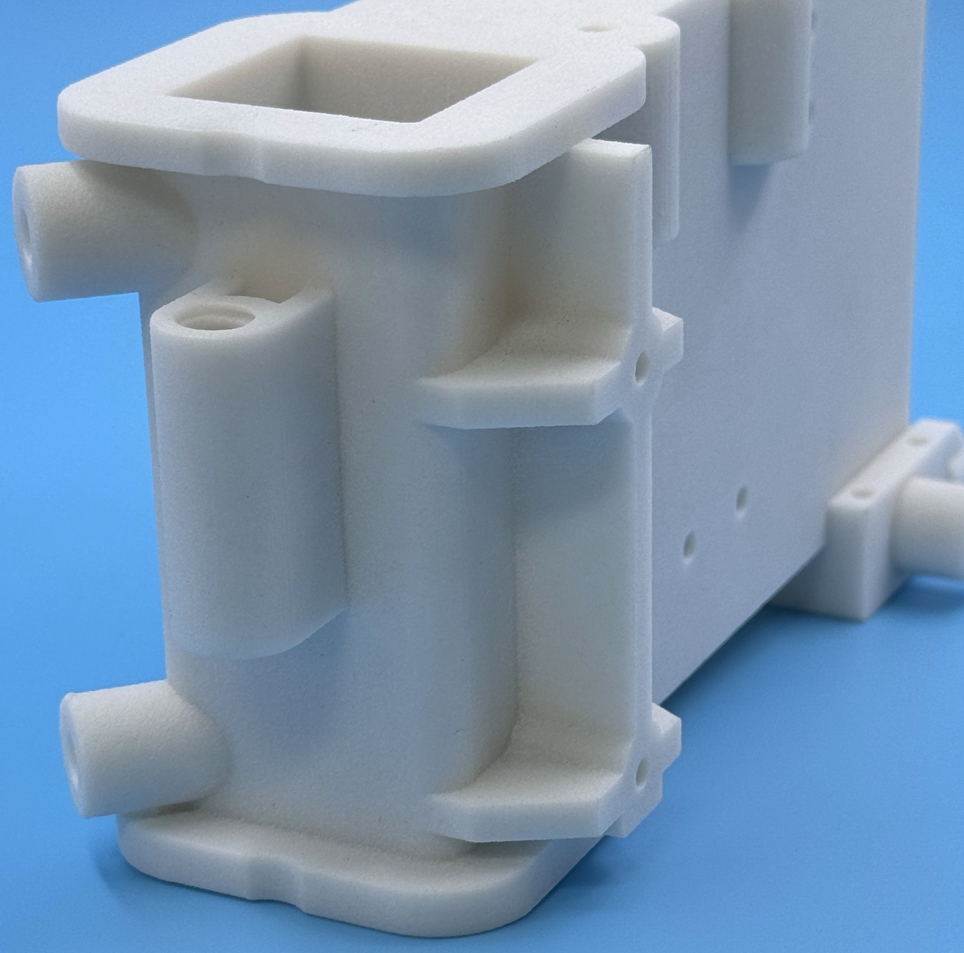
The Advantages of SLS Nylon 3D Printing
1. Complex Geometries and Design Freedom
● Intricate Designs: SLS can produce highly complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
● No Support Structures: Unlike other 3D printing technologies, SLS doesn't require support structures, allowing for even more design freedom and reducing post-processing time.
● Nested Assemblies: SLS enables the creation of interlocking or nested assemblies in a single print, reducing the need for multiple parts and assembly steps.
2. High Strength and Durability
● Isotropic Properties: SLS nylon parts exhibit uniform mechanical properties in all directions, unlike FDM prints, which can have weaker interlayer bonding.
● Impact Resistance: Nylon parts produced through SLS are known for their high impact resistance and durability.
● Chemical Resistance: SLS nylon parts offer good resistance to many chemicals, oils, and solvents.
3. Functional Prototyping and End-Use Parts
● Functional Testing: The mechanical properties of SLS nylon parts closely resemble those of injection-molded parts, making them ideal for functional prototyping and testing.
● End-Use Applications: The durability and quality of SLS nylon parts make them suitable for end-use applications in various industries.
4. Cost-Effective for Small to Medium Runs
● No Tooling Required: SLS doesn't require molds or tooling, making it cost-effective for small to medium production runs.
● Quick Turnaround: Parts can be produced quickly without the lead times associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
● On-Demand Production: SLS allows for on-demand production, reducing the need for large inventories.
5. Material Efficiency
● Powder Recycling: Unused nylon powder can be recycled and reused in subsequent prints, reducing material waste and cost.
● Nesting Efficiency: Multiple parts can be nested closely together in the build chamber, maximizing the use of available space.
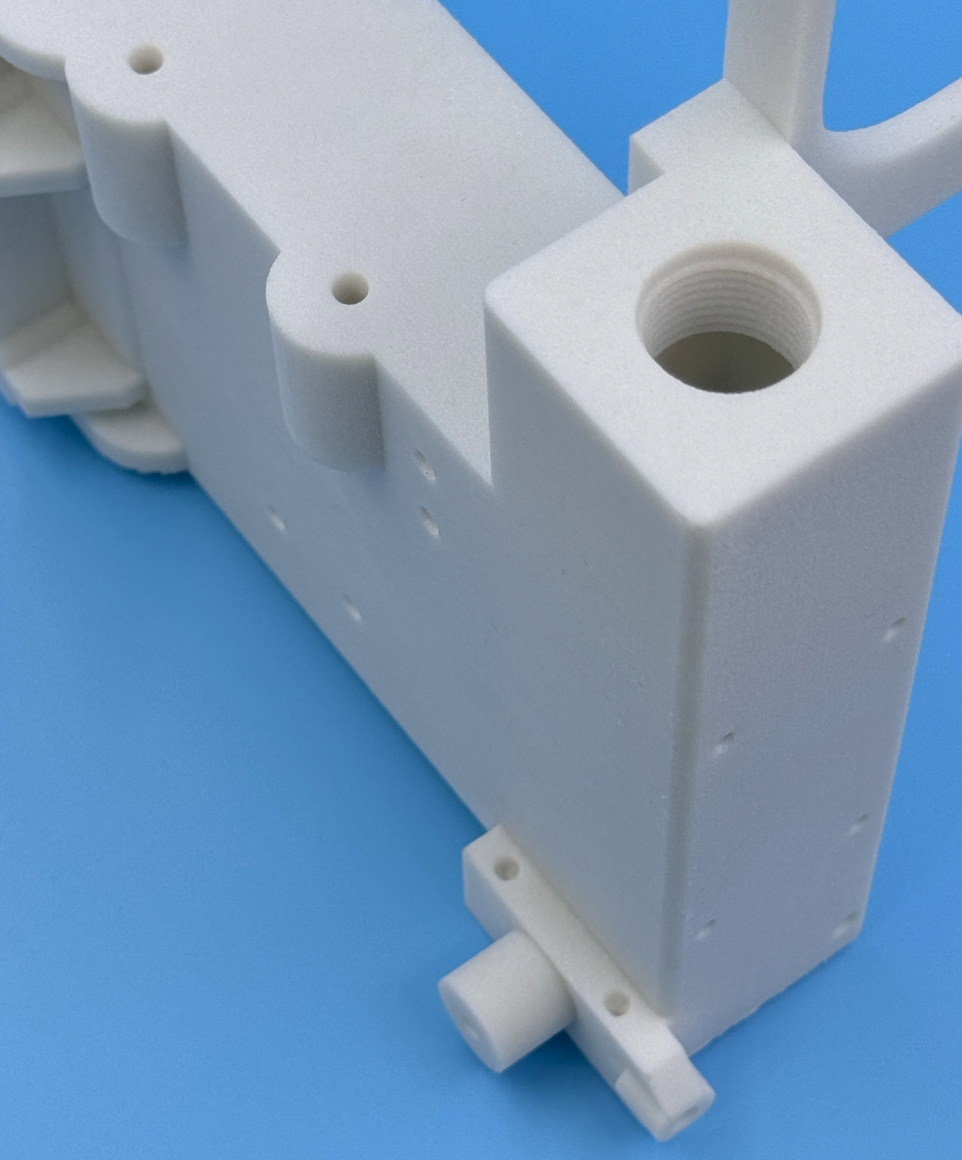
The Limitations of SLS Nylon 3D Printing
1. Size Limitations
● Build Volume Restrictions: The maximum size of parts is limited by the dimensions of the printer's build chamber. Large parts may need to be printed in sections and assembled later.
● Minimum Feature Size: There are limitations on the smallest features that can be accurately produced, typically around 0.3-0.5 mm, depending on the specific printer and material.
2. Surface Finish and Post-Processing
● Grainy Texture: SLS parts often have a slightly grainy or powdery surface finish, which may require post-processing for certain applications.
● Post-Processing Requirements: Achieving a smooth surface or specific color may require additional finishing steps, increasing production time and cost.
3. Material Properties and Limitations
● Porosity: SLS nylon parts can be slightly porous, which may affect water-tightness and surface quality.
● Heat Sensitivity: Nylon has a relatively low melting point, which can limit its use in high-temperature applications.
● Moisture Absorption: Nylon is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air, which can affect part dimensions and properties over time.
4. Color Limitations
● Limited Color Options: SLS nylon parts are typically produced in white or gray, with limited options for color during the printing process. Color is usually added through post-processing.
Applications of SLS Printed Nylon
Aerospace and Aviation
1. Lightweight Components: SLS nylon is used to create lightweight, complex parts for aircraft interiors and non-critical components.
2. Prototyping: Rapid prototyping of aerospace parts for testing and validation.
3. Tooling and Jigs: Custom tools and jigs for aircraft maintenance and assembly.
Automotive Industry
1. Functional Prototypes: Testing new designs for automotive parts before mass production.
2. Custom Parts: Small-batch production of specialized components for luxury or vintage cars.
3. Ducting Systems: Complex air intake and ventilation systems.
Medical and Healthcare
1. Prosthetics and Orthotics: Customized, lightweight prosthetic limbs and orthotic devices.
2. Surgical Guides: Patient-specific surgical guides for improved accuracy in operations.
3. Medical Device Prototypes: Rapid prototyping of new medical devices for testing.
Consumer Goods
1. Eyewear: Custom frames and prototypes for glasses and sunglasses.
2. Sports Equipment: Customized grips, protective gear, and performance-enhancing components.
3. Electronics Housings: Durable casings for consumer electronics and gadgets.
Industrial Manufacturing
1. End-of-Arm Tooling: Custom grippers and end effectors for robotic systems.
2. Functional Prototypes: Testing new product designs before investing in tooling.
3. Low-Volume Production: Small batch manufacturing of specialized industrial components.
Fashion and Accessories
1. Jewelry: Intricate, customized jewelry pieces and prototypes.
2. Textile Innovations: Flexible, interlocking structures for avant-garde fashion designs.
3. Footwear Components: Custom soles, insoles, and other shoe components.
Robotics
1. Structural Components: Lightweight yet strong parts for robotic frames and casings.
2. Functional Mechanisms: Complex gears, joints, and actuators for robotic systems.
3DSPRO SLS 3D Printing Solutions
3DSPRO offers comprehensive SLS 3D printing solutions, providing high-quality, industrial-grade parts for prototyping and production needs. High-qiality nylon materials is used to create complex, durable parts with excellent mechanical properties. We offer a range of nylon options, including PA12, PA11, and glass-filled variants, to suit diverse application requirements.
Our online platform streamlines the ordering process, allowing customers to upload their 3D models, receive instant quotes, and track their orders in real time. Additionally, 3DSPRO provides extensive post-processing services to enhance the functionality and aesthetics of SLS-printed parts. These services include dyeing, vapor smoothing, and various surface finishing techniques to achieve the desired look and feel. With our expertise in SLS technology and commitment to customer satisfaction, 3DSPRO delivers reliable, cost-effective 3D printing solutions to everyone.

COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!

























