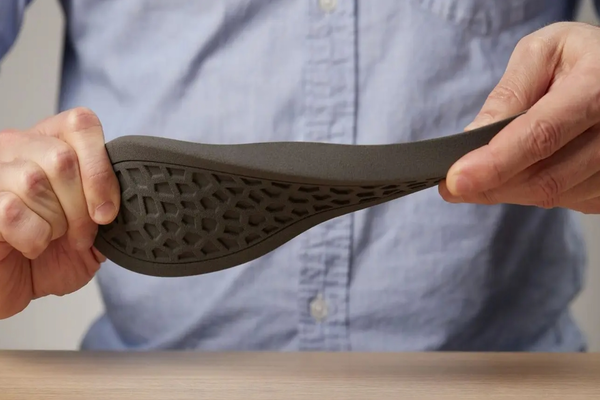
What is TPU filament?
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) filament is a versatile and durable material used in 3D printing. It is known for its flexibility, elasticity, and resistance to oils, greases, and abrasion. TPU is a type of thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) with added benefits that stem from its unique molecular structure, which provides a perfect balance between plastic and rubber.

Image Source: ERYONE
Mechanical Properties of TPU Filament
● Elasticity and Flexibility: TPU’s most notable property is its high elasticity. It can be stretched to significant extents and still return to its original shape without permanent deformation, which is quantified by its high elongation at break, typically ranging from 200% to 600%.
● Tensile Strength: TPU filaments exhibit impressive tensile strength, which measures the resistance of the material to breaking under tension. It generally has a tensile strength value of around 25 to 50 MPa (MegaPascals), making it strong enough for parts that are subjected to constant stress.
● Abrasion Resistance: TPU is highly resistant to wear and tear, which is essential for parts that will be in contact with abrasive surfaces or materials. This property extends the lifespan of TPU-printed parts in demanding environments.
● Impact Resistance: The filament’s ability to absorb energy makes it excellent for applications requiring impact resistance. It can withstand shocks and repeated impacts without cracking or breaking.
● Hardness: The hardness of TPU can vary depending on the formulation, but it typically falls within the 60A to 90A range on the Shore A hardness scale. This range allows for a balance between flexibility and rigidity tailored to specific application needs.
● Thermal Properties: TPU maintains its properties across a wide temperature range. It has a good heat resistance, with a melting point around 225°C to 250°C. However, it’s also capable of withstanding low temperatures without becoming brittle.
● Chemical Resistance: TPU is resistant to many oils, greases, and various chemicals, making it suitable for industrial applications where chemical exposure is common.
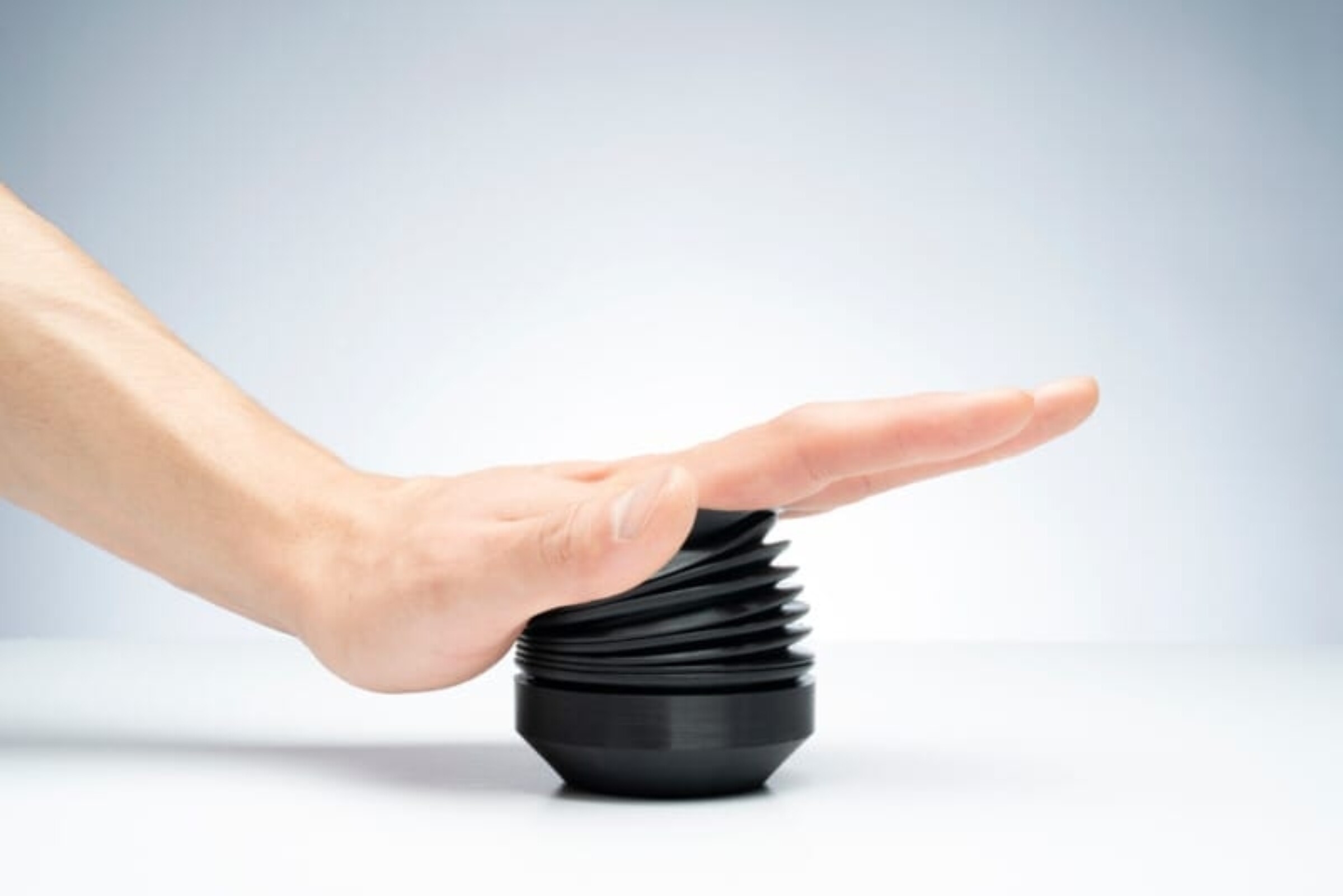

Image Source: Markforged
TPU Filament Variants
● Standard TPU: This is the most commonly used variant, offering a good balance between flexibility and strength. It’s suitable for a wide range of applications, including protective cases, gaskets, and wearable items.
● Medical Grade TPU: Designed for biocompatibility, this variant is used in medical applications where flexibility and skin contact are required. It’s often used for medical devices, prosthetics, and orthopedic models.
● High-Temperature TPU: With enhanced thermal properties, this TPU can withstand higher temperatures without deforming. It’s ideal for parts that will be exposed to heat, such as under-the-hood automotive components or industrial machinery parts.
● Alloyed TPU: This type combines TPU with other materials, such as polycarbonate (PC), to create filaments with unique properties. Alloyed TPUs can offer increased stiffness, impact resistance, and improved thermal stability.
● Conductive TPU: Infused with conductive materials, this variant allows for the creation of flexible electronic components, antistatic jigs, or parts that require electromagnetic shielding.
● UV-Resistant TPU: This variant includes additives that protect the material from UV radiation, making it suitable for outdoor applications where sunlight exposure is a concern.
● Eco-Friendly TPU: Made from renewable resources or recycled materials, eco-friendly TPU aims to reduce the environmental impact of 3D printing while maintaining performance.
Printer Setting for TPU Filament
1. Extruder Temperature: TPU melts at a higher temperature than some other filaments. Set your extruder temperature between 220°C and 250°C. Start at the lower end and increase if you notice poor layer adhesion.
2. Bed Temperature: A heated bed helps with first-layer adhesion. Set the bed temperature to 50°C to 70°C. Use a bed adhesive or a glue stick if needed to prevent warping.
3. Print Speed: Slow and steady wins the race with TPU. Due to its flexibility, printing too fast can lead to issues. Aim for a print speed of 15-30 mm/s for detailed parts and up to 40 mm/s for less intricate objects.
4. Retraction: Retraction can be tricky with flexible filaments. Start with a low retraction distance of about 1-2 mm and a slow retraction speed to prevent the filament from clogging.
5. Layer Height: A layer height of 0.1-0.3 mm works well with TPU. Thinner layers may provide better detail but will increase print time.
6. Fan Speed: Cooling is essential, but too much can affect adhesion. Set the fan speed to 50% after the first few layers to ensure proper cooling without causing layer separation.
7. Nozzle Type: Use a 0.4 mm or larger nozzle to reduce the risk of clogging. Stainless steel or hardened steel nozzle can withstand the abrasion of filled TPUs better than brass.
8. Enclosure: While not mandatory, an enclosure can help maintain a consistent temperature around the print, reducing the chances of warping or layer separation.
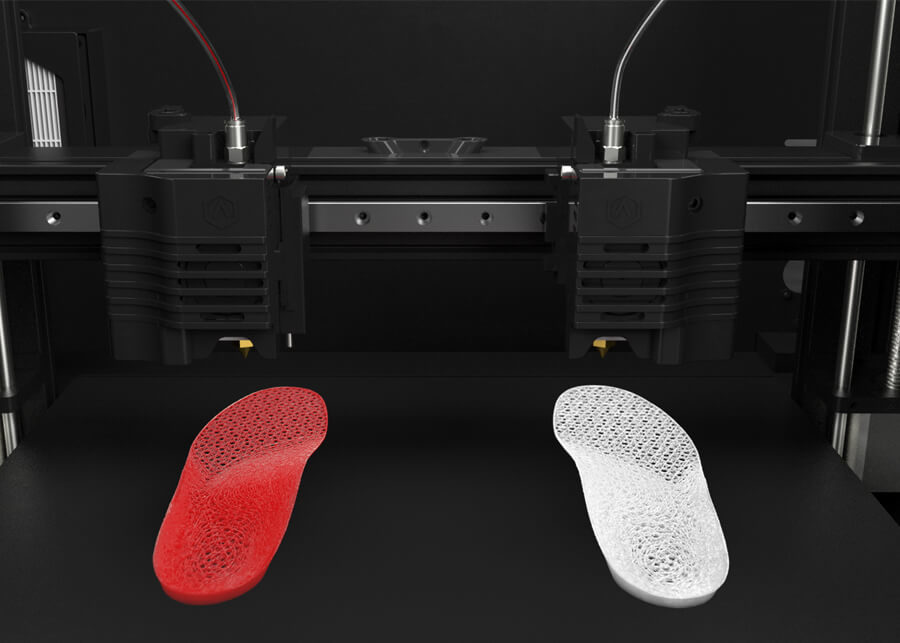

Image Source: Raise3D
TPU Filament Applications
1. Protective Cases: TPU’s shock-absorbing qualities make it perfect for phone cases, tablet covers, and camera skins that need to withstand drops and impacts.
2. Wearable Devices: Its skin-safe nature and flexibility are ideal for wristbands, watch straps, and other wearable technology accessories.
3. Sports Equipment: TPU is used in sports gear such as mouthguards, swim fins, and water bottle holders, offering both comfort and resilience.
4. Industrial Seals and Gaskets: The material’s resistance to abrasion and chemicals makes it suitable for creating industrial seals, gaskets, and hoses that can endure harsh conditions.
5. Footwear: TPU’s flexibility and strength are beneficial for shoe soles, insoles, and other components that require a combination of comfort and wear resistance.
6. Custom Grips and Handles: Tools, sports equipment, and household items can benefit from custom TPU grips that provide comfort and non-slip properties.
Best TPU Filaments
1. EOLAS PRINTS TPU Filaments
Eolas Prints’ TPU Filament promises to bring your designs to life with its exceptional flexibility and strength. The TPU Filament from Eolas Prints stands out with its impressive density of 1.21 g/cm³ and a Shore hardness of 93 A, ensuring that your prints will not only look spectacular but also withstand the test of time.
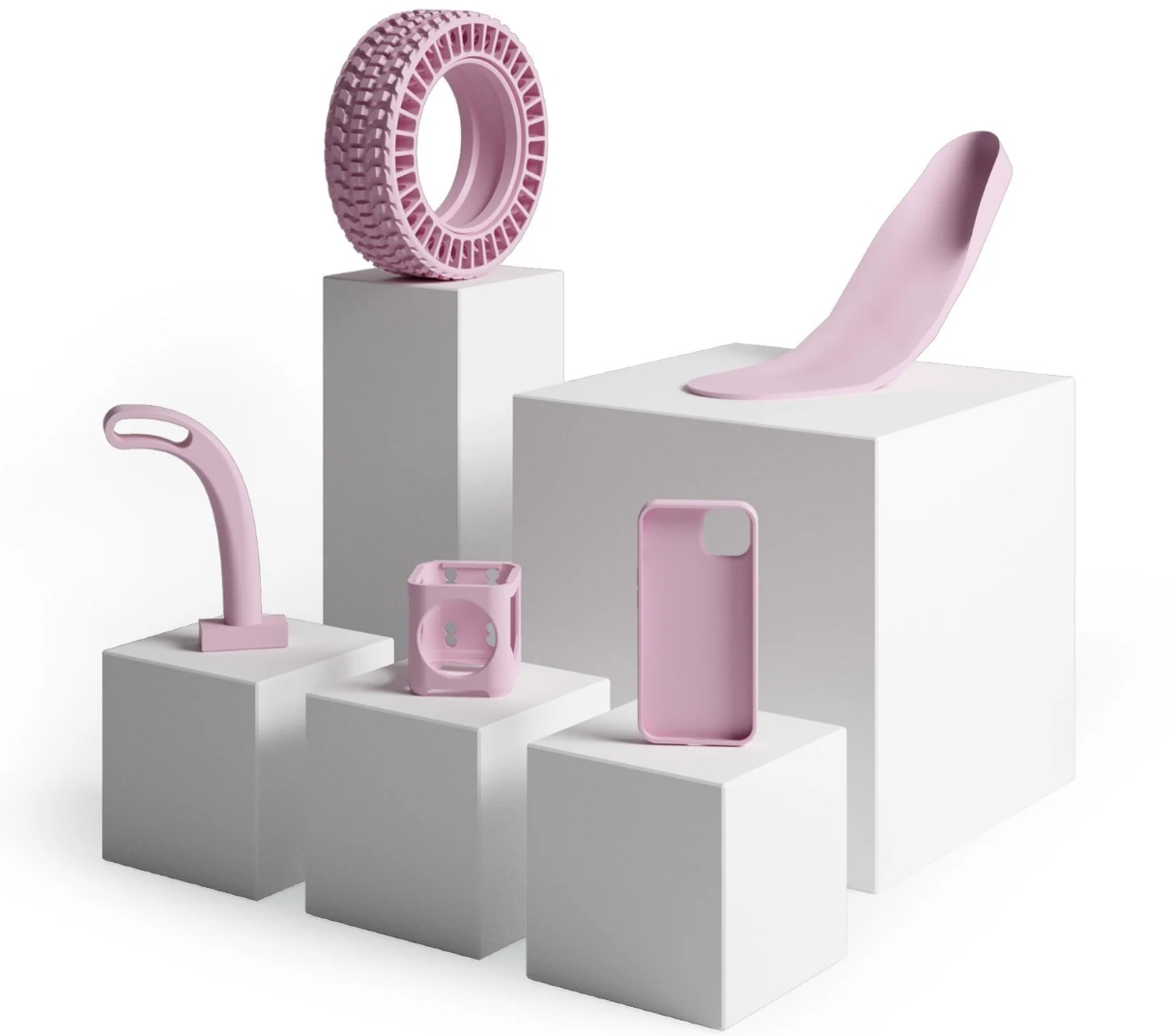

Image Source: EOLAS PRINTS
2. Bambu Lab TPU 95A HF
This innovative material is designed to revolutionize your printing experience, offering three times the speed of traditional TPU filaments without sacrificing quality. The TPU 95A HF filament boasts remarkable flexibility and toughness, coupled with outstanding impact resistance, making it an ideal choice for projects that demand durability and resilience.

Image Source: Bambu Lab
3. Raise3D Premium TPU-95A Filament
Raise3D’s TPU-95A is versatile and suitable for a wide array of uses, such as insoles, tubes, seals, and bushings. Its 1.75mm diameter and 1kg spool ensure that it fits seamlessly into your printing setup, supporting a variety of Raise3D printers.
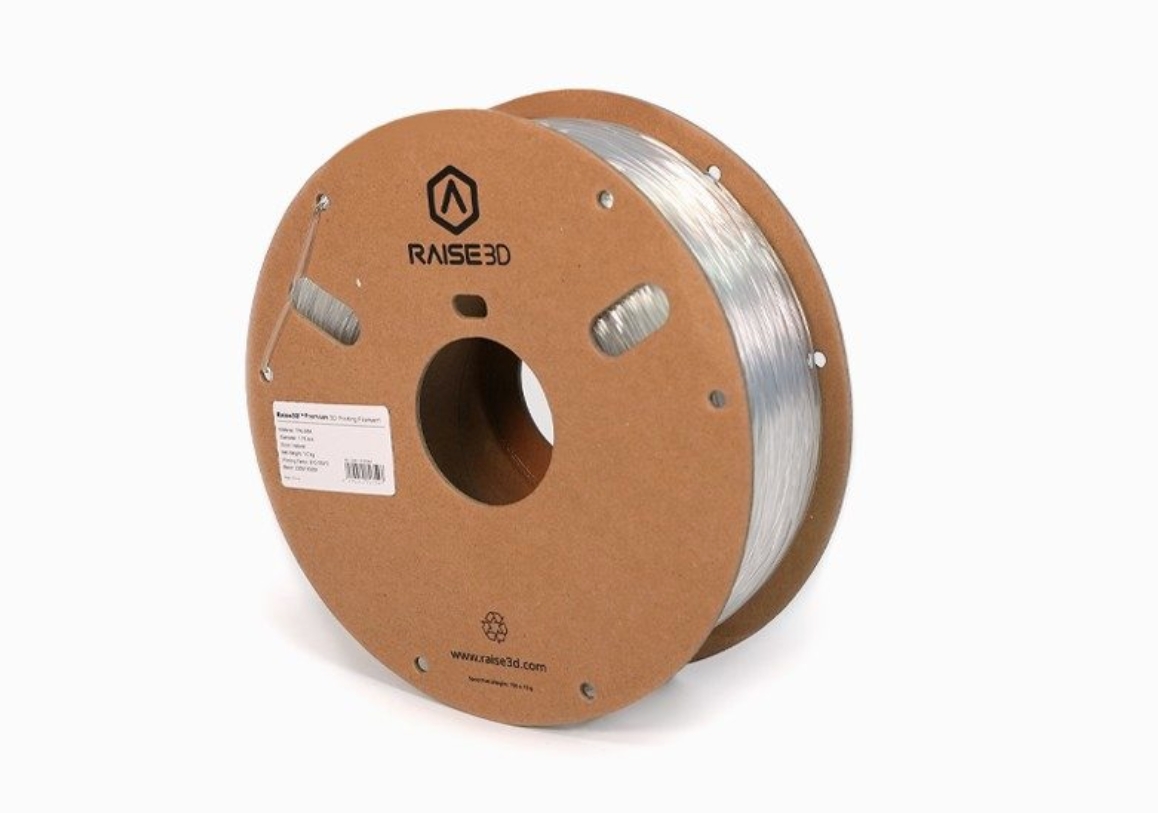

Image Source: Raise3D
4. Filamatrix TPU 95A 3D Printing Filament
Filamatrix’s TPU 95A stands out for its ease of printing and speed. It allows you to achieve higher print speeds of up to 100 mm/s at 250 °C without compromising on the physical properties of your final product. Its wide processing temperature range and excellent layer-to-layer adhesion mean that even the most intricate designs will look sharp and durable.
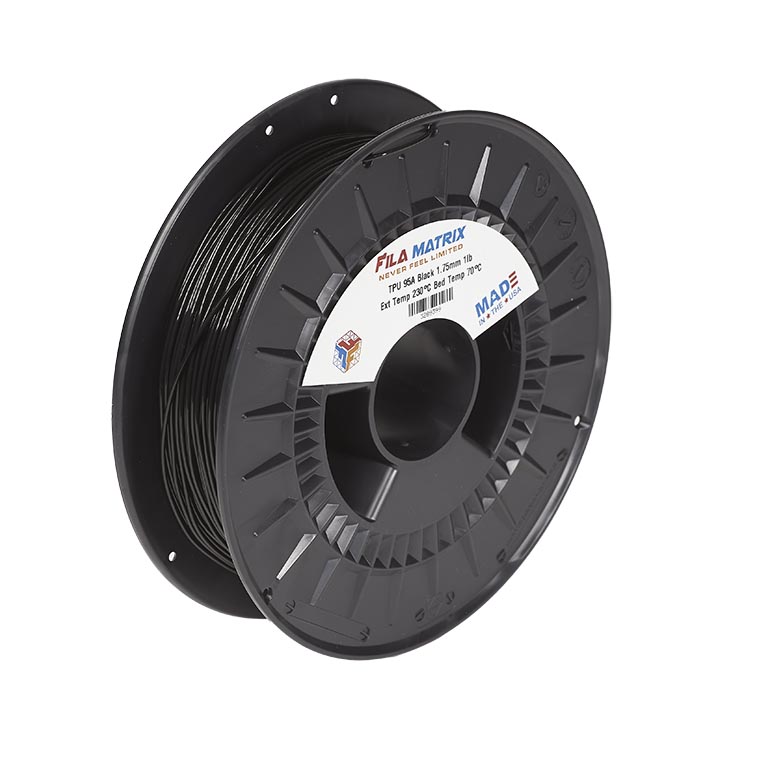

Image Source: Filamatrix
5. Overture TPU 3D Printer Filament
Overture’s TPU Filament, thanks to its patented manufacturing process, is designed to ensure a clog-free and bubble-free printing experience. It promises a smooth and stable flow, with a dimensional accuracy of +/—0.03 mm and a 1 kg spool, making it compatible with most common 3D printers. The filament comes in a variety of colors, enabling you to choose the perfect shade for your project.
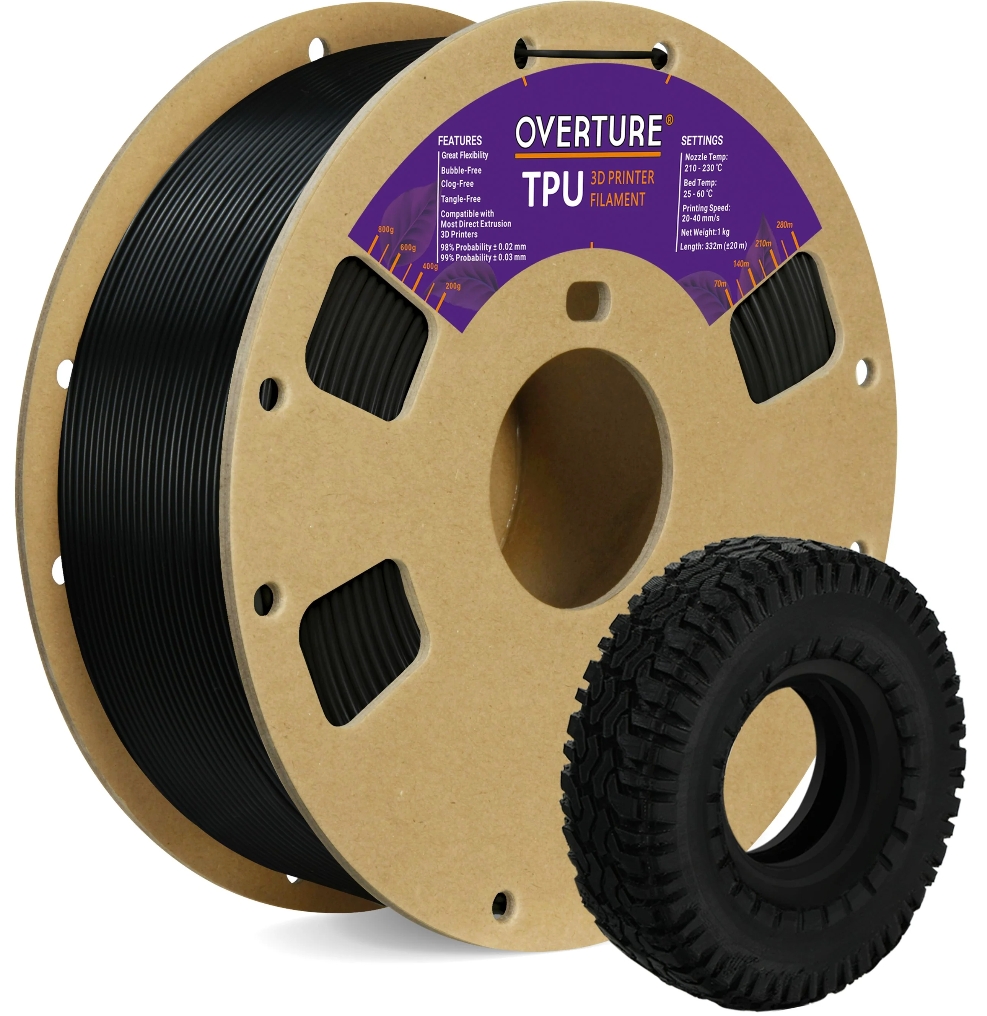

Image Source: Overture
6. Gizmo Dorks 3D Printing Flexible TPU Filament
Gizmo Dorks has crafted this TPU filament to be semi-transparent and highly elastic. It’s perfect for a variety of uses, from automotive parts to medical devices, and especially for protective cases for electronics due to its high flexibility. It’s recommended to print at a speed of 30 - 50 mm/s and a layer thickness above 0.1mm.
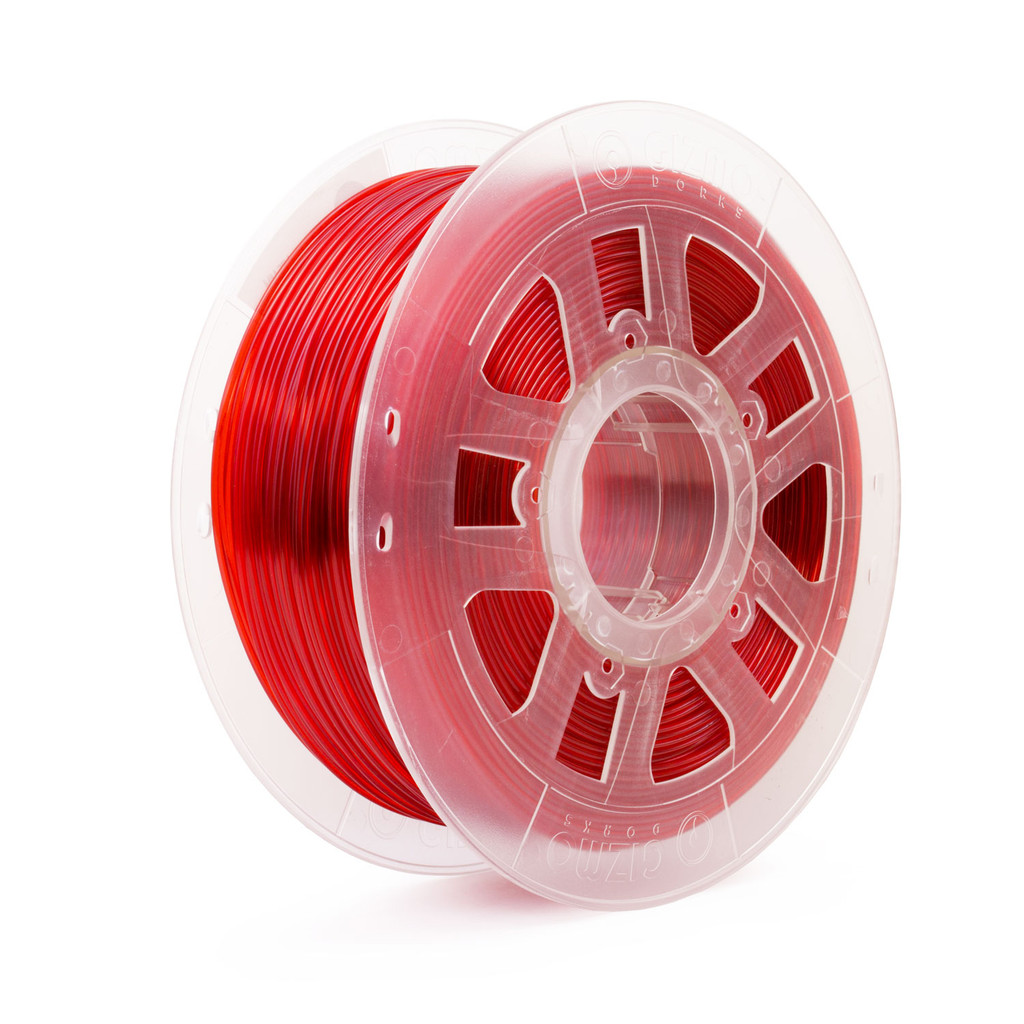

Image Source: Gizmo Dorks
7. MH Build Series TPU Flexible Filament
The MH Build Series TPU is celebrated for its affordability without compromising on quality. With a variety of colors available, your projects can now come to life in the most visually striking way. This filament is compatible with a wide range of printers and is especially suited for producing parts that need to withstand wear and tear.

Image Source: MatterHackers
8. MH PRO Series TPU Filament
MatterHackers’ Black PRO Series TPU is a filament that embodies the perfect synergy of flexibility and durability. This 1.75mm thermoplastic polyurethane material is engineered for those who demand precision and performance in their prints. Its rubber-like qualities provide the necessary energy return and fatigue resistance for parts that need to withstand repeated use.

Image Source: MatterHackers
9. HATCHBOX 95A TPU Filament
Hatchbox’s commitment to quality is evident in every aspect of this filament, from its elasticity strength to its abrasion resistance, ensuring that your prints can handle the wear and tear of everyday use. It offers a seamless printing experience with a recommended extrusion temperature range of 190°C - 235°C.

Image Source: HATCHBOX
10. colorFabb VarioShore TPU
The filament’s active foaming technology allows it to expand to approximately 1.4-1.6 times its original volume, reducing its density to 0.7 to 0.9 g/cm³ when printed at temperatures between 200 and 250°C. With colors turning lighter when the material is fully foamed, colorFabb VarioShore TPU filament provides a unique aesthetic dimension to your prints.
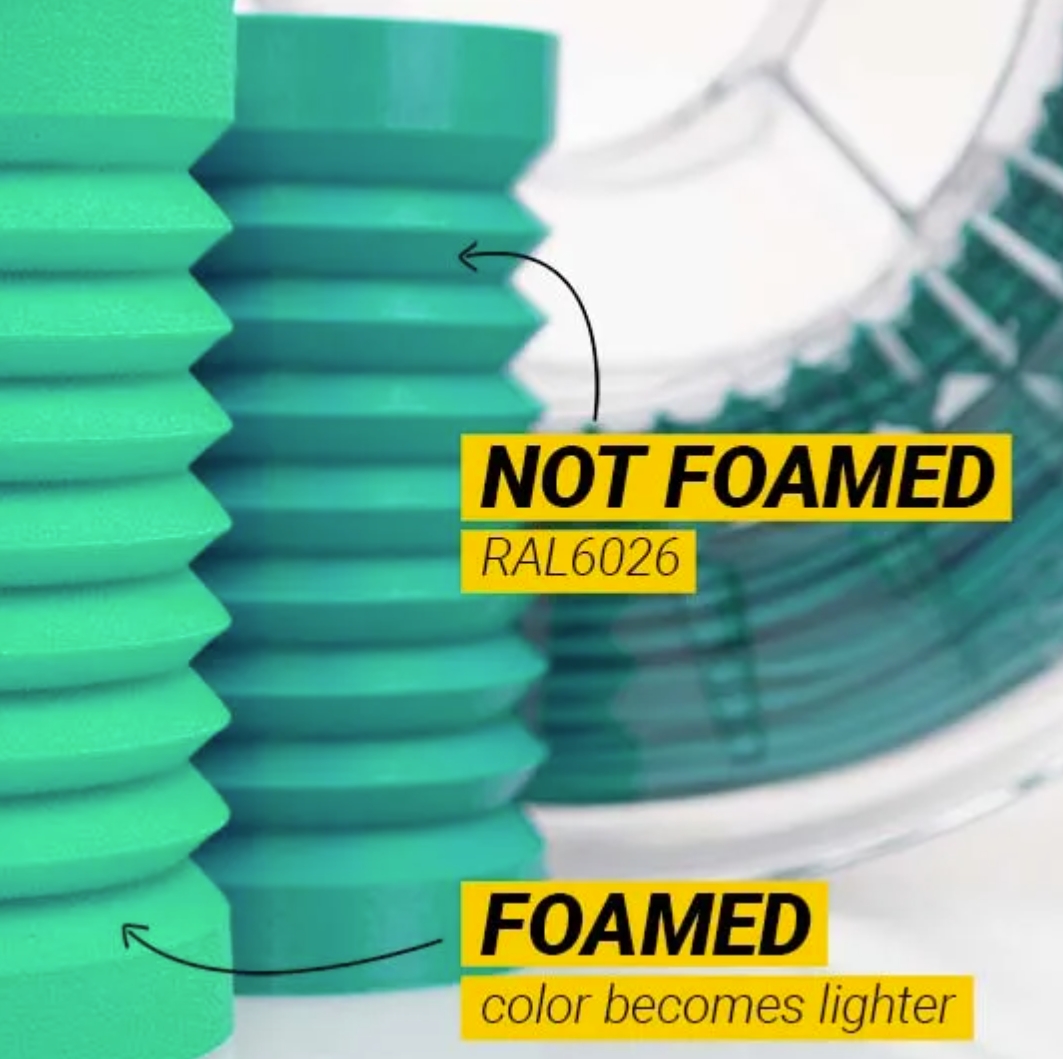
Image Source: colorFabb
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!
Check out Our Special Offers
Featuring Process
- Coming Soon
Featuring Materials
- Coming Soon

























