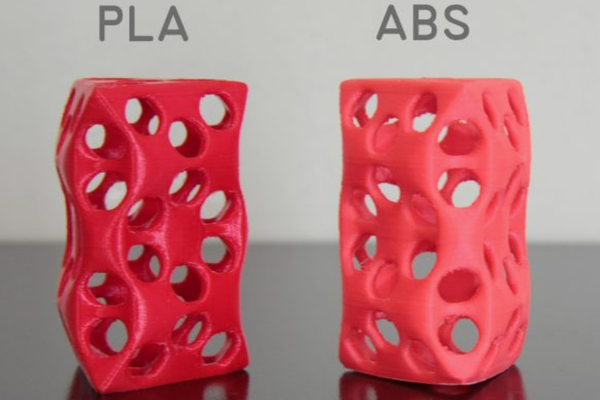
What is ABS filament?
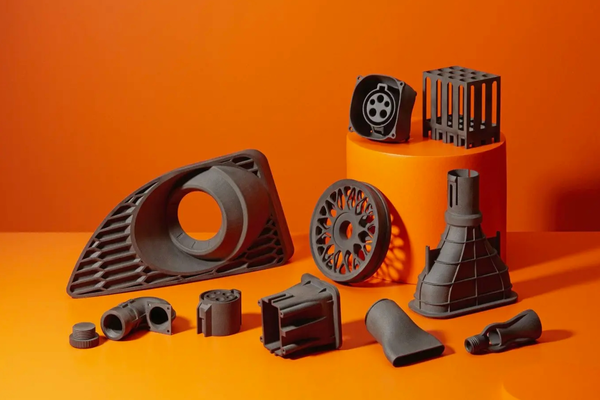
ABS filament, short for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a thermoplastic polymer widely recognized for its robustness, thermal stability, and versatile applications.
As a popular material choice for 3D printing, ABS stands out for its ability to withstand high temperatures and its impressive structural integrity. It is an ideal material for creating durable parts and products that demand strength and resilience.
In this guide, we'll learn the composition of ABS filament, its benefits and limitations, applications of 3D printing ABS filament, explore its properties, and understand why it's a go-to material. Let's get started!

Image Source: MatterHackers
Types of ABS Filament
ABS filament comes in various types, each tailored to specific applications and performance requirements.
Standard ABS Filament
● Features: It is the most common type of ABS filament, known for its good mechanical properties and ease of use.
● Best for: General-purpose printing, prototyping, and educational projects.
High-Impact ABS Filament
● Features: It is enhanced for increased toughness; this filament can absorb more impact without cracking.
● Best for: Parts that require extra durability, such as protective gear or automotive components.
ABS+ Filament
● Feature: An improved version of standard ABS with better adhesion and less warping during printing.
● Best for: Complex prints that need to maintain dimensional accuracy and fine details.
Flame Retardant ABS Filament
● Features: Contains additives that reduce flammability, making it safer for electrical and electronic enclosures.
● Best for: Applications near heat sources or where fire resistance is a priority.
Transparent ABS Filament
● Features: Allows light to pass through, providing a semi-transparent finish.
● Best for: Light covers, lenses, and objects requiring a degree of translucency.
Glow-in-the-Dark ABS Filament
● Features: Infused with phosphorescent materials that emit light after being charged by a light source.
● Best for: Novelty items, toys, and decorative pieces that stand out in the dark.
Conductive ABS Filament
● Features: Blended with conductive carbon particles, enabling the creation of electrically conductive components.
● Best for: DIY electronics, sensors, and circuits integrated into 3D printed objects.
ABS Filament Pros and Cons
Pros of ABS Filament
1. Durability: ABS is known for its toughness and resistance to physical impacts, making it suitable for parts that must endure stress.
2. Heat Resistance: ABS has a higher melting point, so it can withstand temperatures that would warp or deform other plastics.
3. Finish and Aesthetics: It can be sanded and painted post-printing, allowing for a more polished final product.
4. Cost-Effective: ABS is generally less expensive than many other filaments, offering a good balance between cost and performance.
5. Flexibility: While strong, ABS still maintains a degree of flexibility, which helps in preventing breakage.
Cons of ABS Filament
1. Warping: ABS tends to warp if cooled too quickly during printing, requiring a heated bed and controlled environment.
2. Fumes: Printing with ABS releases fumes that can be unpleasant and should be ventilated.
3. UV Sensitivity: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can degrade ABS, affecting its color and properties.
4. Print Difficulty: Printing with ABS can be more challenging due to its need for precise temperatures and settings.
5. Environmental Impact: ABS is not biodegradable and requires proper recycling to manage waste.
How to dry ABS filament?
Properly drying ABS filament is crucial for maintaining its printing quality and mechanical properties. Moisture can cause issues such as bubbling, weak layer adhesion, and poor surface finish. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to dry ABS filament:
1. Recognize the Signs of Moisture
Symptoms: Popping sounds during printing, steam coming from the nozzle, and a rough surface finish.
Preventive Measures: Store filament in airtight containers with desiccants to minimize moisture absorption.
2. Use a Filament Dryer
Procedure: Place the spool in a filament dryer set to 80-85°C for 6-8 hours.
Tip: Ensure the dryer is designed for ABS to avoid melting or deforming the filament.
3. Oven Drying Method
Precautions: Use an oven thermometer to verify the temperature, as ovens can be inaccurate.
Temperature: Preheat the oven to 75-80°C.
Duration: Bake the filament for 4-6 hours, checking periodically to prevent overheating.
4. Sun Drying (Not Recommended)
Risks: UV exposure can degrade ABS, and uneven heating can cause warping.
Alternative: If no other method is available, spread the filament under the sun but monitor closely and rotate frequently.
5. Vacuum Sealing After Drying
Benefit: Vacuum sealing with desiccants prolongs the dryness of the filament.
Suggestion: Use vacuum bags specifically designed for filament storage.
6. Regular Maintenance
Dry filaments regularly, especially if they’ve been exposed to humid conditions or stored for long periods.
ABS Filament Applications
Consumer Products
Due to its strength and durability, ABS is extensively used in the manufacturing of everyday items such as toys, phone cases, and household appliances.
Automotive Parts
The automotive industry utilizes ABS for components like dashboards, panels, and trim parts because of its heat resistance and toughness.
Medical Devices
ABS is suitable for creating non-implantable medical device prototypes, such as casings for monitors and surgical instruments, owing to its rigidity and ease of sterilization.
Sporting Goods
Sporting equipment like helmets, protective gear, and accessories benefit from ABS’s impact resistance and structural integrity.
Custom Fabrication
ABS’s ability to be easily sanded and painted makes it ideal for custom DIY projects, cosplay items, and models.
Prototyping
Engineers and designers often choose ABS for prototyping mechanical parts and assemblies due to its accurate representation of the final product’s strength and aesthetics.
Educational Models
In educational settings, ABS is used to create durable models and teaching aids that can withstand frequent handling.
Robotics
ABS is a preferred material for building robotic parts and chassis because it can endure the wear and tear of moving components.
Functional Tools
Due to its robustness, ABS can be used to print functional tools and fixtures that are subjected to stress and strain.
Art and Design
Artists and designers appreciate ABS for its versatility, allowing them to produce intricate sculptures and design elements.
Best ABS Filaments of 2025
1. Hatchbox ABS
1.75mm $23.99~42.99/kg
Hatchbox ABS is renowned for its high quality and reliability, offering excellent value for its price. It’s compatible with most ABS printers and comes in a variety of colors. The filament is praised for its consistent print results and comes in resealable bags for temporary air-tight storage.

Image Source: Hatchbox
2. eSun ABS+
1.75mm $16.99~23.99/kg
eSun’s ABS+ is an upgraded variant designed to reduce curling, warping, and cracking while maintaining the toughness of standard ABS. It enhances layer bonding and delivers a smooth surface finish, and it is available in a range of vibrant colors.

Image Source: eSun
3. Polymaker PolyLite ABS
1.75mm $21.99~22.99/kg
PolyLite ABS by Polymaker uses a unique bulk-polymerized ABS resin, which reduces volatile content and minimizes odors during printing. It’s a low-cost ABS filament that doesn’t compromise on quality, ensuring reliable print results.

Image Source: Polymaker
4. IC3D ABS
1.75mm $35/kg
IC3D ABS is a premium choice for those seeking top-tier durability and strength in their prints. It’s known for producing strong prints and comes in a variety of colors.

Image Source: IC3D
5. Overture ABS
1.75mm $19.99~21.99/kg
Overture ABS is easy to use and is a great option for those new to printing with ABS. It requires slightly higher-than-normal printing temperatures but is very reliable once the slicer profile is tuned.
Image Source: Overture
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!
Check out Our Special Offers
Featuring Process
- Coming Soon
Featuring Materials
- Coming Soon