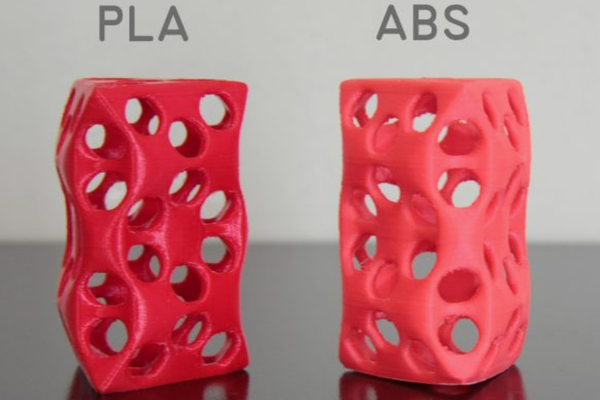
What is PLA filament?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) filament is a biodegradable and eco-friendly 3D printing material derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. It's one of the most popular filaments used in 3D printing due to its ease of use and the fact that it doesn't emit harmful fumes during printing, making it safe for use in homes and schools.
PLA filament is known for its good tensile strength and surface finish, which makes it ideal for a wide range of printing applications, from prototypes to final products. As we explore the world of PLA filament, we'll learn about its properties, variations, advantages, and limitations, as well as practical tips for storage and usage. Let's get started!

Image Source: Flashforge Silk Dual-color PLA
Properties of the PLA Filament
Ultimate Tensile Strength
PLA filament typically has an ultimate tensile strength of around 65 MPa, which is considered high. However, it’s important to note that PLA can be brittle and may not absorb impacts well.
Stiffness
PLA is rated high in stiffness and can be further increased with additives like carbon fiber, which enhances model stability and stiffness.
Maximum Service Temperature
PLA can generally withstand temperatures up to 52°C. Beyond this point, the material may begin to deform, which is a relatively low threshold compared to other polymers.
Durability
In terms of wear and abrasion, PLA is less durable compared to other materials and can degrade with extensive use.
Density
The density of PLA filament is about 1.24 g/cm³, which is on the higher side relative to most polymers.
Extruder Temperature
For optimal printing, the extruder temperature should be set between 190°C and 220°C. This lower melting point makes PLA easier to print across different machines.
Bed Temperature
The recommended bed temperature for PLA is 45°C to 65°C, which is considered low for typical polymers and suitable for all types of 3D printers.
PLA Filament Pros and Cons
Pros
● Eco-Friendly: PLA is made from renewable resources, making it biodegradable and more environmentally friendly than petroleum-based plastics.
● Ease of Use: It prints at lower temperatures and does not require a heated bed, making it user-friendly, especially for beginners.
● Odorless: PLA does not emit a strong odor during printing, unlike some other materials, which makes it suitable for indoor use.
● Finish and Detail: It offers a sharp print finish with good detail, ideal for models and prototypes that require a high-quality appearance.
● Color Variety: PLA's extensive range of colors and translucencies allows it to accommodate a wide array of aesthetic preferences.
Cons
● Low Heat Resistance: PLA has a low melting point, which can be a disadvantage for objects that will be exposed to heat or left in hot environments.
● Brittleness: While it has good tensile strength, PLA can be brittle and may crack under pressure or impact.
● Hygroscopic: PLA absorbs moisture from the air, which can lead to printing problems and reduced shelf life if not stored properly.
● Limited Mechanical Properties: Compared to other filaments like ABS or PETG, PLA has limited mechanical properties, making it less suitable for functional parts that require flexibility or durability.
● Degradation Over Time: PLA can degrade over time, especially when exposed to the elements, which can affect the longevity of the printed objects.
Types of PLA Filaments
The versatility of PLA filament is one of its most appealing features, offering a range of types to suit various printing needs and aesthetic preferences.
1. Standard PLA: The most common type, known for its ease of use and good quality prints.
2. PLA+/Plus: An enhanced version that offers improved strength and thermal resistance.
3. Tough PLA: Modified to be stronger and more durable, suitable for more functional parts.
4. PLA Blends: These are PLA filaments mixed with other materials to create unique properties:
● Wood PLA: Contains fine wood particles, giving prints a wood-like appearance and texture.
● Metallic PLA: Infused with metallic powders, providing a shiny, reflective finish.
● Glow-in-the-Dark PLA: Contains phosphorescent materials that make prints glow in the dark.
● Silk PLA: Has a shiny, silky appearance for prints that stand out with a glossy finish.
● Conductive PLA: Embedded with conductive materials, allowing the creation of electronic circuits.
● Carbon Fiber PLA: Reinforced with carbon fibers for increased stiffness and strength.
● Matte PLA: Offers a matte, non-reflective surface for prints that require a subtle appearance.
Keep in mind that some specialty PLA filaments may require different printing settings or additional post-processing to achieve the best results.
How to store PLA filament?
Proper storage of PLA filament is crucial to maintain its quality and printability. Here are some tips to ensure your PLA filament remains in optimal condition:
1. Airtight Containers
Store PLA filament in airtight containers to protect it from moisture. You can use vacuum-sealed bags, resealable plastic bags, or containers with tight-fitting lids.
2. Desiccants
Include desiccant packs, such as silica gel, inside the storage container to absorb any residual moisture. These can be recharged or replaced as needed.
3. Maintain a Cool and Dry Environment
Store the filament in a cool, dry location, shielded from direct sunlight and heat. The optimal storage temperature for PLA ranges from -20°C to +30°C.
4. Avoid Humidity
If you reside in a humid region, contemplate utilizing a dehumidifier in the storage area for your filament or procure a specialized dry storage container.
5. Monitor and Rotate Stock
Use older filament spools first and regularly check on your stock to ensure they haven’t absorbed moisture over time.
By following these storage tips, you can extend the shelf life of your PLA filament and avoid common printing issues associated with moisture absorption, such as brittleness and poor layer adhesion. Remember, taking care of your filament is just as important as maintaining your 3D printer for achieving the best printing results.
PLA Filament Applications
1. Medical Devices: Its biocompatibility makes it ideal for medical implants and devices that can safely degrade within the body.
2. Food Packaging: PLA is often used in food packaging solutions, such as biodegradable containers and disposable cutlery, due to its food-safe properties.
3. Textiles: They can be spun into fibers for eco-friendly clothing and textiles.
4. Consumer Goods: From phone cases to drink bottles, PLA’s versatility is showcased in a variety of consumer products.
5. Agriculture: PLA is used in agricultural films and biodegradable plant pots that contribute to sustainable farming practices.
6. Automotive: In the automotive industry, PLA is utilized for parts like dashboards and panels, offering a greener alternative to traditional plastics.
Best PLA Filaments of 2025
1. MatterHackers PRO Series Tough PLA
1.75mm $57/kg
MatterHackers PRO Series Tough PLA is a high-performance filament designed for users who require durability and strength in their 3D prints. Engineered to be more impact-resistant and stiffer than standard PLA, it’s an excellent choice for tooling, manufacturing aids, and functional prototypes.

Image Source: MatterHackers
2. Hatchbox Wood PLA Filament
1.75mm $30.99/kg
Hatchbox 3D Wood PLA filament is a creative material that blends PLA with wood fibers to produce prints with a real wood look and feel. This filament allows for the creation of objects with the tactile warmth and unique grain patterns of wood, combined with the ease of printing associated with PLA.

Image Source: Hatchbox
3. Prusament PLA Prusa Galaxy Black
1.75mm $29.99/kg
Prusament PLA Prusa Galaxy Black is a premium 3D printing filament produced by Prusa Research. This filament, known for its glittery black finish, provides a unique aesthetic that adds a touch of elegance to any print.

Image Source: Prusament
4. Amolen Color-Change and Glow-In-The-Dark PLA
1.75mm $32.99/kg
These specialty filaments offer unique properties, such as color-changing with temperature and radiant glow, adding a creative touch to prints.
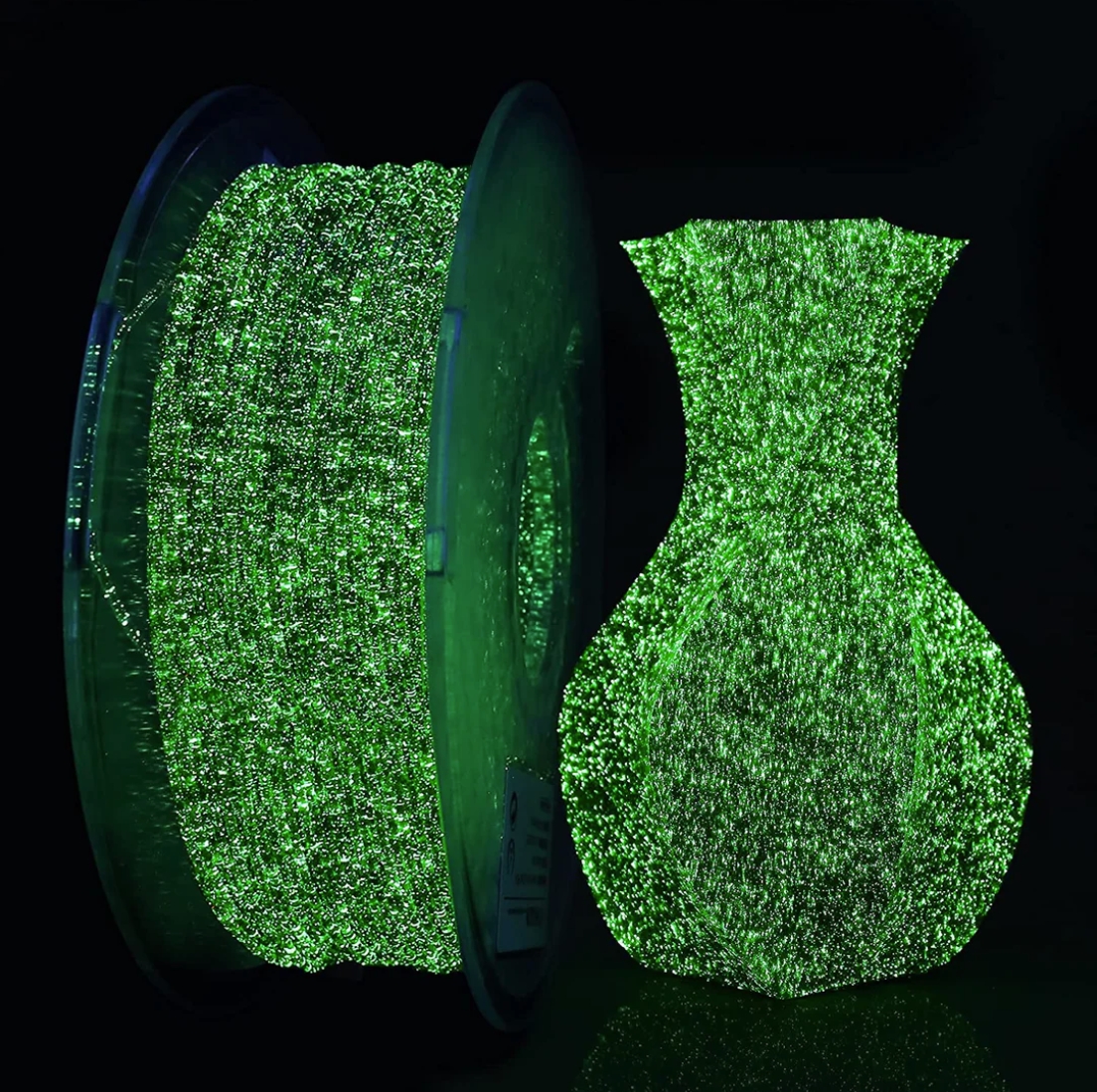
Image Source: Amolen
5. Sunlu Recycled PLA
1.75mm $99.99 for 10KG Wholesale
For those looking to make a more environmentally conscious choice, recycled PLA filament provides a sustainable option without compromising on print quality.
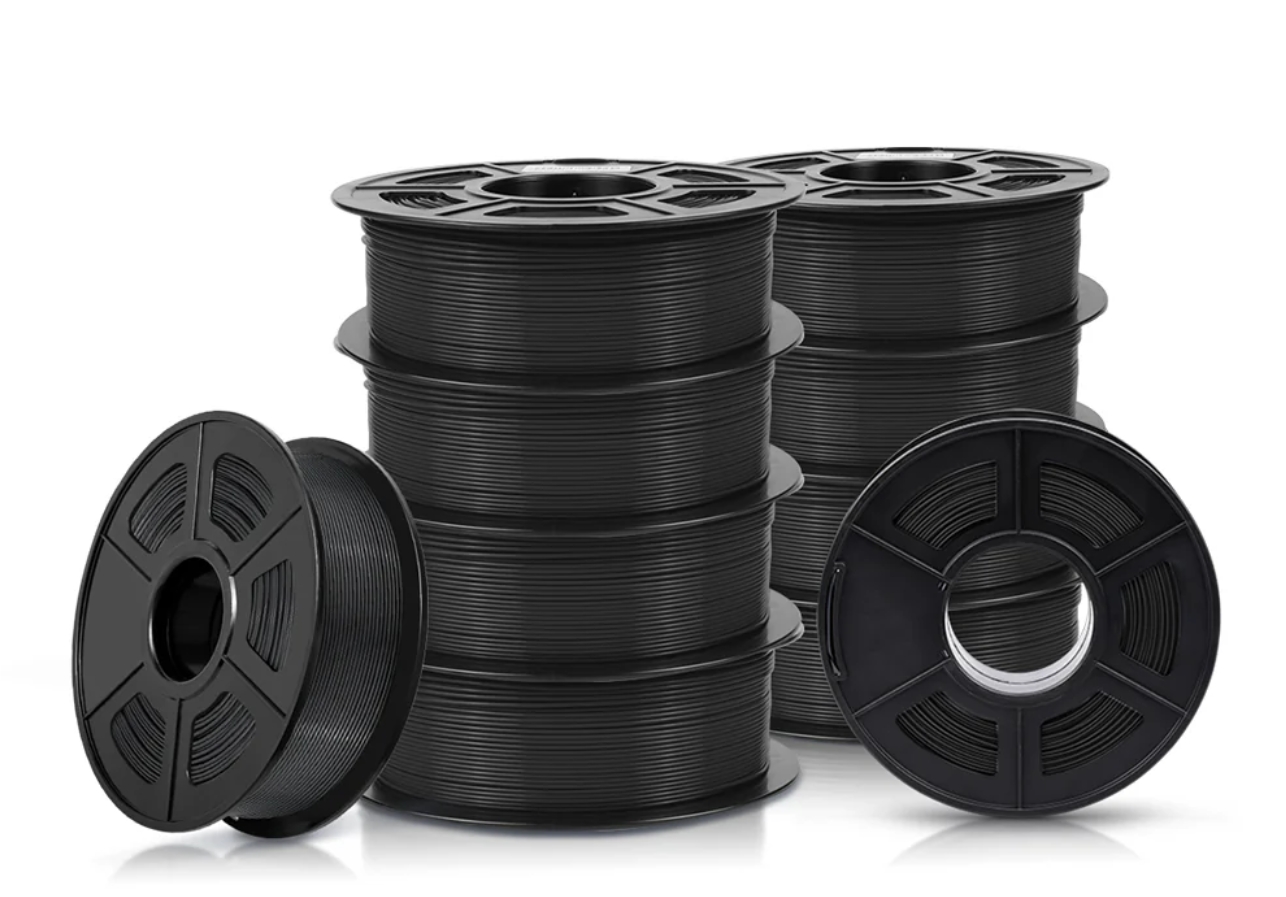

Image Source: Sunlu
6. Bambu Lab PLA Silk Dual Color
1.75mm $29.99/kg
The Bambu Lab PLA Silk Dual Color filament is a unique 3D printing material that combines two vibrant silk colors into a single filament strand. This innovative design allows for dynamic color transformations and a controllable high-gloss finish, adding a new level of aesthetic appeal to 3D-printed objects.
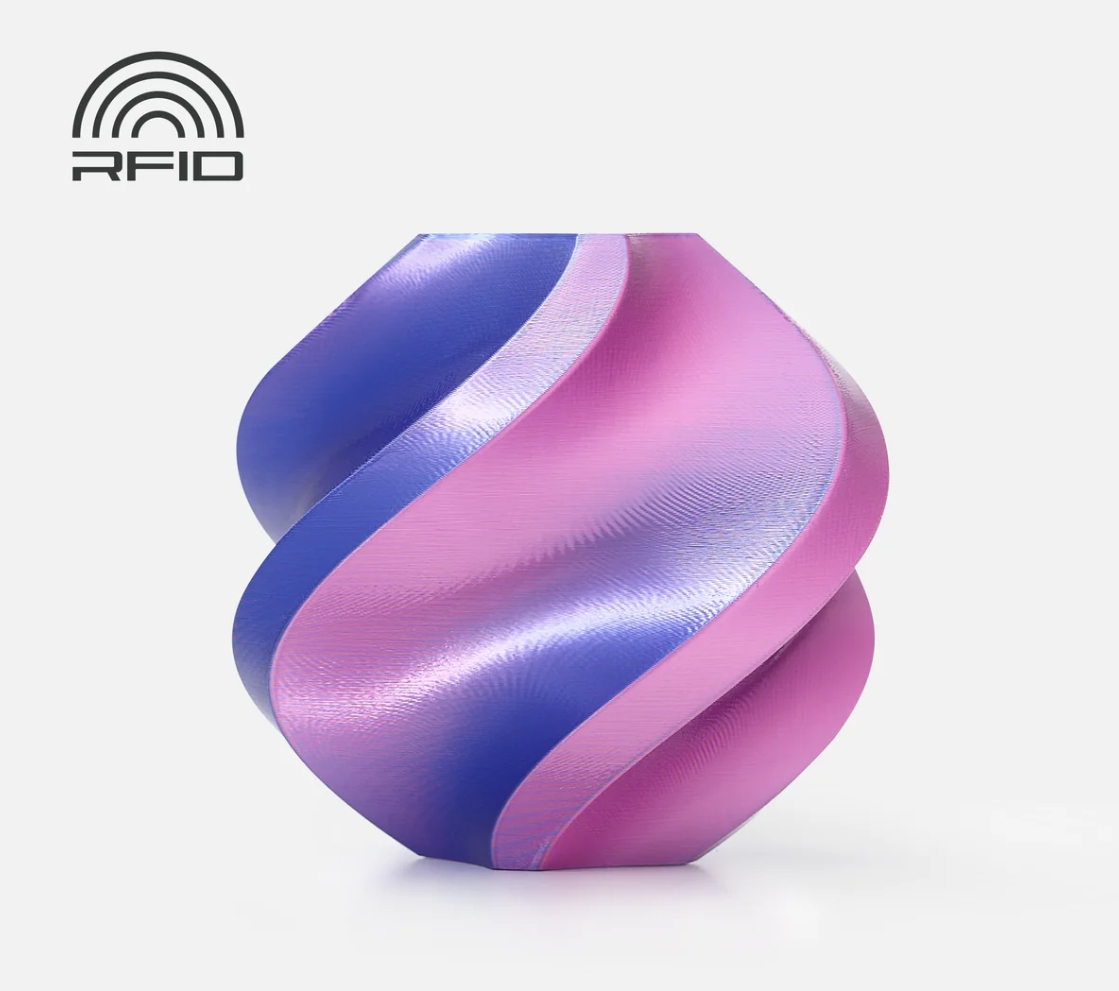

Image Source: Bambu Lab
7. Bambu Lab PLA Metal
1.75mm $29.99/kg
The Bambu Lab PLA Metal filament is a distinctive 3D printing material that offers the aesthetic of metal without the need for actual metal particles. This filament is designed to provide a metallic surface texture and shine, enhancing the visual quality of prints with a sophisticated finish. It boasts relatively high impact strength and maintains the comprehensive performance of regular PLA, making it a versatile choice for those seeking a professional look in their 3D-printed creations.
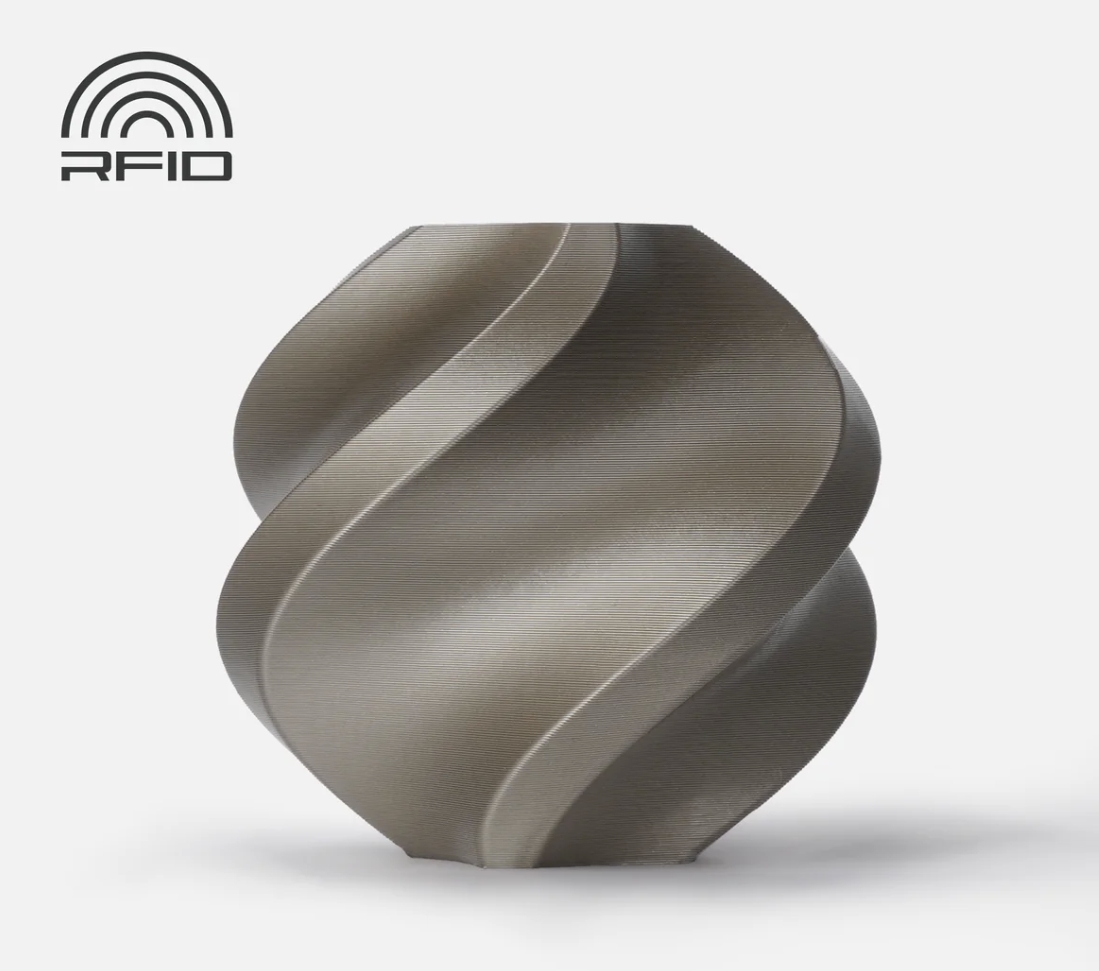

Image Source: Bambu Lab
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!
Check out Our Special Offers
Featuring Process
- Coming Soon
Featuring Materials
- Coming Soon