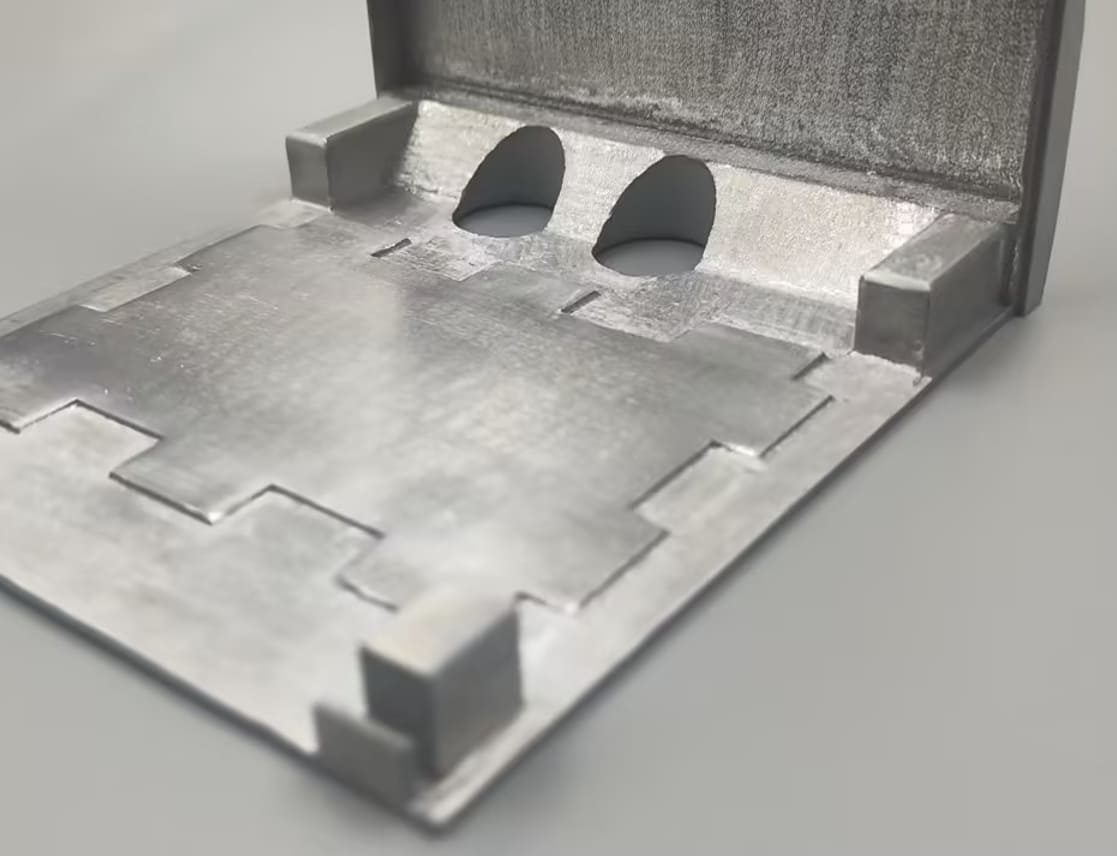
In the world of 3D printing, post-processing techniques like electrocoating can improve the functionality, durability, and aesthetics of printed parts. This guide helps you learn more about electrocoating, its applications, and how it compares to electroplating, powder coating, and anodizing.
What is electrocoating and how does it work?
Electrocoating (or e-coating) is an automated painting process that uses electrical currents to deposit a uniform, protective layer of paint or resin onto conductive materials. It’s widely used in automotive manufacturing but has gained traction in 3D printing for finishing metal or conductive polymer parts.
How Electrocoating Works:
1. Immersion: The printed parts are submerged in a bath of a water-based coating solution containing charged resin particles.
2. Electrodeposition: An electric current is applied, causing the resin particles to migrate and adhere to the part’s surface (cathodic or anodic, depending on the resin type).
3. Rinsing: Rinse off excess paint, leaving a thin, even coat of paint.
4. Curing: Baking the coated parts to harden the resin, creating a durable, corrosion-resistant surface.
Key Benefits:
• Uniform coverage, even on complex geometries.
• Environmentally friendly.
• Excellent adhesion and resistance to chipping, chemicals, and UV degradation.

Electrocoated Applications in 3D Printing
Electrocoating is ideal for enhancing both functional and decorative 3D printed parts:
1. Automotive components: Brackets, housings, and prototypes benefit from e-coating’s corrosion resistance.
2. Medical devices: Biocompatible coatings for surgical tools or prosthetics.
3. Consumer products: Durable finishes for electronics casings, eyewear frames, or outdoor gear.
4. Aerospace parts: Lightweight yet protective coatings for metal 3D-printed components.
5. Material compatibility: Works best with conductive substrates like metals (aluminum, steel) or plastics coated with conductive primers.
3DSPRO 3D Plus™ Electrocoating Service
3DSPRO’s 3D Plus™ Electrocoating service offers a specialized finishing solution tailored for 3D printed metal parts—including those made from aluminum and stainless steel alloys.
The electrocoating process guarantees even coverage, making it ideal for intricate 3D printed parts where traditional painting might miss hard-to-reach areas. Our electrocoating service provides an excellent solution for achieving a sleek, professional finish on your 3D printed components. For more detailed post-processing information or to get started with your project, check out our 3D Plus™ Solutions!
Electrocoating vs. Electroplating
Electroplating involves depositing a thin layer of metal onto the surface of a 3D printed part through an electrochemical process. Electroplating enhances the surface finish of the as-printed parts, improving durability, conductivity, corrosion protection and aesthetics. It can coat complex geometries uniformly and is compatible with a wide range of base materials, with the potential to use different plated metals such as gold, silver, nickel, copper and brass.

|
Factor |
Electrocoating |
Electroplating |
|
Purpose |
Applies protective paint/resin. |
Deposits a metal layer. |
|
Thickness |
Thin, even coatings. |
Thicker metal layers. |
|
Surface |
Medium gloss/matte finish. |
Shiny mirror finish. |
|
Materials |
Works on conductive surfaces. |
Requires conductive substrates. |
|
Applications |
Corrosion resistance, aesthetics. |
Conductivity, wear resistance, decorative. |
|
Best for |
Electrocoating suits 3D prints needing paint protection. |
Electroplating is better for metalizing surfaces. |
Electrocoating vs. Powder Coating
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the surface of as-printed parts to create a durable, high-quality finish. Powder coating uses an electrostatic method to adhere the powder to the part, which is then cured under heat or ultraviolet light to form a smooth, uniform coating. It provides a thicker, more resilient surface than traditional liquid paints and comes in a wide variety of colors and textures. Powder coating offers excellent durability and resistance to chipping, scratching and fading, and it releases very few volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it an environmentally friendly choice.

|
Factor |
Electrocoating |
Powder Coating |
|
Process |
Immersion + electrical deposition. |
Dry powder sprayed + heat-cured. |
|
Coverage |
Better for intricate geometries. |
May struggle with complex shapes. |
|
Thickness |
Thin, even coating. |
Thicker, even coating. |
|
Surface |
Medium gloss/matte finish. |
Matte finish. |
|
Durability |
Superior edge coverage and corrosion resistance. |
Thicker, more impact-resistant. |
|
Environmental |
Low waste, water-based. |
Minimal VOCs but higher energy use. |
|
Best for |
Electrocoating for complex parts |
Powder coating for thicker, rugged finishes. |
Electrocoating vs. Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances the surface properties of metal parts, particularly aluminum. Anodized aluminum has improved wear resistance and electrical insulation and can add vibrant colors through dyes. Types of anodizing include standard anodizing, which offers a colorful and protective layer, and hard anodizing(also known as Type III anodizing), which produces a thicker, more robust oxide layer.

|
Factor |
Electrocoating |
Anodizing |
|
Process |
Applies external paint/resin layer. |
Enhances natural oxide layer on metals. |
|
Surface |
Medium gloss/matte finish. |
Metallic matte finish. |
|
Materials |
Works on metals/conductive plastics. |
Metals only (aluminum, titanium). |
|
Aesthetics |
Wide color options. |
Limited colors (metallic hues). |
|
Protection |
Shields against corrosion, UV, chemicals. |
Hard, wear-resistant surface. |
|
Best for |
Electrocoating for color versatility. |
Anodizing for hardening metal surfaces. |
Electrocoating is a versatile, efficient post-processing method for 3D printed parts, offering excellent uniformity and protection. Compared with electroplating, powder coating or anodizing, electrocoating is best for for complex geometries, environmental sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. We can help you optimize your 3D printing project with 3D Plus™ Electrocoating service to achieve professional-grade durability and appeal!
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!