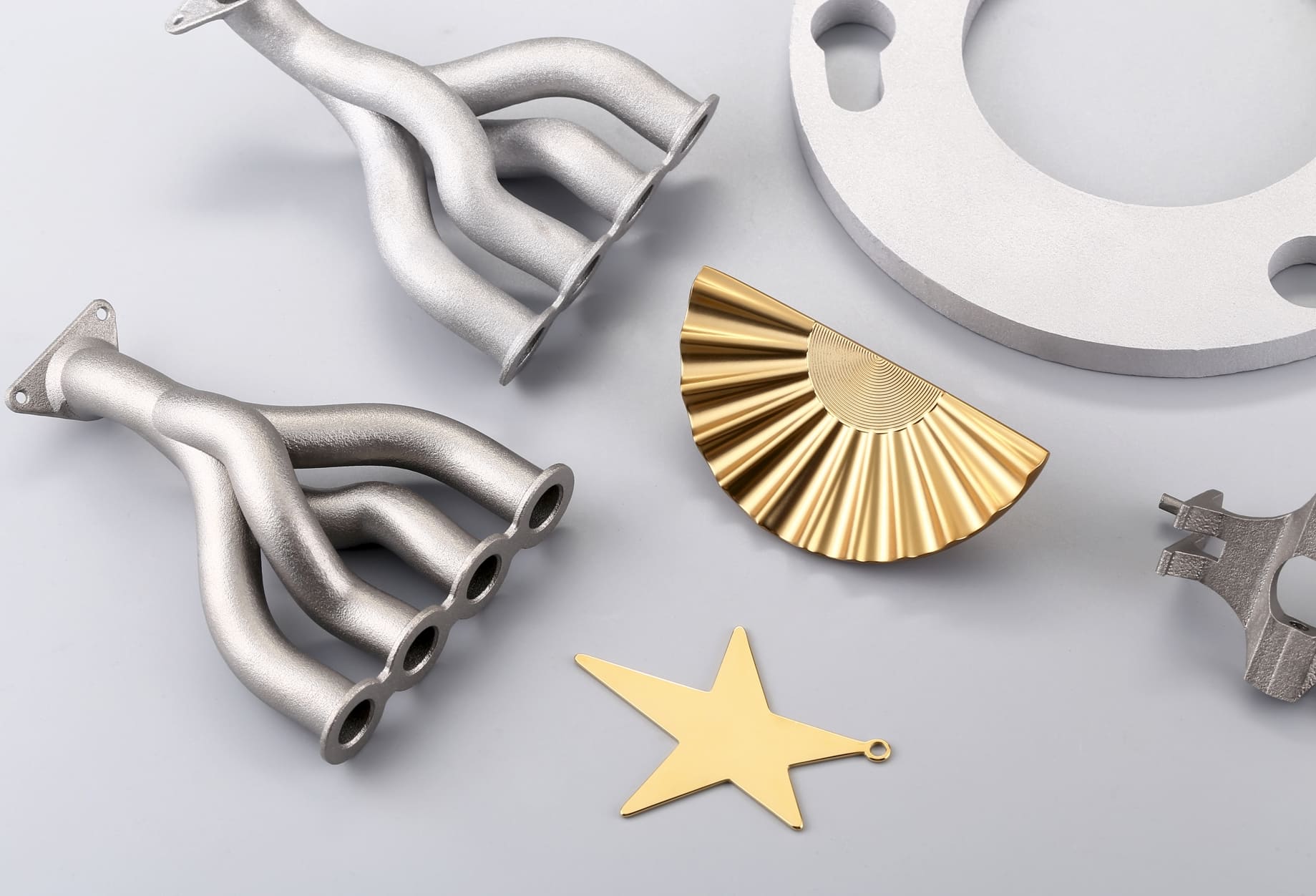
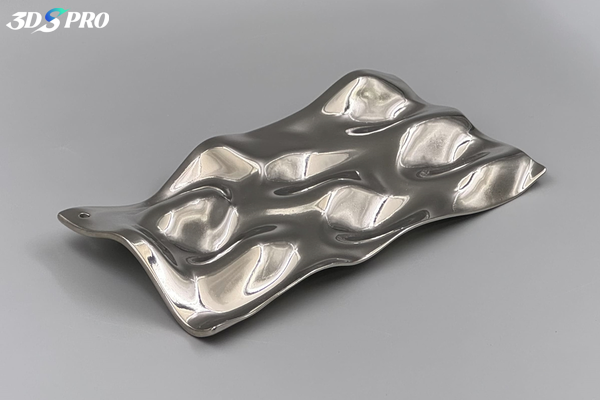
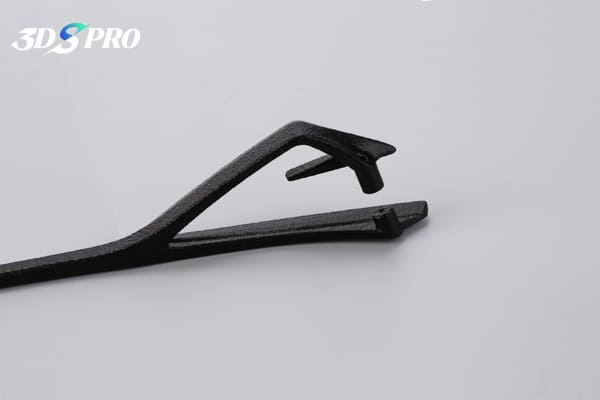
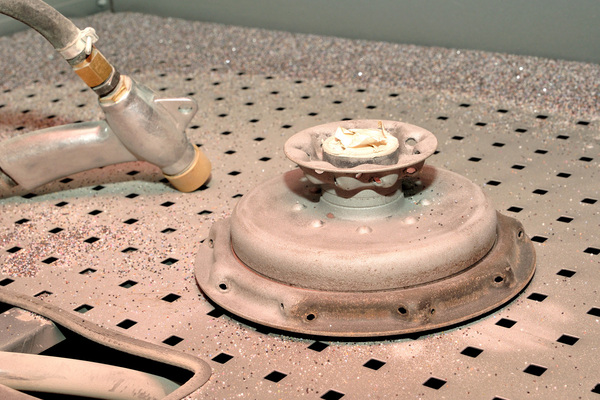
What Is Media Blasting?
Media blasting is a surface treatment that propels abrasive blasting media at high velocity against a workpiece. It uses compressed air or a centrifugal wheel to accelerate particles—such as glass beads, aluminum oxide, or ceramic beads—toward the part. Upon impact, the media strips away residues, smooths rough edges, and refines the surface texture. This process delivers uniform surface finishes on a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites.
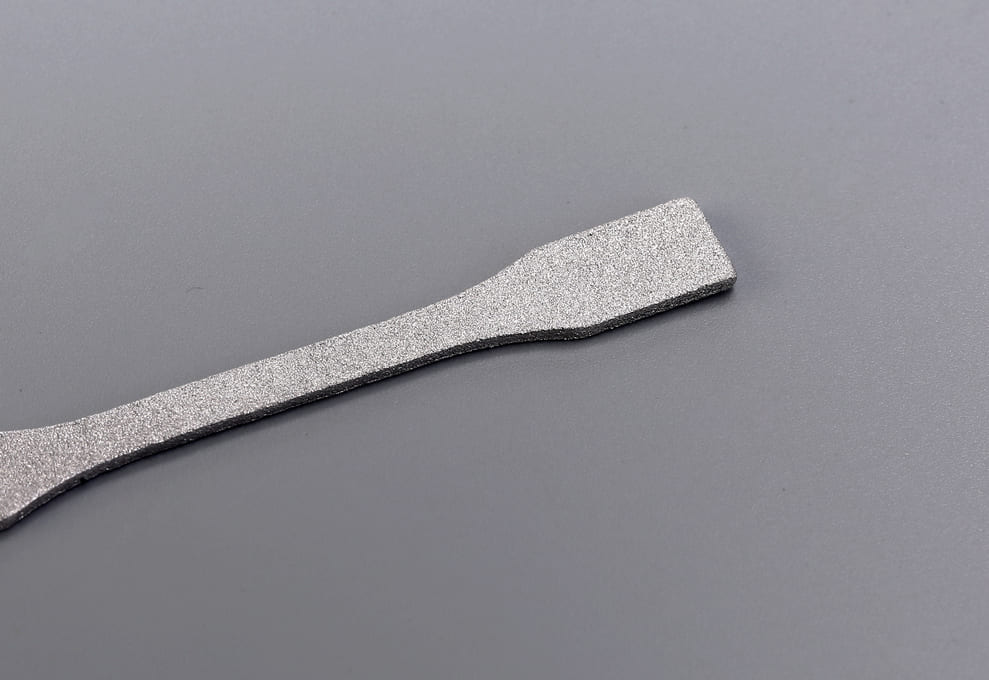

Photo Copyright © 3DSPRO. All rights reserved.
Types of Abrasive Blasting Media
Abrasive blasting media are the heart of media blasting—they determine how aggressively a surface is cleaned, refined, or textured. The media type must match both the print material and the desired finish.
|
Media Type |
Characteristics |
Typical Use Cases |
|
Round, gentle, reusable; moderate hardness |
Matte finish, light deburring for plastics/resins |
|
|
Aluminum Oxide |
Sharp, angular, high hardness; aggressive action |
Heavy duty cleaning, roughening surfaces |
|
Ceramic Beads |
Dense, durable, less dusty; consistent finish |
Surface smoothing of metal and engineering-grade plastics |
|
Plastic Media |
Soft, lightweight, minimal abrasion |
Paint removal, delicate feature preservation |
|
Walnut Shells |
Organic, biodegradable; low hardness |
Cleaning soft plastics or fragile parts |
Impact on Surface Finish and Durability
The shape and size of blasting media particles directly affect the Ra (roughness average) of the finished part:
Fine media (<100 µm) = smoother surface, ideal for cosmetic parts
Coarse media (>200 µm) = more aggressive material removal, better for mechanical bonding
Angular shapes increase abrasion, while spherical media promote a peened, semi-gloss finish
Media Blasting vs. Chemical Smoothing
Media blasting and chemical smoothing both refine 3D printed parts, but they rely on fundamentally different mechanisms.
Process Overview
Media Blasting
Uses compressed air or a centrifugal wheel to propel abrasive blasting media (glass beads, aluminum oxide, etc.) at the part.
Mechanical action removes powder residue, burnishes surface peaks, and creates a uniform matte or satin finish.
Chemical Smoothing
Exposes the part to solvent vapors (commonly acetone for ABS/ASA) or liquid baths.
Solvent melts and reflows the outer layer, filling in layer lines for a glossy, polished look.
Surface Finish & Detail Preservation
|
Attribute |
Media Blasting |
Chemical Smoothing |
|
Finish |
Matte to low-sheen satin |
High gloss |
|
Detail retention |
High—sharp edges and fine features remain intact |
Moderate—very fine details can soften or round off |
|
Layer line removal |
Reduces layer lines by peening peaks |
Eliminates layer lines completely |
|
Texture control |
Adjustable via media type/pressure |
Dependent on solvent concentration and exposure |
Material Compatibility & Applications
Media Blasting
Compatible with most plastics and metals.
Ideal for functional or engineering parts that need consistent surface texture without dimensional distortion.
Common in powder-based prints (SLS, MJF) to clear unbound powder and prep for coating.
Chemical Smoothing
Best suited for solvent-resistant polymers.
Favored for visual prototypes and consumer products where a glossy appearance outweighs tight tolerances.
Not recommended for brittle resins or metal prints.
Benefits of Media Blasting for 3D Printed Parts
Media blasting for 3D printed parts transforms raw prints into production-ready components by delivering consistent, high-quality surface finishes:
1. Consistent surface texture. Blasting media impact every exposed surface uniformly, producing predictable matte or satin finishes across complex geometries.
2. Enhanced feature clarity. By peening peaks and valleys, media blasting preserves sharp edges and fine details better than tumbling or sanding.
3. Improved adhesion and bonding. The slight roughening effect increases surface energy, helping paints, primers, and adhesives adhere more effectively.
4. Efficient removal of supports and artifacts. High-velocity particles strip away support marks, residual powder, and light burrs faster than manual methods.
5. Scalability and repeatability. Whether you’re processing a single prototype or small production batches, media blasting settings can be precisely controlled and repeated.
6. Sustainable and cost-effective. Many types of blasting media are reusable, reducing waste. There’s also no need for hazardous solvents or extensive cleanup.
Try Glass-Bead Blasting for Your Project at 3DSPRO
Glass-bead blasting is ideal for refining 3D printed metal parts, delivering smooth, uniform surfaces without altering critical dimensions. At 3DSPRO, our precision blasting process removes powder residue, light burrs, and surface imperfections. Glass-bead blasting is ideal for refining 3D printed metal parts, delivering smooth, uniform surfaces without altering critical dimensions. At 3DSPRO, our precision blasting process removes powder residue, light burrs, and surface imperfections—enhancing both the aesthetic and functional properties of stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and other metal alloys.ng both the aesthetic and functional properties of stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and other metal alloys.
Getting started is simple: upload your CAD or STL file, specify material and target finish, and receive a detailed quote in a few seconds!
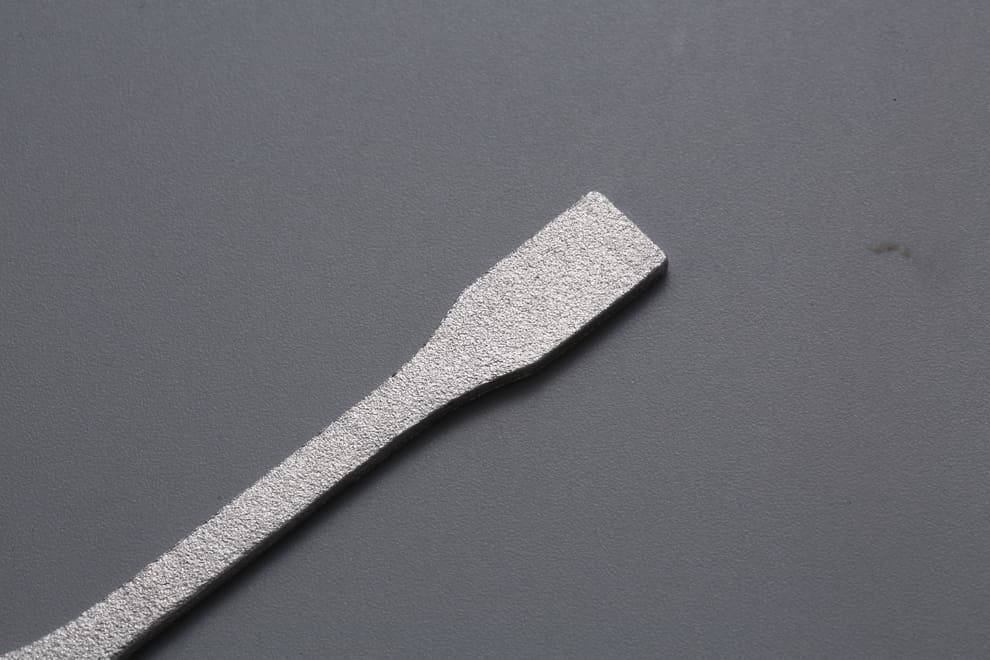

Photo Copyright © 3DSPRO. All rights reserved.
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!