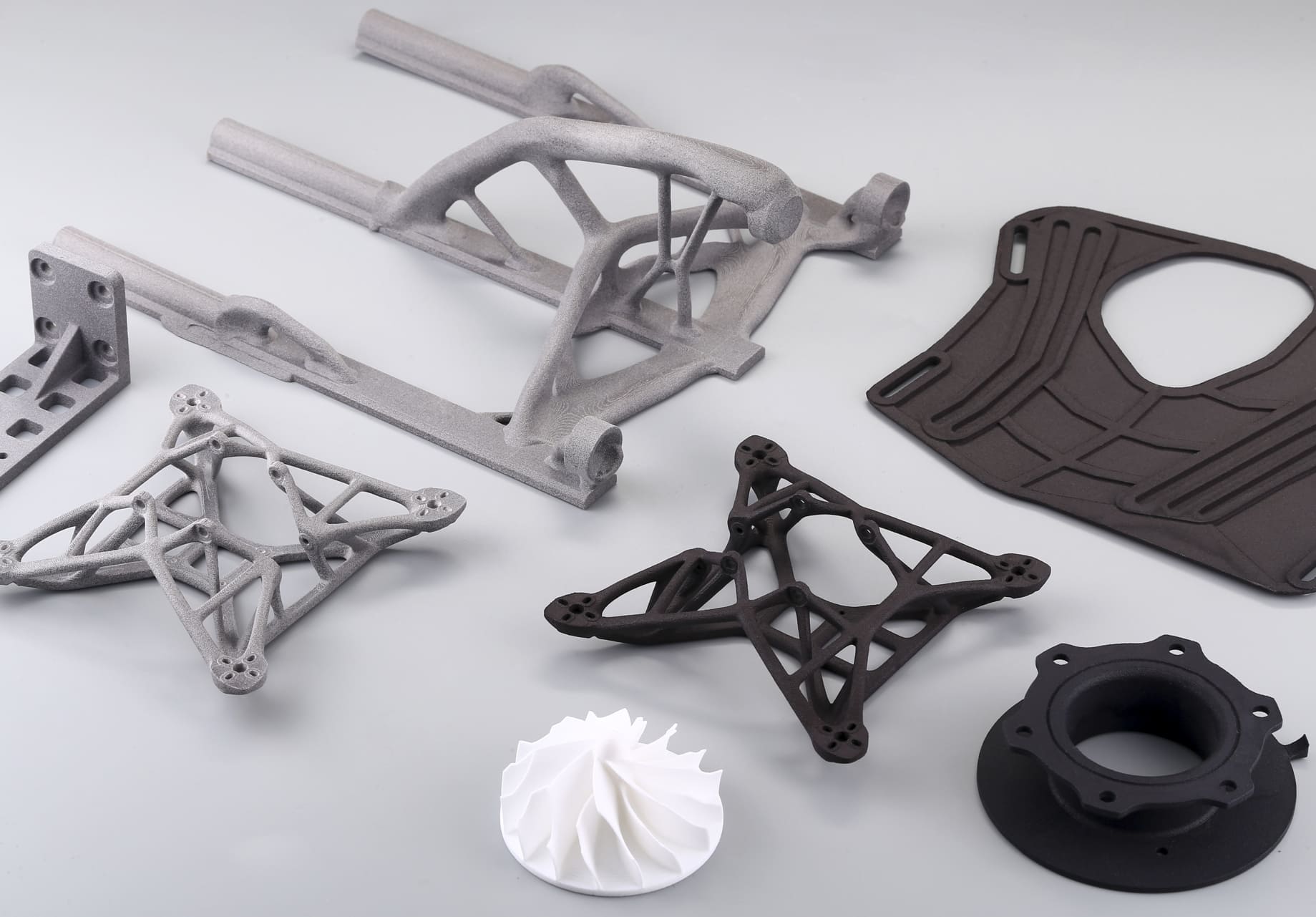
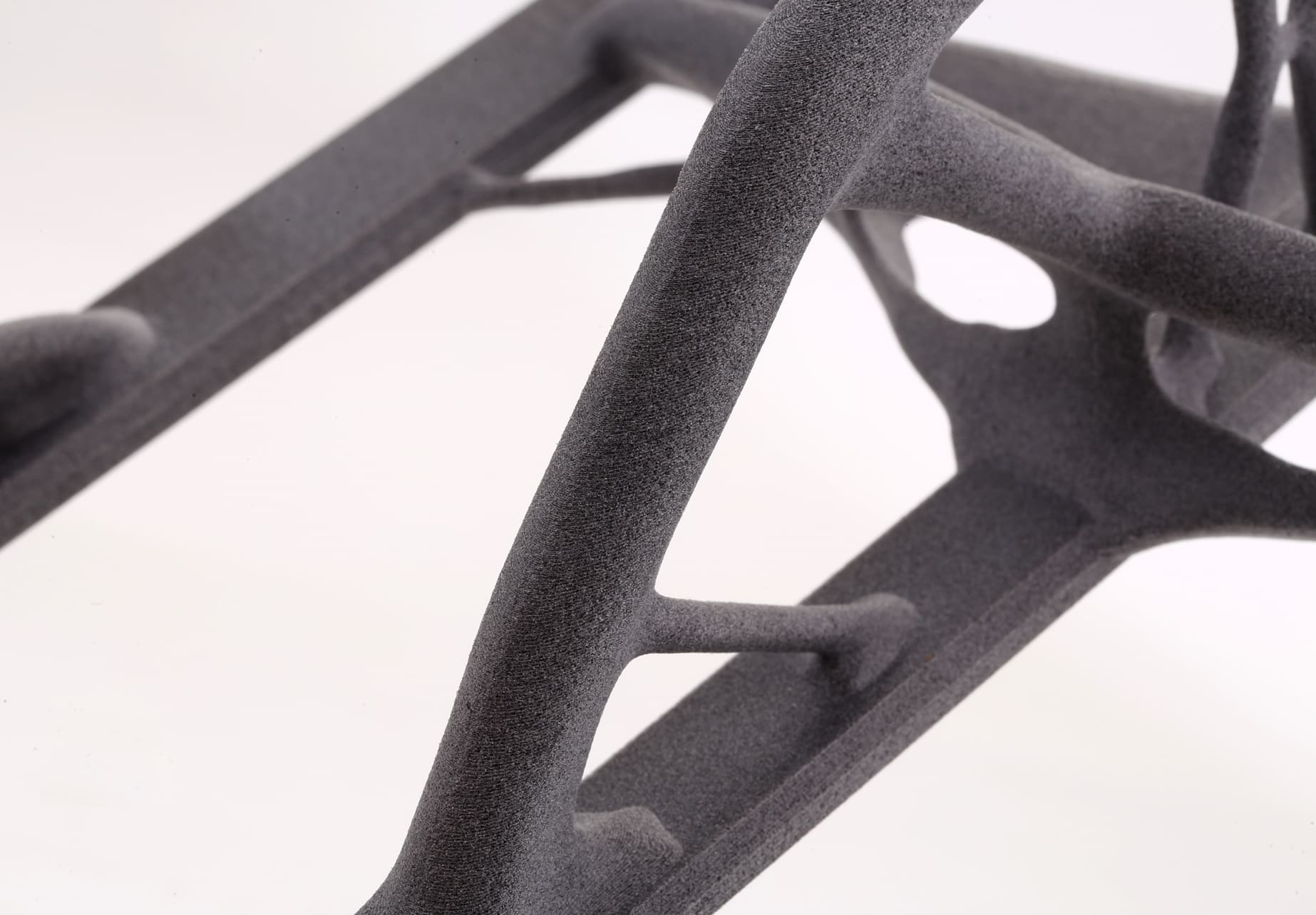
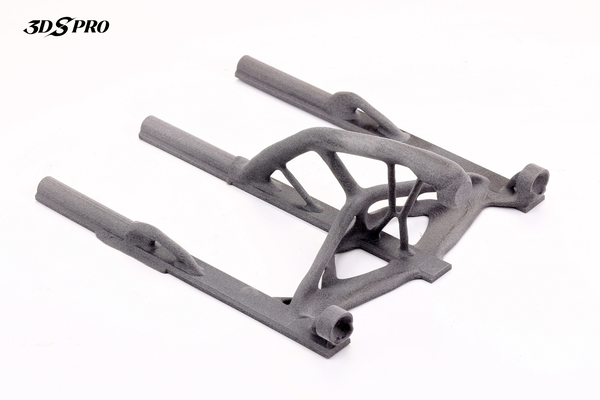
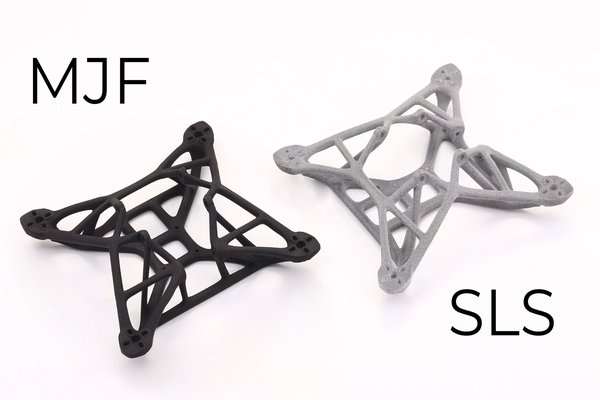
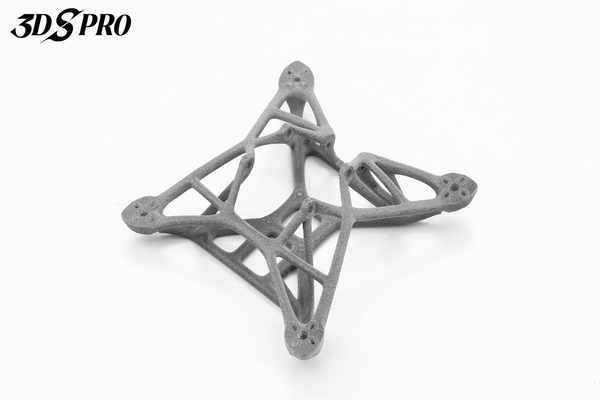
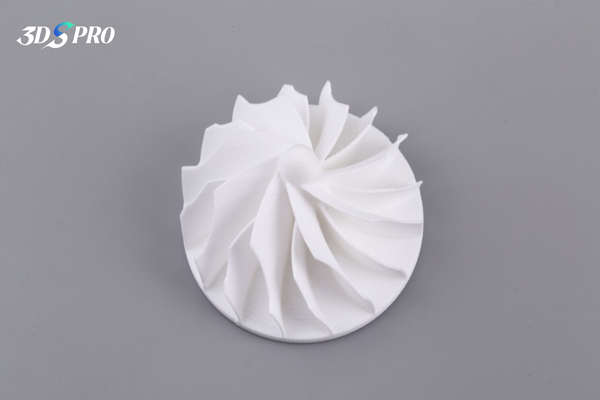
What Is Glass-Filled Nylon?
Glass-filled nylon is a composite thermoplastic that combines a nylon base polymer with short glass fibers dispersed throughout the matrix. This reinforcement boosts stiffness, dimensional stability, and thermal resistance compared to unfilled nylon, making it a go-to choice for demanding engineering parts in 3D printing. In the context of glass-filled nylon 3D printing, the glass fibers align along the print path, further enhancing mechanical performance in the load direction.
Typical characteristics of glass-filled nylon:
• Glass Fiber Content: usually ranges from 15% to 40% by weight
• Fiber Length: short strands (0.1–0.3 mm) optimized for filament extrusion
• Base Polymer: nylon 6, nylon 6/6, or PA12 grades
• Filament Form: wound spools for FFF (fused filament fabrication) or powder for SLS (selective laser sintering)
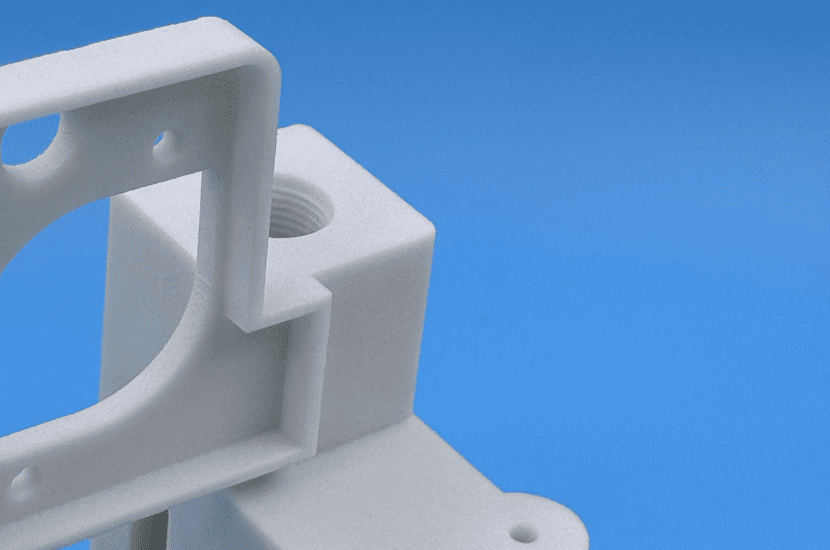
Photo Copyright © 3DSPRO. All rights reserved.
Key Properties of Glass-Filled Nylon
|
Property |
Benefit |
Typical Value / Note |
|
Mechanical Strength & Stiffness |
Resists deformation under load |
+50% tensile strength; ↑ Young’s modulus |
|
Thermal Resistance & HDT |
Performs in higher-temperature settings |
+20–30 °C heat deflection vs. unfilled nylon |
|
Wear & Abrasion Resistance |
Longer life for moving/sliding parts |
Enhanced surface hardness |
|
Dimensional Stability & Creep |
Maintains accuracy in humidity/loads |
Minimal moisture expansion and creep |
|
Density & Specific Strength |
Strong yet relatively lightweight |
1.3–1.4 g/cm³ (vs. ~1.14 g/cm³ for pure PA) |
|
Anisotropic Behavior |
Directional strength—design accordingly |
Fibers align with print path; plan orientation |
Advantages of Glass-Filled Nylon 3D Printing
Glass-filled nylon brings a suite of benefits that elevate functional prototyping and end-use parts well beyond what standard nylon delivers. Here’s why engineers and designers turn to glass-filled nylon 3D printing:
• Enhanced Mechanical Performance: Incorporating 15–40% short glass fibers boosts tensile strength by up to 50% and increases Young’s modulus substantially. Printed components resist bending and deflection under heavy loads, making them ideal for structural brackets, mounts, and fixtures.
• Superior Thermal Stability: The glass reinforcement raises the heat deflection temperature by 20–30 °C, allowing 3D printed glass-filled nylon parts to maintain stiffness in hotter environments—under the hood of vehicles or near industrial machinery—without softening or warping.
• Improved Wear and Abrasion Resistance: Fibers near the surface layer harden the exterior, reducing friction and prolonging the life of gears, bushings, and sliding joints. This makes glass-filled nylon an excellent choice for moving assemblies in robotics and automation.
• Dimensional Accuracy and Creep Resistance: Fiber-filled nylon exhibits minimal moisture uptake and creep under sustained loads. Parts retain their shape and precise tolerances over time, even when exposed to humidity or continuous stress.
• Chemical and Environmental Resistance: Glass-filled nylon is inherently resistant to oils, fuels, solvents, and many chemicals, widening its suitability for automotive, aerospace, and industrial tooling applications.
• Cost-Effective Reinforcement: Compared to metal or carbon-fiber composites, glass-filled nylon provides a balance of elevated properties at a moderate price point, lowering material costs while delivering high performance.
Limitations and Drawbacks
1. Increased nozzle abrasion. If the material is used in FDM 3D printing and as glass fibers are abrasive, it will be wearing down brass nozzles quickly. Swapping to hardened steel, ruby-tipped, or carbide nozzles is essential for longevity.
2. Brittle failure mode. Reinforcement boosts stiffness but reduces ductility. Parts tend to crack or snap under impact rather than flex, making them less forgiving in crash-sensitive designs.
3. Rougher surface finish. Exposed fibers can cause a gritty texture and fiber pull-out. Achieving smooth surfaces requires more intensive post-processing, like sanding, vapor smoothing, or coating.
4. Higher warp and delamination risk. The composite’s higher shrinkage and stiffness amplify internal stresses. You’ll often need an enclosed build chamber, reliable bed adhesion, and slow cooling to prevent warping or layer separation.
5. Moisture sensitivity and filament care. Like all nylons, glass-filled grades absorb water from the air. Wet filament leads to print defects (bubbles, poor layer bonding), so drying and sealed storage are mandatory.
6. Premium material cost. With glass fiber content and specialized formulation, these filaments can cost 20–50% more than standard nylon. Budgeting for both material and hardened tooling is critical.
7. Anisotropic strength considerations. Fiber alignment during FFF printing creates strong axes along extrusion paths but weaker perpendicular layers. Thoughtful part orientation and design adjustments are needed to capitalize on directional properties.
Applications of 3D Printed Glass-Filled Nylon
|
Application Area |
Example Components |
Key Benefits |
|
Automotive |
Under-hood brackets, air-intake manifolds, clips |
High heat resistance, chemical resistance, stiffness |
|
Industrial Tooling |
Jigs, fixtures, end-of-arm grippers |
Wear resistance, creep resistance, dimensional stability |
|
Robotics & Automation |
Robotic arms, gearbox housings, sliding bushings |
High specific strength, low friction, durability |
|
Consumer Electronics |
Drone frames, camera housings, sensor enclosures |
Tight tolerances, thermal stability |
|
Aerospace & Defense |
Cabin components, structural brackets, UAV parts |
Lightweight, temperature-swing resistance |
|
Sports & Recreation |
Handles, mounts, protective guards |
Impact resistance, extended service life |
|
Medical & Orthotics |
Custom braces, prosthetic sockets, support devices |
Precise fit, rigidity, sterilizability |
Try SLS 3D Printing Glass-Filled Nylon at 3DSPRO
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is ideal for glass-filled nylon because it fully melts the powder, eliminating fiber alignment concerns and delivering isotropic mechanical properties. At 3DSPRO, you can leverage industrial-grade SLS machines calibrated for composite powders to produce robust, dimensionally precise parts ready for end-use applications.
How 3DSPRO’s Service Works:
1. Upload your CAD file (STEP, STL, etc.) to the 3DSPRO online portal.
2. Select “Glass-Filled Nylon (PA12-GF/ PA 6-GF)” and post-processing.
3. Review automated DfAM (Design for Additive Manufacturing) feedback.
4. Approve the instant quote, submit payment, and track your build in real time.
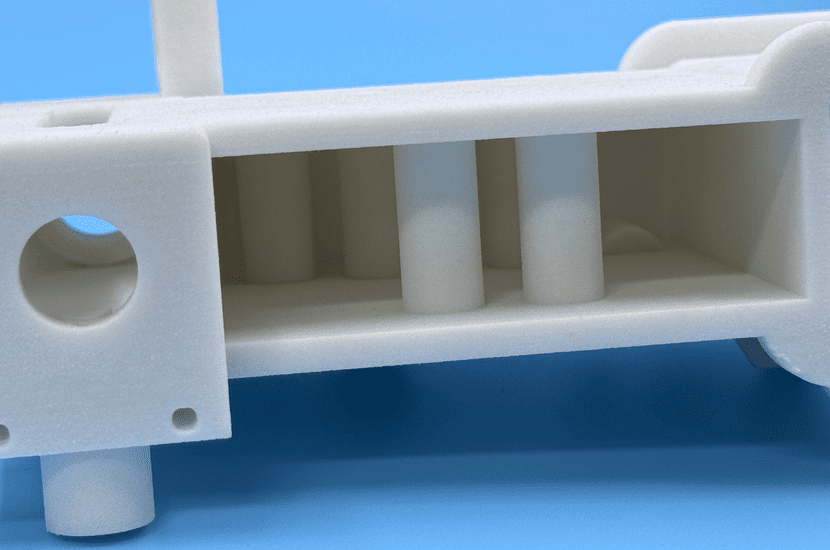
Photo Copyright © 3DSPRO. All rights reserved.
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!



























