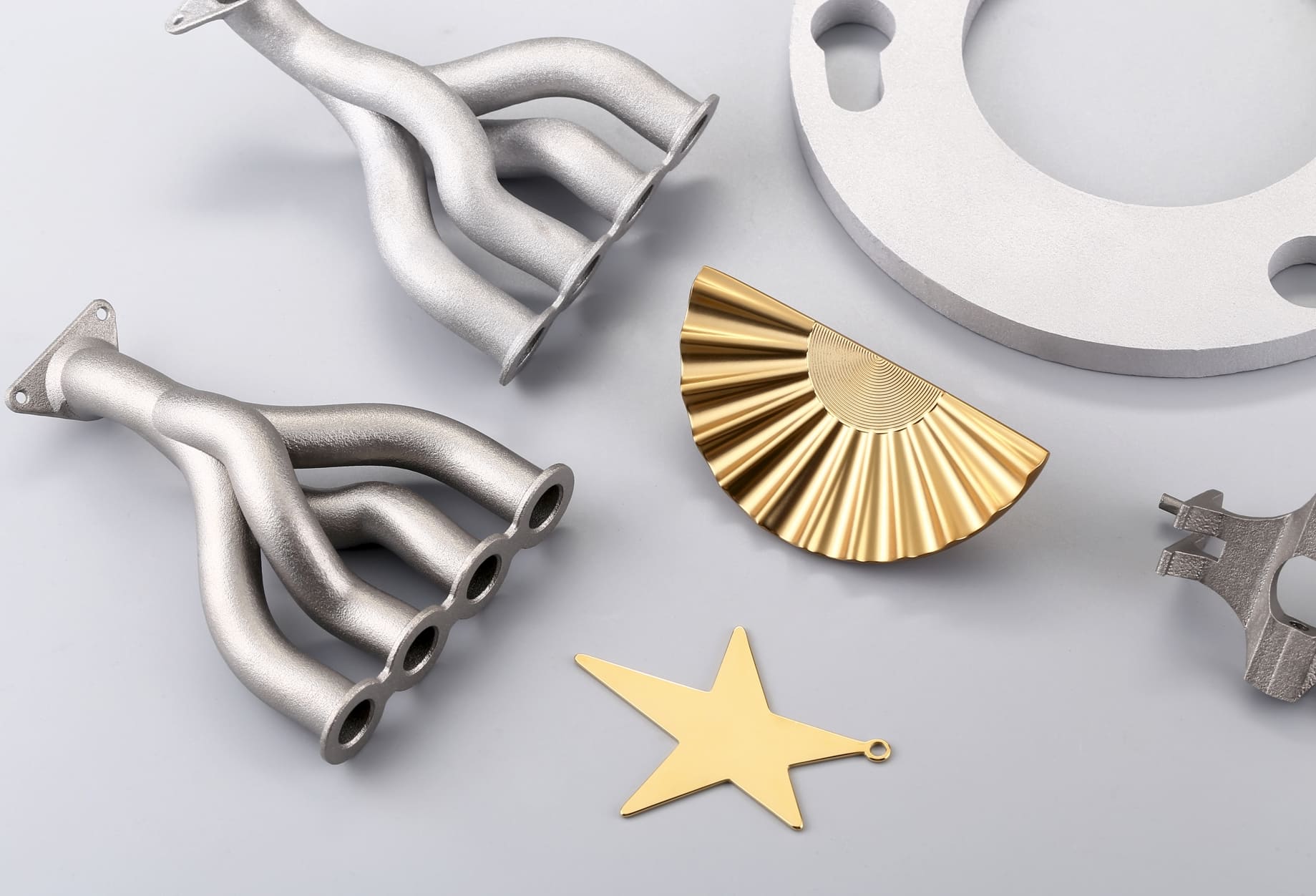
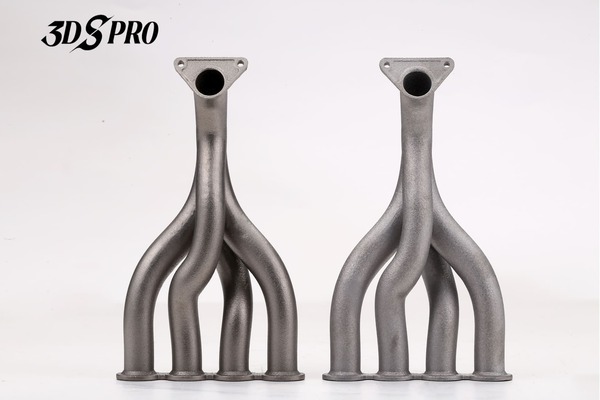
3D Printing Metals
Metal 3D printing, also known as metal additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects from a digital file by layering material, typically metal powder, and fusing it together using a heat source, usually a laser or electron beam.
A wide range of metals can be used in 3D printing, including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and various metal alloys. Each material offers different properties, such as corrosion resistance, strength, or flexibility, making them suitable for specific applications. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare have embraced this technology for its ability to produce complex parts with reduced waste and lead times.

Image Source: Sintavia
SLM 3D Printing Materials
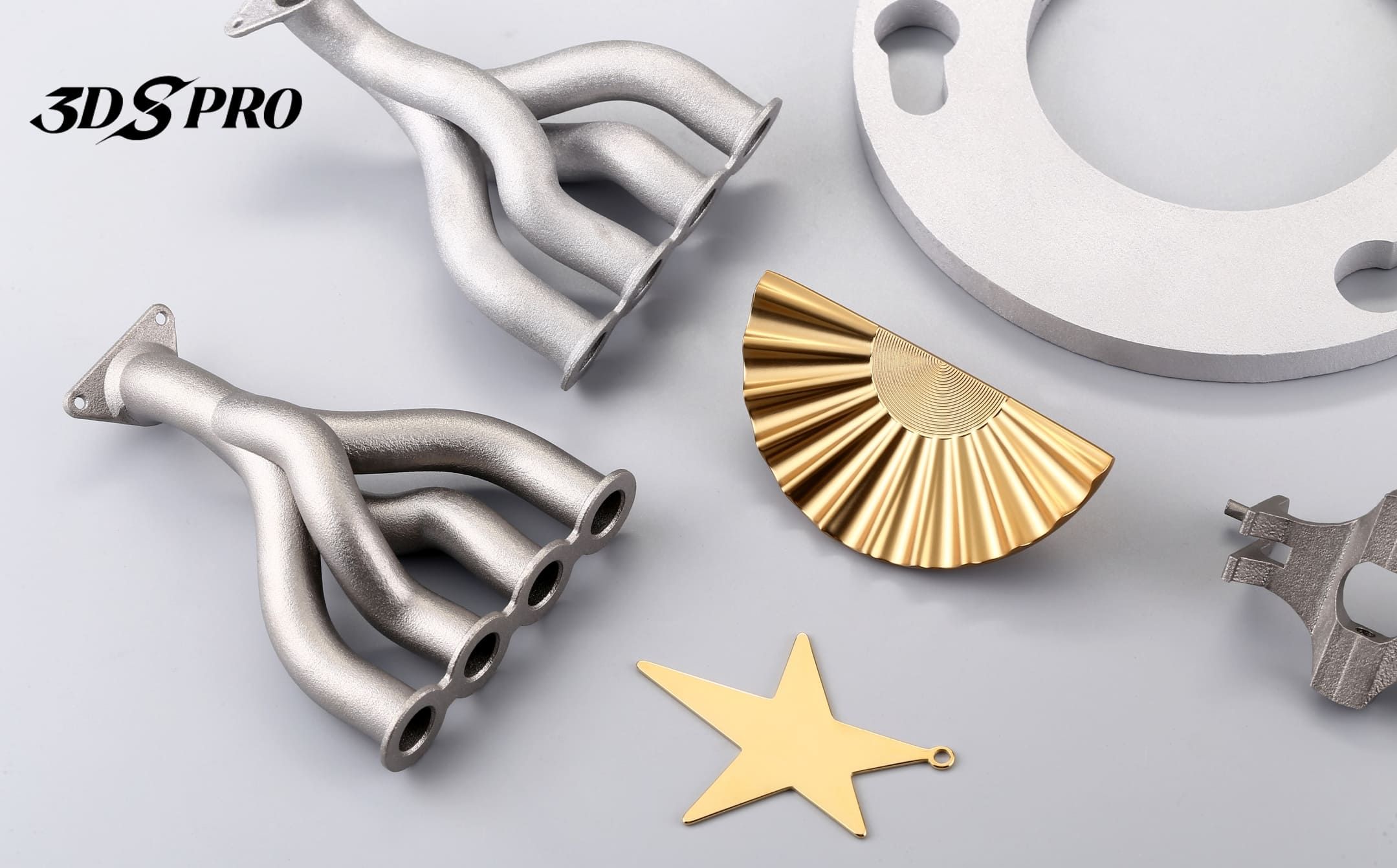
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is capable of fabricating metal parts using a wide range of metals and metal alloys. Common materials for SLM 3D printing are aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and certain superalloys, which have been used in various industries such as aerospace and medical fields. In addition, SLM processes precious metals such as gold, platinum, palladium, and silver for the jewelry industry.
1. Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are known for for their favorable properties, such as lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance. These characteristics make them highly sought after for a range of industrial applications.
Types of Aluminum Alloys for 3D Printing
● AlSi10Mg: This is a common SLM alloy known for its good weldability, high strength, and thermal properties.
● AlSi12: Preferred for its higher ductility and lower weight, making it suitable for parts that require intricate geometries.
● A356: An alloy with good strength and excellent castability, often used for automotive parts.
● A357: Similar to A356 but with enhanced strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for aerospace components.
● A6061: Include magnesium and silicon as its primary alloying elements, contributing to its moderate strength and excellent corrosion resistance.
Mechanical Properties
● High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum alloys are lightweight yet strong, which is essential for aerospace and automotive applications.
● Good Thermal Properties: These alloys dissipate heat effectively, which is beneficial for electronic housings and engine parts.
● Excellent Thermal Conductivity: Alloys such as AlSi10Mg are known for their thermal conductivity, which is important for heat dissipation applications.
● Enhanced Ductility: Alloys like AlSi12 can undergo significant deformation before failure, allowing for the creation of complex shapes.
● Tensile Strength: Aluminum alloys typically exhibit high tensile strength, which is crucial for parts subjected to stress.
● Fatigue Resistance: Aluminum alloys have good fatigue resistance, making them suitable for components that experience cyclic loading.
Applications
● Aerospace: Used for constructing lightweight and durable components such as brackets and engine parts.
● Automotive: Ideal for manufacturing parts that contribute to fuel efficiency and performance.
● Medical: In the medical field, aluminum alloys are used for prosthetic limbs and surgical instruments due to their biocompatibility.
● Consumer Electronics: They are also used in the production of durable and heat-resistant casings for electronic devices.
2. Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys are highly valued for their exceptional strength, low density, and high corrosion resistance. These properties make them ideal for demanding engineering applications.
Types of Titanium Alloys for 3D Printing
The most commonly used titanium alloy in 3D printing is Ti-6Al-4V, known for its good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability. This alpha-beta alloy is used extensively due to its versatility and reliability in various manufacturing contexts. Other titanium alloys, such as Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo and Ti-6Al-7Nb, are also used for their specific properties that cater to niche applications.
Mechanical Properties
● High Tensile Strength: They can withstand significant stress before failing, making them suitable for structural components.
● Good Fatigue Resistance: This allows for their use in applications where parts are subjected to repeated stress cycles.
● Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Titanium alloys resist corrosion even in harsh environmental conditions, extending the lifespan of the parts.
● Low Elastic Modulus: This property gives them a degree of flexibility, which is advantageous in biomedical implants.
Applications
● Aerospace: Used for manufacturing critical components like engine parts and structural elements due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
● Medical: Ideal for creating customized implants and prosthetic devices because of their biocompatibility and mechanical properties.
● Automotive: Employed in high-performance parts where reducing weight without compromising strength is essential.
● Marine: Utilized for parts that must resist saltwater corrosion and withstand high pressures.
3. Stainless Steels
Stainless steels are a group of iron-based alloys known for their corrosion resistance and are widely used in SLM 3D printing. They offer a combination of mechanical properties that make them suitable for a variety of applications.
Types of Stainless Steels for 3D Printing
● Austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 304 and 316L) are known for their good corrosion resistance and formability.
● Martensitic stainless steels (e.g., 17-4 PH) can be heat treated for high hardness and strength.
● Duplex stainless steels, which combine the qualities of austenitic and martensitic steels, offer both high strength and corrosion resistance.
Mechanical Properties
● High Strength: They can maintain structural integrity under high stress.
● Good Ductility: These alloys can deform without breaking, allowing for the creation of complex shapes.
● Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steels withstand exposure to a variety of corrosive environments.
● Wear Resistance: They are durable against wear and tear, making them ideal for parts with moving components.
Applications
● Medical Devices: Surgical tools and implants benefit from the biocompatibility and sterilization capabilities of stainless steel.
● Aerospace: Components like brackets and engine parts require the strength and corrosion resistance that stainless steels provide.
● Automotive: In the automotive industry, stainless steels are used for parts that need to endure harsh conditions while maintaining integrity.
● Consumer Goods: Everything from kitchen appliances to jewelry can be made with stainless steel, taking advantage of its aesthetic appeal and durability.
4. Tool Steels
Tool steels are a group of high-carbon steels that are well-suited for making tools and dies due to their hardness, resistance to abrasion, and ability to hold a cutting edge at elevated temperatures.
Types of Tool Steels for 3D Printing
● High-Speed Steels (HSS): Known for their ability to cut at high speeds, they retain hardness even at red heat.
● Cold Work Steels: These are used in operations performed at room temperature and are known for their wear resistance.
● Hot Work Steels: These steels can withstand high temperatures without losing hardness, making them ideal for molding and casting operations.
Mechanical Properties
● High Hardness: Ensures the material’s ability to resist deformation and wear.
● Toughness: Provides resistance to fracture and chipping during heavy-duty applications.
● Wear Resistance: Crucial for tools that come into contact with other materials, reducing the rate of degradation.
● Thermal Stability: Maintains properties at high temperatures, which is essential for cutting and molding applications.
Applications
● Manufacturing Tools: Dies, punches, and cutting tools that require high wear resistance and durability.
● Molding: Injection molds and die-casting tools that must withstand thermal cycling and corrosive materials.
● Automotive: Specialized tools for stamping and forming metal components in vehicle manufacturing.
● Aerospace: High-precision tools for fabricating components that must meet strict industry standards.
5. Case Hardening Steels
Case hardening steels are a category of carbon and alloy steels that have the unique ability to develop a hard surface layer while maintaining a ductile interior, which makes them particularly suitable for components that require a tough exterior to resist wear and a tough core to absorb impact.
Types of Case Hardening Steels for 3D Printing
● AISI 8620: A low-carbon alloy steel that contains chromium, molybdenum, and nickel. It’s known for its toughness and good torsional strength.
● AISI 1018: A mild low-carbon steel with good ductility, and excellent weldability, making it suitable for parts that require intricate shapes.
● 17NiCrMo6-4 (4320): An alloy steel that offers a good combination of strength, toughness, and wear resistance, often used for higher-stress applications.
Mechanical Properties
● Surface Hardness: Achieved through the case hardening process, which involves diffusing carbon or nitrogen into the surface layer.
● Core Toughness: The interior remains relatively soft and tough, providing good resistance to impact.
● Fatigue Resistance: The hard exterior provides excellent fatigue resistance, essential for parts subjected to cyclic loading.
● Wear Resistance: The surface layer’s hardness makes these steels ideal for components that must endure abrasive conditions.
Applications
● Gearing Systems: For gears and sprockets that require a hard surface to maintain precision under heavy loads.
● Automotive Components: In parts like camshafts and drivetrain components where wear resistance is crucial.
● Aerospace Industry: For fasteners and connectors that must withstand high stress while preventing wear.
● Tooling: In the creation of molds and dies that need a hard surface to extend their service life.
6. Nickel Superalloys
Nickel superalloys are a class of materials that exhibit exceptional mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, making them indispensable in high-performance applications. These superalloys are characterized by their superior strength, resistance to thermal creep deformation, good surface stability, and resistance to corrosion or oxidation.
Types of Nickel Superalloys for 3D Printing
● Inconel 718: Known for its high yield, tensile strength, and creep-rupture properties at temperatures up to 700°C.
● Inconel 625: Offers excellent fatigue strength and stress-corrosion cracking resistance to chloride ions.
● Hastelloy X: Distinguished by its oxidation resistance and strength at temperatures up to 1200°C.
Mechanical Properties
● High-Temperature Strength: Maintain structural integrity under extreme thermal conditions.
● Creep Resistance: Ability to resist deformation under mechanical stress at high temperatures.
● Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance: Withstand aggressive environments, which is crucial for aerospace and marine applications.
● Fatigue Life: Long service life under cyclic temperature and stress conditions.
Applications
● Aerospace: Turbine blades, exhaust systems, and other engine components that require high-temperature capability.
● Power Generation: Components in nuclear reactors and gas turbines where high-temperature strength is essential.
● Chemical Processing: Equipment that must resist corrosion from harsh chemicals.
● Oil and Gas: Drilling and wellhead hardware for high-pressure and corrosive environments.
7. Cobalt Chrome Superalloys
Cobalt Chrome (CoCr) superalloys are renowned for their exceptional strength, resistance to wear and corrosion, and biocompatibility.
Types of Cobalt Chrome Superalloys for 3D Printing
● CoCrMo: This alloy is known for its high strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for medical implants.
● CoCrW: Adding tungsten improves the alloy’s wear resistance, which is beneficial for high-wear applications like turbine blades.
Mechanical Properties
● High Yield Strength: They can withstand significant loads without permanent deformation.
● Excellent Wear Resistance: The alloys’ hardness ensures longevity in abrasive conditions.
● Superior Corrosion Resistance: CoCr superalloys resist corrosion, even in harsh chemical environments.
● Biocompatibility: CoCrMo, in particular, is compatible with biological tissues, making it suitable for medical applications.
Applications
● Medical Devices: Used extensively for dental and orthopedic implants due to their biocompatibility and mechanical properties.
● Aerospace: Components like turbine blades and exhaust systems benefit from the material’s ability to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments.
● Automotive: High-performance engine parts are made using CoCr superalloys for their durability and heat resistance.
● Industrial Tooling: The material’s wear resistance makes it suitable for cutting tools and molds that require a long service life.
8. Copper
Copper, a metal with outstanding thermal and electrical conductivity, is opening up a plethora of possibilities for applications that require efficient heat dissipation or electrical conduction.
Types of Copper for 3D Printing
SLM typically uses copper alloys rather than pure copper to enhance certain properties. A notable example is CuNi2SiCr, an alloyed copper material that combines excellent mechanical properties with high thermal and electrical conductivity. This alloy can be used in environments where pure copper would not be feasible due to its improved corrosion resistance.
Mechanical Properties
● High Thermal Conductivity: Essential for components like heat exchangers that need to manage heat effectively.
● Excellent Electrical Conductivity: Ideal for electrical applications, including wiring and electromagnetic components.
● Good Corrosion Resistance: Makes it suitable for use in various industrial environments.
● High Ductility and Tensile Strength: Allows for the creation of durable parts that can withstand mechanical stress.
Applications
● Electronics: Copper’s electrical conductivity is leveraged for components like induction coils and connectors.
● Heat Exchangers: Its thermal properties are utilized in designs that require efficient heat transfer.
● Aerospace and Automotive: Used in parts that benefit from copper’s heat and electrical properties, contributing to the overall performance of systems.
● Customized Jewelry: The aesthetic appeal and workability of copper make it a choice material for intricate jewelry designs.
9. Precious Metals
Precious metals, with their luster and rarity, have always held a special place in human culture and industry.
Types of Precious Metals for 3D Printing
● Gold (Au): Known for its excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity.
● Silver (Ag): Valued for its thermal and electrical conductivity, as well as its antibacterial properties.
● Platinum (Pt): Offers remarkable resistance to wear and tarnish, making it ideal for high-end applications.
● Palladium (Pd): Similar to platinum, it is durable and has excellent catalytic properties.
Mechanical Properties
● Ductility: They can be stretched into thin wires without breaking, allowing for intricate designs.
● Malleability: These metals can be deformed under compression, which is beneficial for creating complex shapes.
● Conductivity: Gold and silver, in particular, are highly conductive, making them perfect for electronic components.
● Corrosion Resistance: Precious metals resist corrosion, ensuring longevity in various environments.
Applications
● Jewelry: The ability to create complex, custom designs with a high level of detail is revolutionizing the jewelry industry.
● Electronics: Precious metals are used in connectors and switches, where reliable conductivity is essential.
● Dental: Gold and silver alloys are used for crowns and bridges, benefiting from their biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal.
● Aerospace: Platinum and palladium can be found in sensors and other components that require stability under extreme conditions.
SLM Materials at 3DSPRO
|
SLM Materials |
Hardness |
Tensile Strength |
Elastic Modulus |
Elongation |
|
Titanium Alloy Ti₆Al₄V |
340 HV |
980 MPa |
110 GPa |
14% |
|
Stainless Steel SS316L |
200 HV |
530 MPa |
180 GPa |
50% |
|
17-4PH Stainless Steel |
38 HRC |
1230 MPa |
170 GPa |
13% |
|
Aluminum AlSi10Mg |
100 HV |
300 MPa |
300 MPa |
2% |
|
Aluminum 6061 |
95 HB |
290 MPa |
- |
10% |

COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!