What is PLA filament?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable and bioactive thermoplastic derived from renewable resources, such as corn starch, sugarcane, tapioca roots, or other similar materials. It is a type of polyester that consists of lactic acid building blocks, which are the key to its biodegradability and environmentally friendly profile.
PLA was first discovered in 1932 by Wallace Carothers and has since evolved significantly. Initially, only low-density PLA was available, but now, high-density PLA can be produced. The high-density PLA is particularly useful in biomedical applications due to its biocompatibility and ability to be safely absorbed by the human body.
In 3D printing, PLA is known for its ease of use and affordability. PLA filament has a relatively low melting point of 150 to 160°C (302 to 320°F) and a glass transition temperature of 60-65°C, which makes it manageable and convenient for a wide range of 3D printing applications. PLA filament stands out in the 3D printing industry for its biodegradability, sustainable production, and user-friendly properties.

Image Source: ColorFabb PLA Dual Light Blue
What is ABS filament?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a robust thermoplastic polymer widely recognized for its strength, flexibility, and heat resistance. It is composed of three distinct monomers: acrylonitrile, which contributes to its chemical resistance and strength; butadiene, which adds toughness and impact resistance; and styrene, which offers a glossy finish and rigidity.
ABS was first patented in the 1940s and has since become a popular material in various industries due to its versatile properties. It is commonly found in items ranging from automotive components to consumer electronics and is the material of choice for LEGO bricks.
ABS's value in 3D printing lies in its durability and ability to withstand temperature fluctuations. With a high melting point of approximately 210 to 250°C (410 to 482°F) and a glass transition temperature of around 105°C (221°F), ABS is ideal for printing objects that will be exposed to high temperatures or require structural integrity, making it a popular choice for creating automotive parts, electronic casings, and even functional prototypes.

Image Source: Overture PLA Blue
Properties Comparison Cheat Sheet
|
Property |
PLA Filament |
ABS Filament |
|
Mechanical Strength |
Higher tensile strength but more brittle. |
Tougher with better impact resistance. |
|
Thermal Properties |
Lower melting point (150-160°C), lower glass transition temperature (60-65°C). |
Higher melting point (210-250°C), higher glass transition temperature (105°C). |
|
Printability |
Easier to print, minimal warping, no heated bed required. |
Prone to warping, requires heated bed and enclosed chamber. |
|
Durability |
Less durable, prone to degrading under prolonged sun exposure. |
More durable, better suited for long term use. |
|
Finish |
Can achieve a glossy finish with proper settings. |
Generally has a matte finish, can be sanded for smoothness. |
|
Post-Processing |
Less post-processing required, can be glued or painted. |
Often requires sanding, acetone smoothing, or painting. |
|
Environmental Impact |
Biodegradable, made from renewable resources. |
Not biodegradable, made from petroleum-based resources. |
|
Application |
Suitable for decorative items, prototypes, and non-functional parts. |
Ideal for functional parts, automotive components, and items requiring durability. |
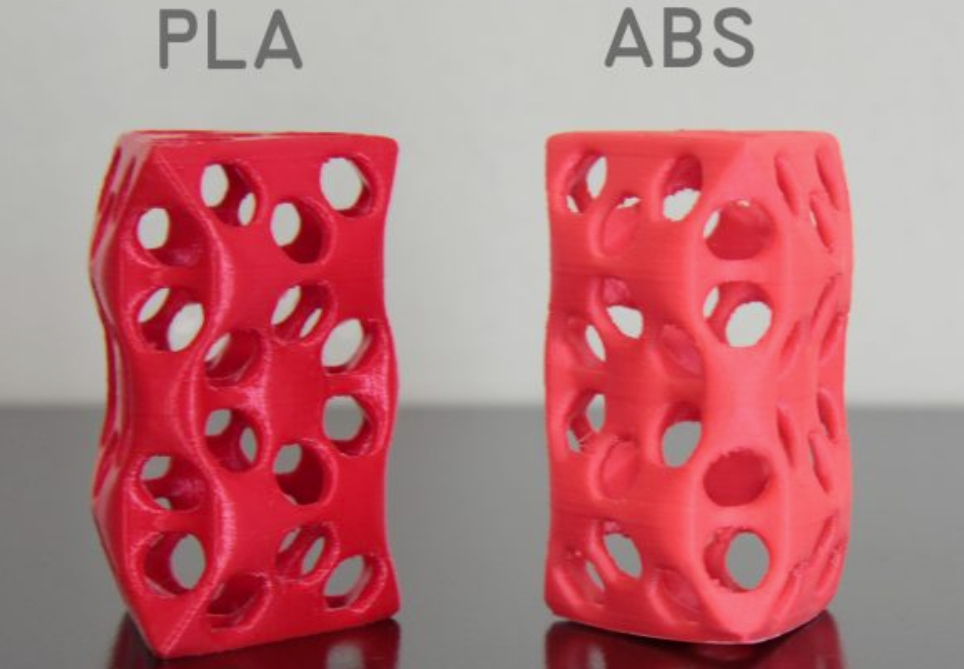
Image Source: FABTOTUM
Which one is stronger?
Tensile Strength
● PLA: Known for its high tensile strength. PLA filament can withstand a good amount of pulling force without stretching or breaking. This characteristic makes it suitable for objects that are not subject to sudden impacts or prolonged stress.
● ABS: Has good tensile strength and excels in its ability to absorb impact without cracking because of its inherent flexibility. ABS 3D prints can be bent slightly under pressure rather than snap.
Impact Resistance
● PLA: Tends to be more brittle. PLA 3D prints may crack or break under sudden impacts or when subjected to heavy loads.
● ABS: Recognized for its superior impact resistance. It can withstand shocks and stresses that would cause PLA to fail, making it the preferred choice for parts that need to endure rough handling or mechanical stress.
Which is faster and easier to print?
Printing Speed
Both PLA and ABS can be printed at similar speeds, typically ranging from 45 to 60 mm/s. However, the optimal speed may vary depending on the printer’s capabilities and the complexity of the object being printed.
Ease of Printing
● PLA: Considered easier to print with than ABS. It can be printed at lower temperatures, usually between 190-220°C, and does not require a heated bed or an enclosed print chamber, although using a heated bed set to 40-70°C can improve adhesion.
● ABS: Requires higher temperatures, around 220-250°C, and must be printed on a heated bed set to 95-110°C to reduce warping. An enclosed chamber is also crucial to maintain a consistent temperature and prevent drafts from affecting the print.
Warping and Cracking
● PLA: Experiences minimal warping, making it more forgiving when printing larger flat surfaces or sharp corners.
● ABS: Prone to warping and cracking, especially in parts with a large footprint or thin walls. It may lead to less accurate prints and may require additional measures to mitigate these issues.
Cooling and Ventilation
● PLA: Requires a cooling fan during printing to prevent deformation, especially in overhanging parts.
● ABS: It does not typically require a cooling fan, but some users may use ABS filament for very small parts to improve detail.
Oozing and Stringing
● PLA: Prone to oozing and stringing, which can affect the print’s aesthetics and may require post-processing to clean up.
● ABS: Less susceptible to these issues, resulting in cleaner prints with less need for post-print cleanup.
Which one has a smoother finish?
● PLA 3D Print's Surface Finish: PLA generally provides a smoother finish straight off the printer due to its lower melting temperature, which allows for finer detail and sharper corners. PLA 3D prints can achieve a glossy finish if printed at the right temperature and with proper cooling settings. However, PLA is more prone to stringing, which can leave fine threads between parts of the print, requiring post-processing to remove.
● ABS 3D Print's Surface Finish: ABS typically has a matte finish when printed, which can be preferable for some applications. One of the major advantages of ABS is that it can be post-processed with acetone vapor smoothing. The process melts the surface, giving the print a glossy, smooth finish that can also strengthen the part. Besides, ABS is less prone to stringing than PLA, resulting in cleaner prints with less need for post-print cleanup.
Which one is more durable?
● PLA: Can degrade over time, especially when exposed to elements like UV light, which can weaken its structure.
● ABS: Maintains its structural integrity over a longer period and under more demanding conditions, such as outdoor environments or in applications where the part is subject to varying temperatures.
Which one is more environmentally friendly?
● PLA: Renowned for its biodegradability. It is made from annually renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, which contributes to its status as a more sustainable option.
● ABS: A petroleum-based plastic, which means its production is reliant on non-renewable fossil fuels. It is not biodegradable, which can lead to longer-term environmental accumulation if not properly recycled.
Which one should I choose for my 3D printing project?
● Considerations for Choosing PLA: If you’re new to 3D printing, PLA is generally easier to work with. If you need a material that prints quickly and with less hassle, choose PLA filament, as it requires lower temperatures and doesn’t warp as much. Besides, choose PLA if you’re creating objects that won’t be exposed to high temperatures or heavy loads, such as decorative items or simple prototypes.
● Considerations for Choosing ABS: Choose ABS if you require your printed object to be tough, durable, and able to withstand higher temperatures. If you have access to a printer with a heated bed and an enclosed chamber, ABS can be a good choice for functional parts that need to be strong and impact-resistant.
PLA is best for quick and easy projects where aesthetic quality is important, while ABS is ideal for more demanding applications that require durability and strength. Your choice should align with the specific needs of your project, considering factors such as strength, flexibility, precision, and environmental impact.
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!
Check out Our Special Offers
Featuring Process
- Coming Soon
Featuring Materials
- Coming Soon

























