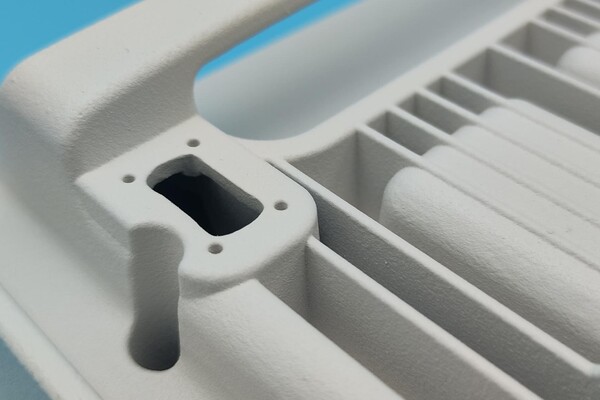
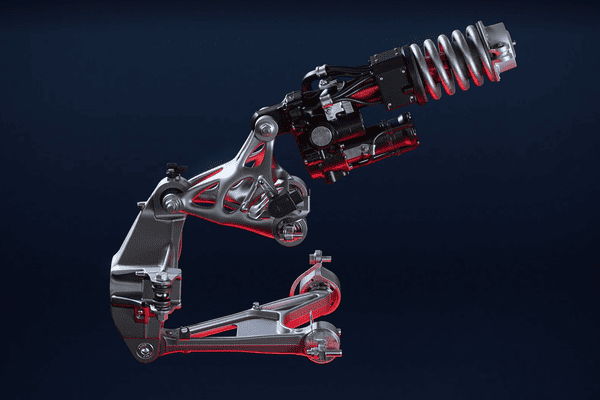
Among the many metal alloys available for 3D printing, stainless steels stand out for their balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility. One particular grade, Stainless Steel 17-4 PH, has become a key material in industries ranging from aerospace to medical devices. Known for its precipitation-hardening properties, 17-4 PH combines high mechanical strength with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for demanding environments.
In this article, we’ll explore what makes 17-4 PH unique, how it performs in Selective Laser Melting (SLM) 3D printing, its mechanical properties, applications, and pros and cons.
What is Stainless Steel 17-4 PH?
Stainless Steel 17-4 PH, also known as Type 630, is a precipitation-hardening martensitic stainless steel. Its name reflects its composition: approximately 17% chromium and 4% nickel, along with copper, niobium, and trace elements.
Key Characteristics:
• High strength and hardness: Achieved through heat treatment (precipitation hardening).
• Corrosion resistance: Comparable to other stainless steels, suitable for mildly corrosive environments.
• Heat treatability: Mechanical properties can be tuned by applying different heat treatment conditions (H900, H1025, etc.).
• Versatility: Used in aerospace, petrochemical, medical, and energy industries.
Unlike austenitic stainless steels such as 316L, 17-4 PH offers superior strength while maintaining good corrosion resistance, which makes it particularly attractive for parts that must withstand high stress and exposure to harsh conditions.
17-4 PH in SLM 3D Printing
Selective Laser Melting (SLM), also known as Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF), is one of the most common processes for printing 17-4 PH. In SLM, a high-powered laser selectively melts layers of fine stainless steel powder to build complex geometries.
Why 17-4 PH Works Well in SLM:
• Near-wrought density: Printed parts can achieve >99% density, rivaling conventionally manufactured components.
• Dimensional stability: Maintains precision even after heat treatment.
• Complex geometries: Enable designs that are impossible with subtractive manufacturing.
• Surface finish: With optimized parameters, SLM delivers smooth surfaces suitable for functional parts.
SLM of 17-4 PH requires careful control of parameters to minimize residual stresses, porosity, and distortion. Post-processing steps such as heat treatment, machining, and polishing are often necessary to achieve final specifications.
Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed 17-4 PH
• Strength and hardness: Printed 17-4 PH offers high tensile strength and hardness, especially after heat treatment, which makes it suitable for load-bearing and high-stress applications.
• Corrosion resistance: Its resistance to corrosion is comparable to wrought stainless steels, allowing use in marine, chemical, and medical environments.
• Heat treatability: One of its standout features is the ability to tailor properties through heat treatment. Different conditions (like H900 or H1025) can adjust strength, hardness, and ductility to match specific needs.
• Density and integrity: With optimized printing parameters, parts can achieve near-full density, minimizing porosity and ensuring reliability.
• Microstructure: The fine martensitic structure formed during printing contributes to its strength, while precipitation hardening enhances toughness.
• Ductility: While strong, it is less ductile than austenitic stainless steels like 316L, meaning it sacrifices some flexibility for higher strength.
SLM 3D Printed Stainless Steel 17-4 PH Properties at 3DSPRO:
|
Properties |
Test Methods |
Parameters |
|
Hardness |
ASTM E18 |
38 HRC |
|
Relative Density |
ASTM B923 |
96.4% |
|
Tensile Strength |
ASTM E8 |
1230MPa |
|
Tensile Modulus |
ASTM E8 |
170GPa |
|
Elongation at Break |
ASTM E8 |
13% |
|
Yield Strength |
ASTM E8 |
1050MPa |
|
Corrosion |
ASTM F1089 |
PASS |
Applications of 3D Printed 17-4 PH
Aerospace
• Structural brackets and housings: Lightweight yet strong, reducing aircraft weight while maintaining reliability.
• Turbine blades and engine components: Withstand high temperatures and stresses, critical for propulsion systems.
Medical
• Surgical instruments: Corrosion-resistant tools that maintain sharpness and strength after repeated sterilization.
• Dental implants and orthodontic devices: Biocompatibility and mechanical strength make 17-4 PH suitable for long-term use.
• Custom prosthetics: Additive manufacturing allows patient-specific designs, improving comfort and functionality.
Energy
• Valves, pumps, and impellers: Operate in corrosive environments such as offshore platforms and chemical plants.
• Pipeline components: High strength and corrosion resistance extend service life in harsh conditions.
• Turbomachinery parts: Reliable under high stress and temperature, essential for power generation.
Automotive
• High-performance engine parts: Strong, heat-resistant components for racing and performance vehicles.
• Brackets, fasteners, and housings: Durable parts that withstand vibration and mechanical stress.
• Rail and marine applications: Corrosion resistance makes it suitable for coastal and humid environments.
Industrial Equipment and Tooling
• Jigs and fixtures: Strong, durable tools for manufacturing environments.
• Custom tooling: Tailored designs reduce production time and improve precision.
• Wear-resistant components: Handles repetitive stress in industrial machinery.
Pros and Cons
|
Aspect |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Strength & Hardness |
High tensile strength and hardness, especially after heat treatment |
Less ductile than austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 316L) |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Comparable to wrought stainless steels, suitable for marine and chemical environments |
Not as resistant as specialized alloys like duplex stainless steels |
|
Heat Treatability |
Properties can be tailored through precipitation hardening (H900, H1025, etc.) |
Requires careful heat treatment to avoid brittleness |
|
Density & Integrity |
Near-wrought density (>99%) achievable with optimized SLM parameters |
Residual stresses and porosity possible if parameters are not well controlled |
|
Design Freedom |
Enables complex geometries and lightweight structures not possible with traditional methods |
Surface finish may require polishing or machining for critical applications |
|
Cost & Accessibility |
High-performance material available through additive manufacturing services |
More expensive than common stainless steels like 304 or 316L |
|
Reliability |
Stable mechanical properties after post-processing, suitable for critical industries |
Post-processing (heat treatment, machining) adds time and cost |
3D Printing Stainless Steel 17-4 PH at 3DSPRO
At 3DSPRO, we deliver advanced Selective Laser Melting (SLM) 3D printing services designed for high-performance applications, specializing in materials like 17-4 PH stainless steel for exceptional strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Our proprietary 3D Plus™ solution enhances precision, efficiency, and consistency across complex geometries, enabling clients to achieve production-ready parts with superior mechanical properties and surface quality. Whether for aerospace, medical, or industrial innovation, 3DSPRO combines cutting-edge technology with expert engineering to transform ideas into reliable, high-value components.
Upload 3D Files to 3D Print 17-4 PH Today >>
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!