The automotive industry adopted 3D printing as it allows manufacturers to create complex geometries, light structures, and custom-designed parts at a speed that is unimaginable. From designing dashboards to creating high-performance engine brackets, additive manufacturing is reshaping how cars are built and designed.
But, while 3D printing can provide remarkable design options, the final components typically have visible layers, rough textures or porosity, which limit their application in the most demanding automotive conditions. Therefore, surface finishing is essential. With the help of specialized methods of finishing, manufacturers are able to improve mechanical strength, increase the resistance to corrosion and attain the elegant appearance that is expected of modern automobiles. Surface finishing directly affects safety, performance and conformity with the industry's standards.
Benefits of Surface Finishing
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Finishing processes reduce micro-defects, eliminate stress concentrators, and improve load-bearing capacity. For structural automotive parts such as brackets or housings, this added strength is critical to long-term reliability.
Corrosion and Wear Resistance
Automotive environments expose parts to moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. Protective coatings like anodizing, plating, or epoxy sealing shield components from corrosion and wear, extending their lifespan.
Surface Smoothness and Precision
Techniques such as polishing, sanding, or vapor smoothing eliminate visible layer lines and rough textures, which ensures tight fits in assemblies, reduces friction in moving parts, and enhances aerodynamic performance.
Aesthetic Appeal and Branding
Finishes such as painting, dyeing, or plating deliver sleek, professional looks. Interior trims, dashboards, and branded components benefit from customizable finishes that align with a manufacturer’s design language.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Automotive parts must meet strict ISO and ASTM benchmarks for surface roughness, durability, and safety. Finishing ensures that 3D printed components achieve OEM acceptance and regulatory approval.
Functional Integration
Smooth finishes improve sealing surfaces, ergonomic comfort, and overall system performance. In high-performance vehicles, finishing can even contribute to reduced drag and improved efficiency.
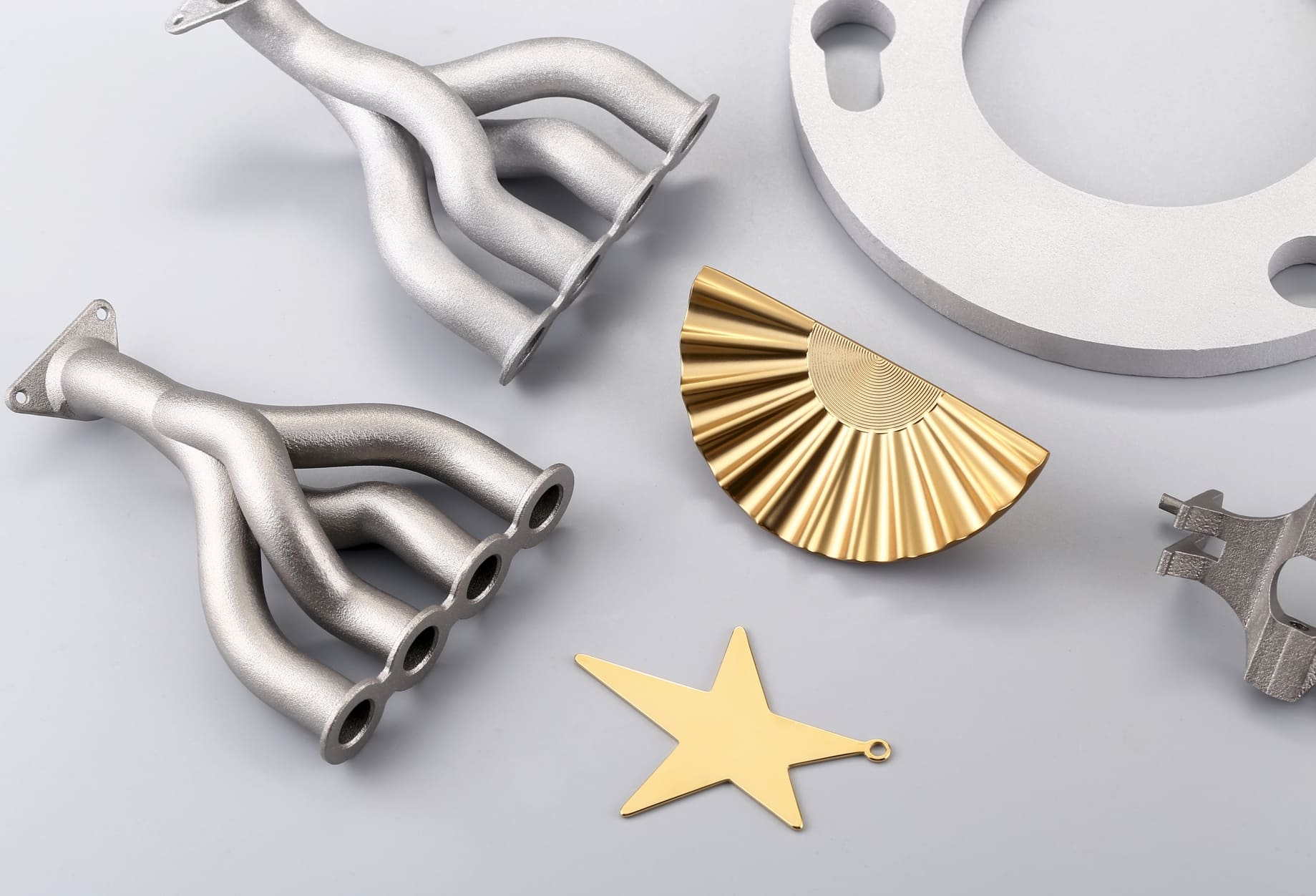
Surface Finishes for Metal Automotive Components
Common Metals in Automotive 3D Printing
• Aluminum alloys: valued for lightweight strength and corrosion resistance.
• Stainless steel: durable, versatile, and widely used in structural parts.
• Titanium: aerospace-grade strength and heat resistance, ideal for performance vehicles.
• Inconel and nickel alloys: exceptional resistance to heat and oxidation, used in exhaust systems.
Machining & CNC Milling
Precision machining improves dimensional accuracy and surface finish, ensuring parts fit reliably in assemblies. It’s often the final step for critical mating features, threads, and tight-tolerance surfaces.
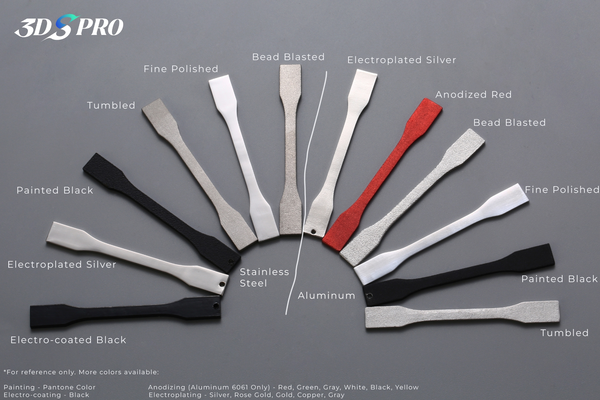
Polishing (Mechanical, Chemical, and Electropolishing)
Polishing smooths and brightens surfaces while reducing micro-cracks and burrs. Mechanical and chemical methods remove surface roughness; electropolishing is particularly effective for stainless steel as it produces a bright, clean finish and improves corrosion resistance by selectively removing contaminated surface layers.
Bead Blasting / Shot Blasting
Blasting creates a uniform matte finish, removes loose powder or scale, and lightens surface contaminants. It also produces a controlled surface profile that improves adhesion for paints and coatings and can be tuned by media size and intensity.
Heat Treatments
Heat treatment processes (annealing, quenching, tempering, etc.) change a metal’s microstructure to increase hardness, improve fatigue resistance, relieve residual stresses, and enhance thermal stability. Select the specific cycle based on alloy and mechanical requirements.
Coatings & Plating
1. Anodizing (aluminum): Adds corrosion resistance, increased surface hardness, and color options through controlled oxide growth.
2. Electroplating (nickel, chrome): Provides wear resistance, improved appearance, and enhanced surface durability for both functional and decorative uses.
3. Ceramic coatings: Offer high-temperature protection and reduced wear (common for exhaust and thermal-barrier applications).

Image Copyright © 3DSPRO Limited. All rights reserved.
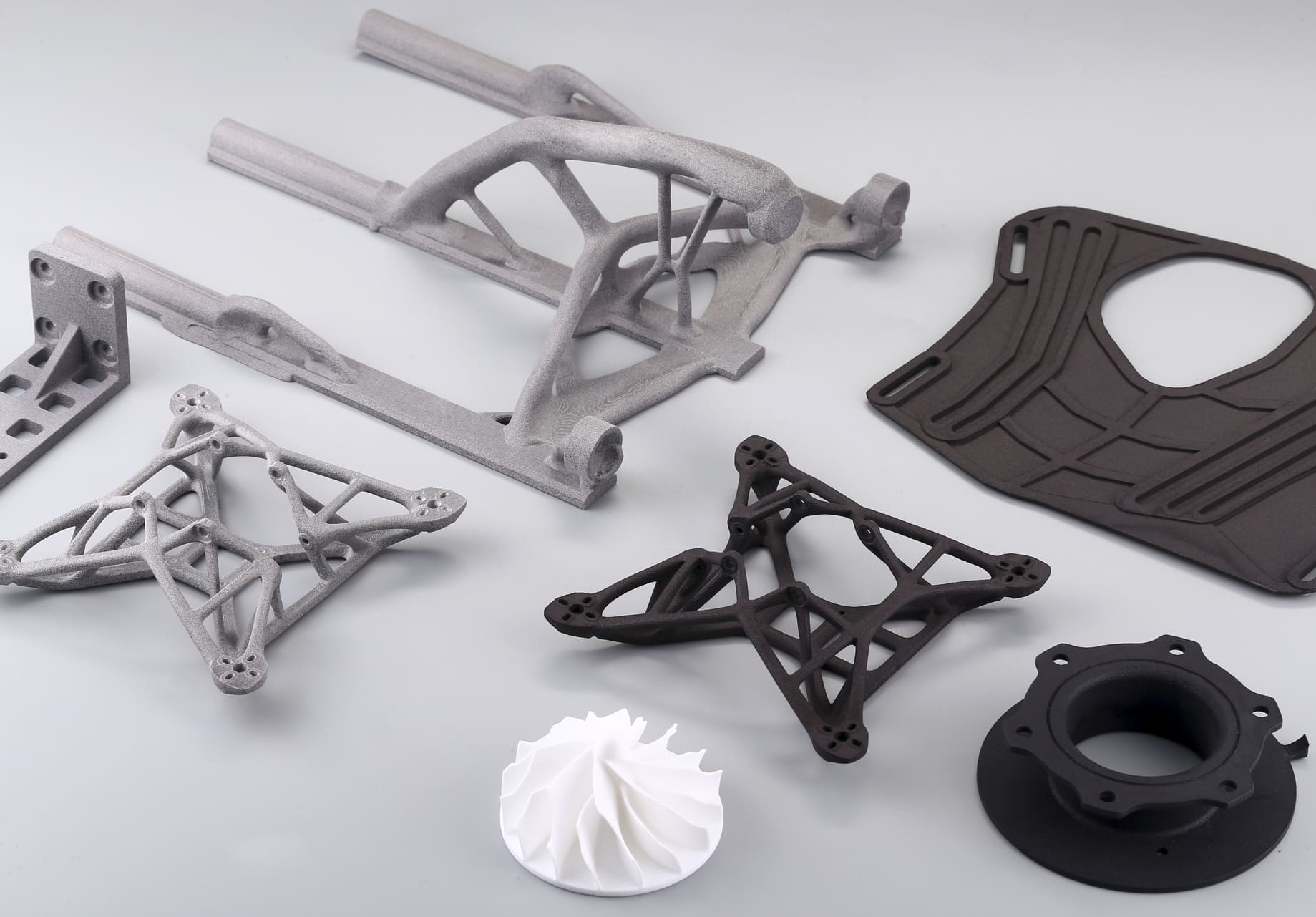
Surface Finishes for Plastic Automotive Components
Common Plastics in Automotive 3D Printing
• ABS: widely used for interior trims and housings.
• Nylon (PA 12, PA 11, PA 6): strong, flexible, and ideal for functional prototypes.
• ULTEM™ (PEI): high-temperature resistance, suitable for under-the-hood applications.
• Polycarbonate: transparent and impact-resistant, used in lenses and covers.
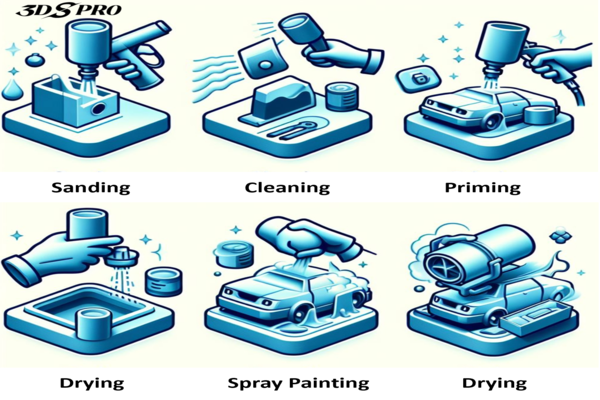
Sanding & Priming
Hand or machine sanding removes layer lines and surface irregularities, creating a smooth profile for subsequent coatings. Priming fills minor imperfections, improves paint adhesion, and helps achieve an even, durable topcoat.
Painting & Dyeing
Liquid paints or dyes add color, branding, and UV protection. Choose formulations formulated for the base polymer (e.g., acrylics for PLA, specialty coatings for ABS/PC) and consider primers or adhesion promoters when needed to prevent peeling and ensure long-term color stability.
Chemical Vapor Smoothing
Solvent-based vapor treatments (for example, acetone for ABS or engineered solvents for certain nylons) chemically meld the surface to produce a glossy, sealed finish that reduces porosity and hides printing artifacts. Use only manufacturer-recommended solvents and follow strict ventilation and PPE protocols — these processes can be hazardous if done improperly.
Epoxy or Polyurethane Coatings
Thin layers of epoxy or polyurethane create a hard, protective skin that improves impact and chemical resistance, seals porous prints, and can produce high-gloss or satin finishes. They’re excellent for parts that require extra abrasion resistance or watertight sealing.
Sandblasting
Low-pressure sandblasting provides a controlled matte texture and removes machining marks or loose particles. It works well with Nylon and ABS to create consistent surface profiles that are ready for dyeing or painting.

Image Copyright © 3DSPRO Limited. All rights reserved.
How to Lower the Costs
Surface finishing adds value but also increases production costs. Automotive manufacturers can adopt several strategies to balance quality with affordability:
Design for Finishing
Incorporate finishing requirements into the design stage. Smooth geometries and reduced support structures minimize post-processing needs.
Selective Finishing
Apply high-end finishes only to visible or critical parts, while using simpler methods for hidden components.
Automated Processes
Invest in robotic blasting, polishing, or coating systems to reduce labor costs and improve consistency.
Batch Processing
Group similar parts together for finishing, reducing setup times and material waste.
Material Choice
Select materials that require less intensive finishing. For example, Nylon parts may need only minimal smoothing compared to metals.
Outsourcing Specialized Finishes
Partner with service providers who offer economies of scale and advanced finishing technologies.
3DSPRO’s 3D Plus™ Surface Finishing Services
To meet the growing demand for high-quality automotive components, 3DSPRO offers its proprietary 3D Plus™ Surface Finishing Services. This comprehensive solution is designed to deliver consistent, professional finishes across both metal and plastic parts.
What is 3D Plus™?
3D Plus™ is an integrated finishing system that combines mechanical, chemical, and coating processes into a streamlined workflow. It ensures that every 3D printed automotive part meets industry standards for performance, durability, and aesthetics.
Key Features
Multi-Material Capability
Supports metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium, as well as plastics such as Nylon, Polypropylene, and TPU.
Advanced Polishing and Smoothing
Proprietary techniques deliver mirror-like finishes for metals and glossy, sealed surfaces for plastics.
Protective Coatings
Options include anodizing, plating, epoxy sealing, and nano-coatings for enhanced resistance.
Automated Consistency
Robotic systems ensure uniform results across batches, reducing variability and human error.
Eco-Friendly Processes
Sustainable methods minimize chemical waste and energy consumption.
Benefits for Automotive Manufacturers
• Reduced Lead Times: streamlined finishing accelerates production schedules.
• Cost Efficiency: economies of scale lower per-part finishing costs.
• OEM Compliance: parts meet ISO standards for surface quality and durability.
• Customization: tailored finishes for branding, aesthetics, and functional requirements.
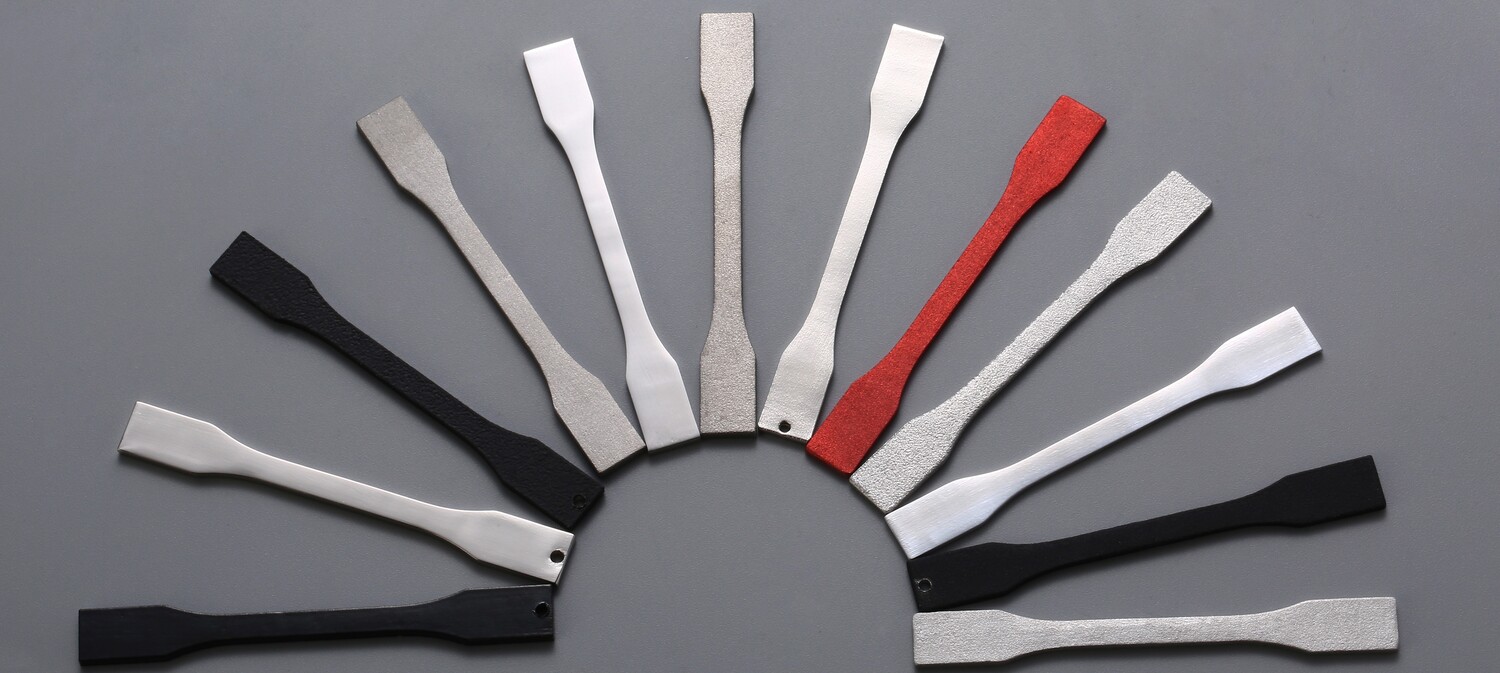

Image Copyright © 3DSPRO Limited. All rights reserved.
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!