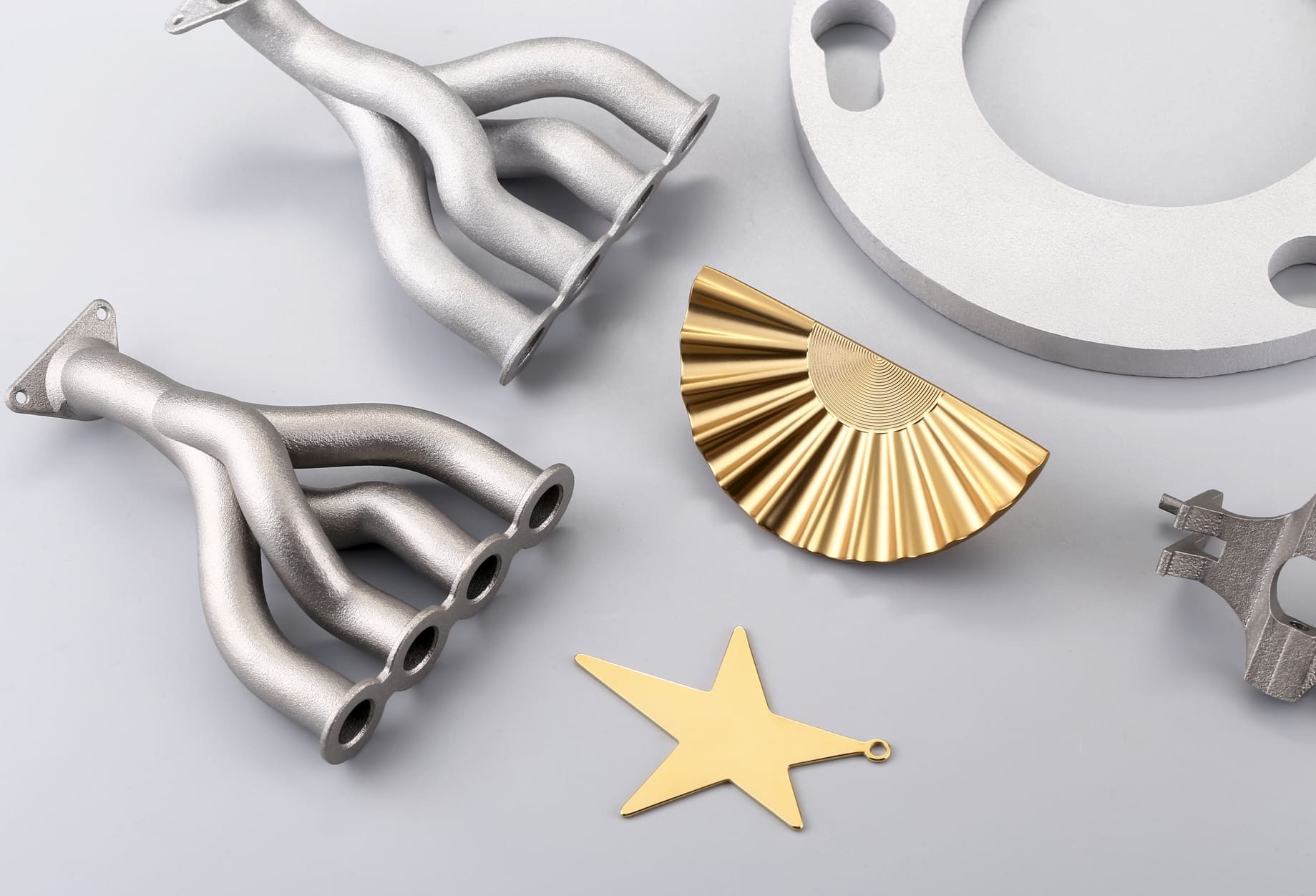
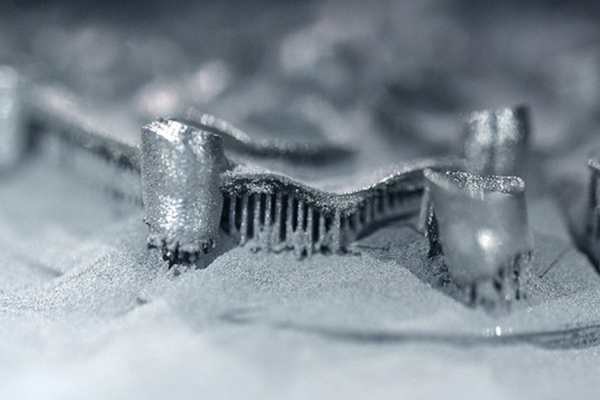
In November 2025, Apple revealed that its latest Apple Watch models were manufactured using 3D printed titanium cases made entirely from recycled aerospace‑grade titanium powder. Metal 3D printing saved over 400 metric tons of raw titanium in a single year, halving the material required compared to conventional machining.
This achievement is a sustainability milestone. Apple demonstrated that metal 3D printing can scale to millions of consumer devices, proving that additive manufacturing is not limited to prototypes or niche industries. Instead, it is a viable path toward material efficiency, reduced waste, and greener supply chains.
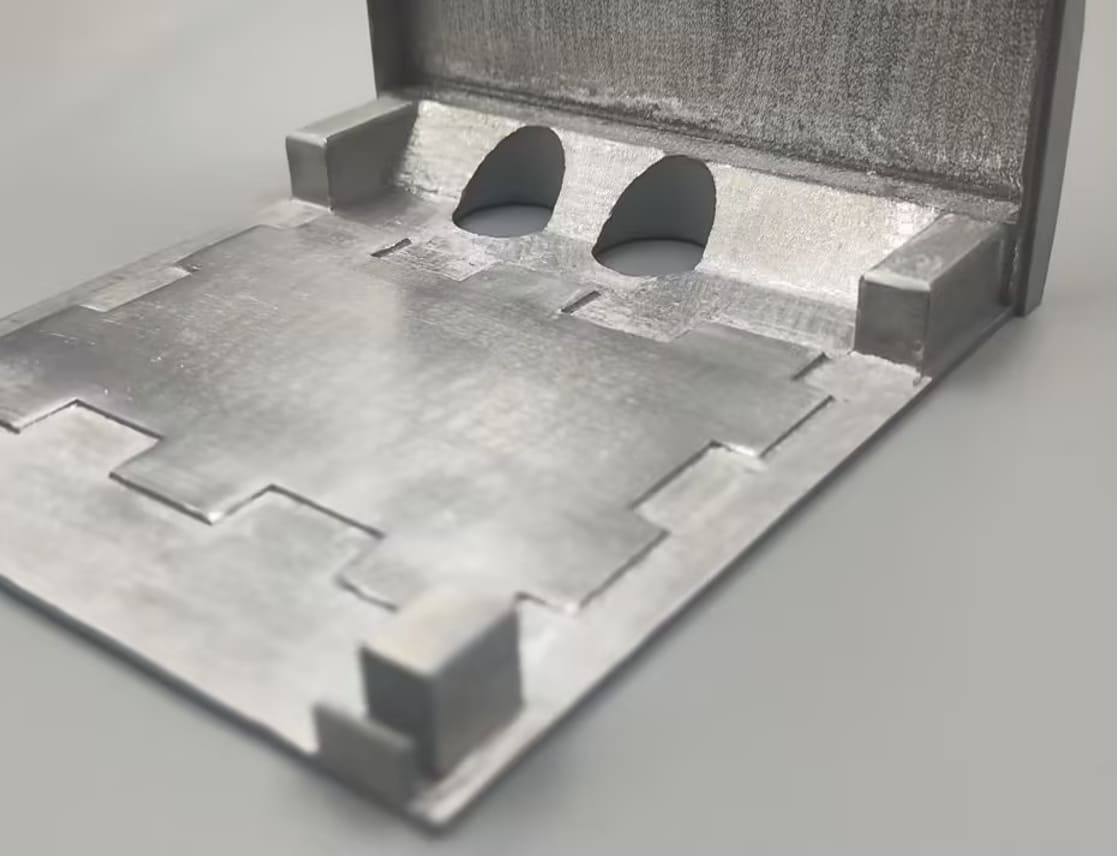
Metal 3D printing builds parts layer by layer using powdered metals such as titanium, aluminum, or steel. Unlike subtractive methods that carve parts out of solid blocks, additive processes use only the material needed.
Precision Material Use
Traditional machining often wastes 60–70% of the raw block of titanium or steel, as excess material is cut away. In contrast, metal 3D printing deposits powder exactly where needed, minimizing scrap.
• Aerospace applications: Jet engine components printed in titanium alloys can reduce waste by up to 90%.
• Medical implants: Custom orthopedic devices are printed to patient-specific dimensions, eliminating excess machining.
• Consumer electronics: Apple’s titanium watch cases showcase how precision deposition halves raw material use.
Metal 3D printing conserves resources but also lowers costs associated with recycling or disposing of scrap metal. For industries where materials like titanium are expensive and energy-intensive to process, the savings are critical.
Design Freedom Meets Resource Savings
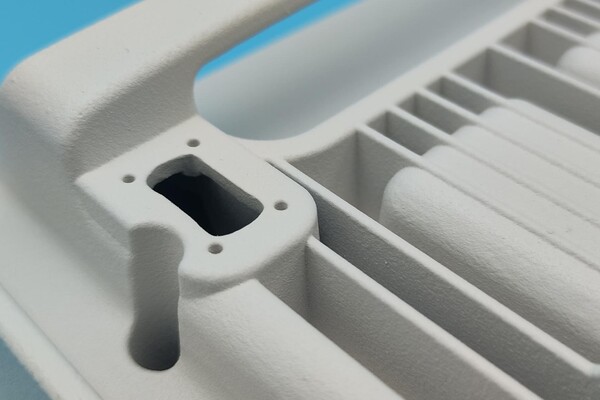
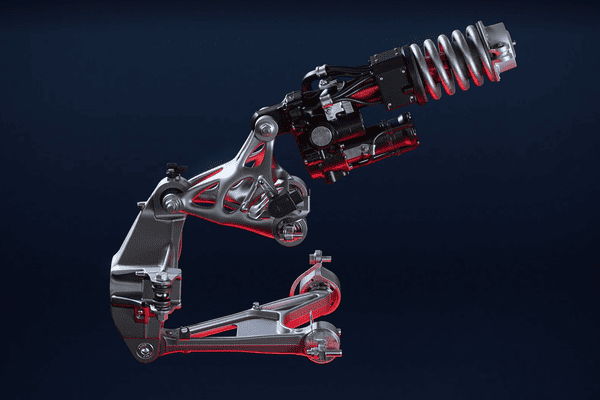
Metal 3D printing enables complex geometries and lightweight structures that are impossible or impractical with traditional methods.
• Topology optimization: Engineers can design lattice structures that maintain strength while reducing weight.
• Part consolidation: Multiple components can be printed as a single piece, reducing assembly steps and material use.
• Lightweighting: In aerospace and automotive, lighter parts mean less fuel consumption and lower emissions.
Circular Economy Potential
Metal 3D printing aligns naturally with the principles of the circular economy, where materials are reused, recycled, and kept in circulation as long as possible.
• Recyclable powders: Unused metal powder from the printing process can be reclaimed and reused.
• Closed-loop systems: Manufacturers can recycle scrap metal into powder feedstock, reducing reliance on virgin materials.
• Repair and remanufacturing: Damaged parts may be repaired by printing new layers, extending product lifespans.
Apple’s use of 100% recycled aerospace‑grade titanium powder is a good example of circularity at scale. By sourcing recycled material and applying additive manufacturing, Apple reduced both raw material demand and waste.
In heavy industries, companies are exploring how to recycle machining scrap into powder feedstock, creating a closed loop that minimizes environmental impact.
Energy Efficiency Gains
Energy consumption is a critical factor in sustainability. While metal 3D printing requires significant energy for lasers or electron beams, it often uses less energy overall compared to traditional forging or casting.
• Forging titanium: Extremely energy-intensive due to high melting points and machining hardness.
• Additive manufacturing: Builds near-net-shape parts, reducing the need for extensive machining and finishing.
• Lifecycle efficiency: Lightweight printed parts reduce energy consumption during product use (e.g., fuel savings in aircraft).
Apple’s shift from CNC machining to 3D printing not only saved raw titanium but also reduced the energy intensity of production. For industries where energy costs are rising and carbon neutrality is a priority, these gains are significant.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Metal 3D printing contributes to lower carbon emissions across the supply chain:
• Localized production: Parts can be printed closer to where they are needed, reducing transportation emissions.
• On-demand manufacturing: Eliminates the need for large inventories and warehousing.
• Lightweight parts: Reduce fuel consumption in aerospace, automotive, and shipping.
3DSPRO Metal 3D Printing Service
While Apple’s achievement highlights consumer electronics, the broader industrial ecosystem is also evolving. 3DSPRO, as a provider of metal 3D printing services, is helping companies across sectors harness these benefits.
What 3DSPRO Offers
• Material efficiency consulting: Helping clients reduce waste by optimizing designs for additive manufacturing.
• Application-specific expertise: From aerospace-grade titanium to stainless steel for different industries.
• Sustainability integration: Advising on closed-loop powder recycling and energy-efficient production.
• Customization at scale: Enabling bespoke parts for industries like healthcare, automotive, and robotics.
3DSPRO’s approach combines technical expertise with sustainability goals, ensuring that clients not only innovate but also reduce their environmental impact.
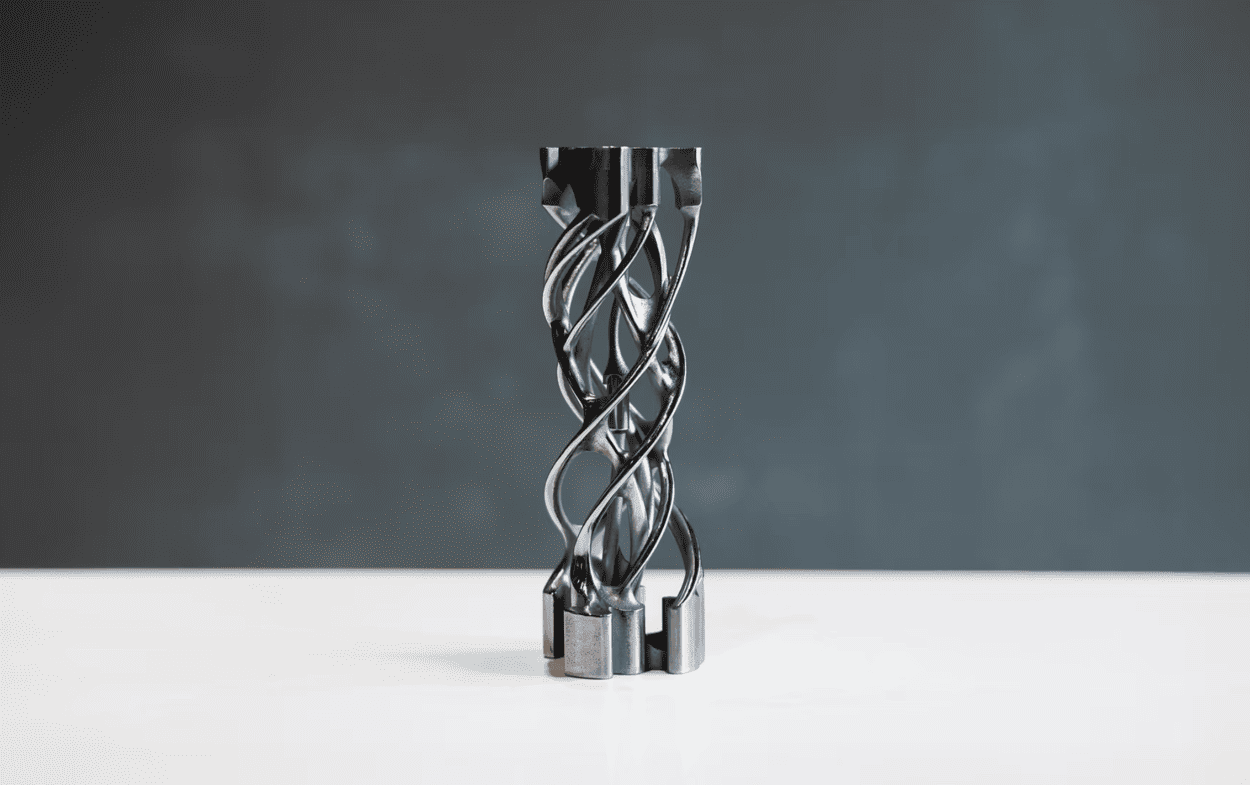

Image Source: Felix
COMMENTS
- Be the first to share your thoughts!